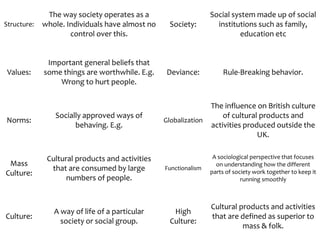
The functionalist view of culture sees culture as essential for holding society together. It views culture as composed of beliefs, values, and norms that dictate social behaviors and link individuals to the wider society. Functionalists believe that all aspects of culture serve important functions that contribute to social stability and solidarity.


![(Remote indian tribe in Brazil)
• The Indians sit next to him [the leader of the
anthropolgists], laughing with him. The chief, Shishu, puts
his arm around him for half an hour. Shishu makes us tea by
grating a vine over a club encrusted with monkey-teeth, and
then wetting and squeezing the result. One man pulls up my
shirt to see if I have breasts and looks down the trousers of
Possuelo’s long haired teenage son.
• 1. What do you think the significance of making tea?
• 2. The tribe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12soc6-141015162211-conversion-gate02/85/1206-Functionalist-View-of-Culture-3-320.jpg)