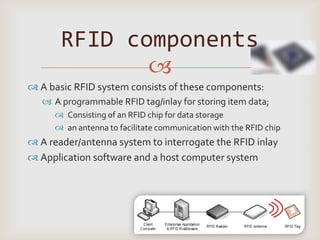
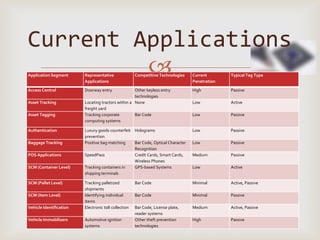
The document discusses RFID technology including its components, types of tags, applications, and survey results. RFID systems consist of tags, readers, and software. Tags can be passive, semi-passive, or active. Common applications include asset tracking, supply chain management, electronic toll collection, and smart cards. A survey found potential uses in inventory control, logistics, libraries, and security. Further development of RFID is seen in medical and library applications.