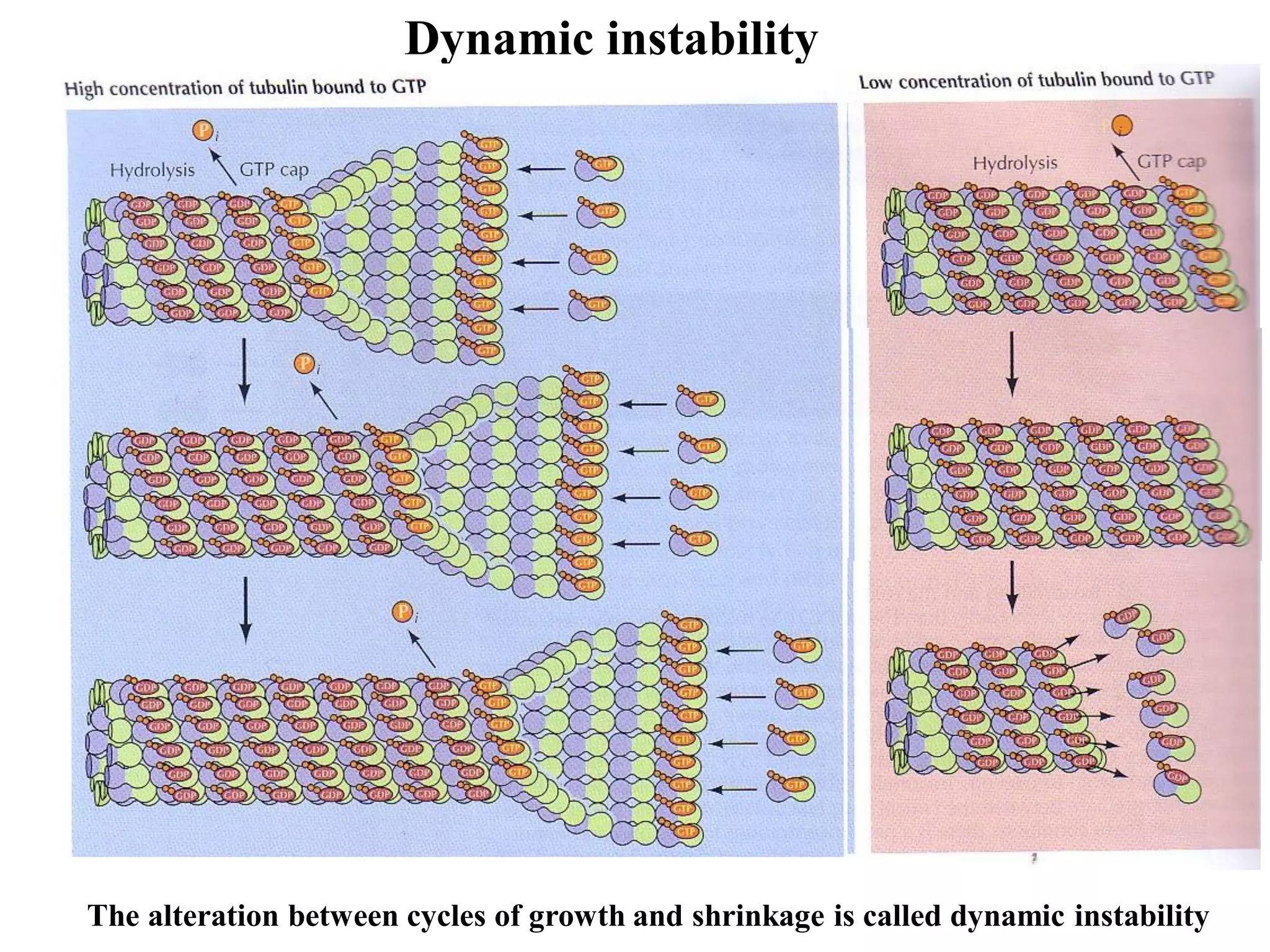
