Sociological theories view socialization as the process by which individuals learn the norms, values, roles, and customs of their culture. This document discusses key aspects of socialization according to sociological theories:
- Socialization begins primarily within the family, where children learn language, morals, and rules, and then expands to other institutions like formal education.
- Sociologists identify agencies of socialization as the institutions where people learn culture, like family, education, religion, media, and peers. The influence of these agencies changes throughout life.
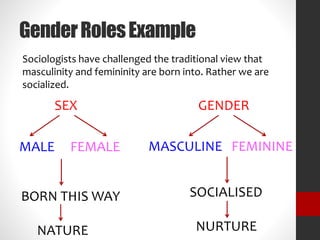
- Theories see gender roles as socially learned rather than innate, through the socialization children receive portraying masculinity and femininity in different ways. Socialization