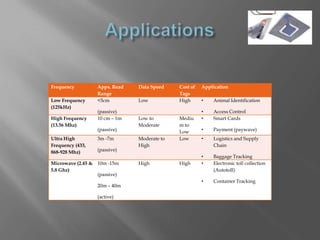
The document discusses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, including how RFID systems work, different types of RFID tags, common RFID frequencies and their applications. It also analyzes the current and potential future uses of RFID in various industries like logistics, healthcare, and retail based on a survey that was conducted. The document concludes that RFID provides benefits over barcodes but also still faces challenges around costs and standardization that need to be addressed for broader adoption.