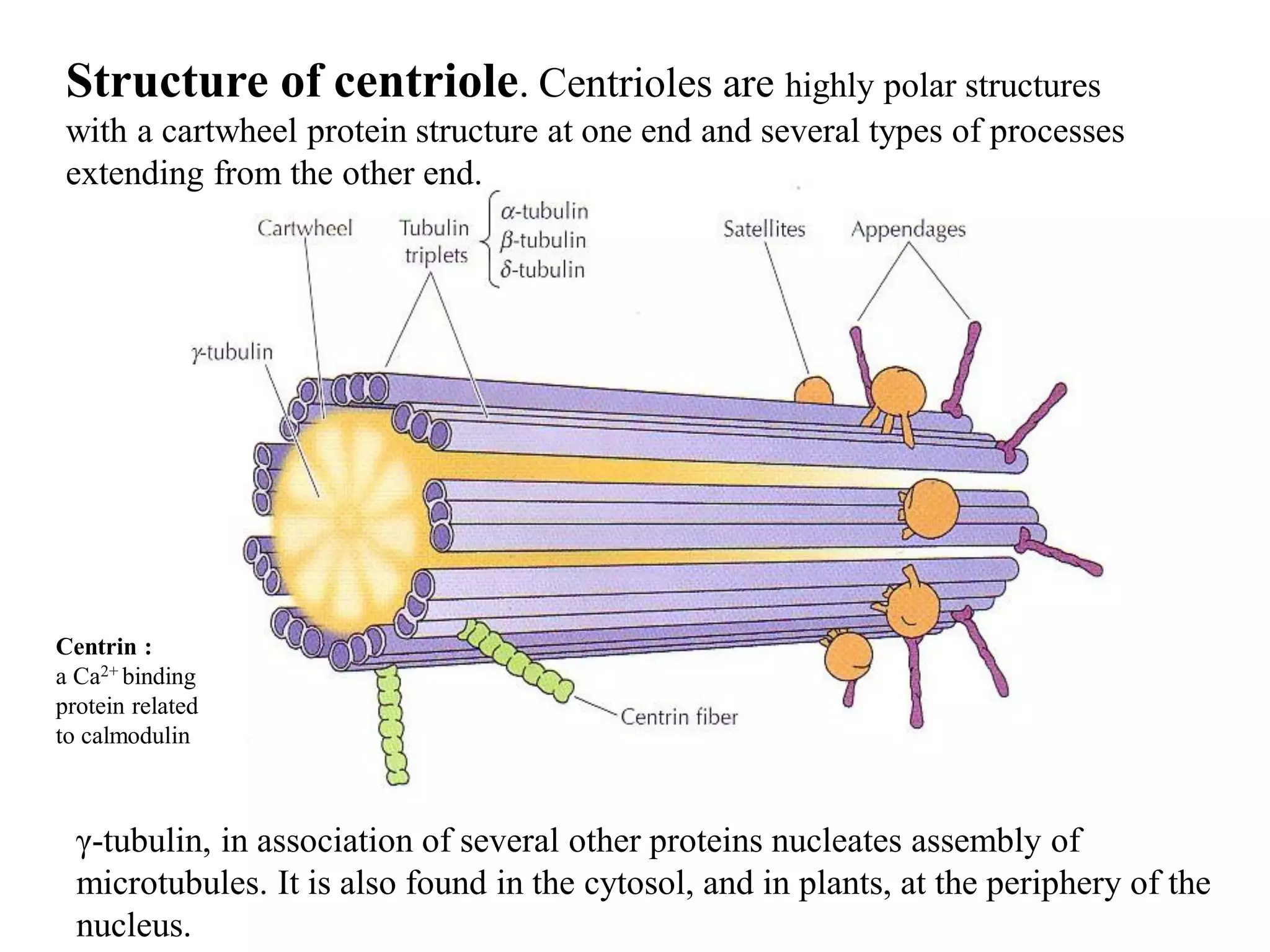
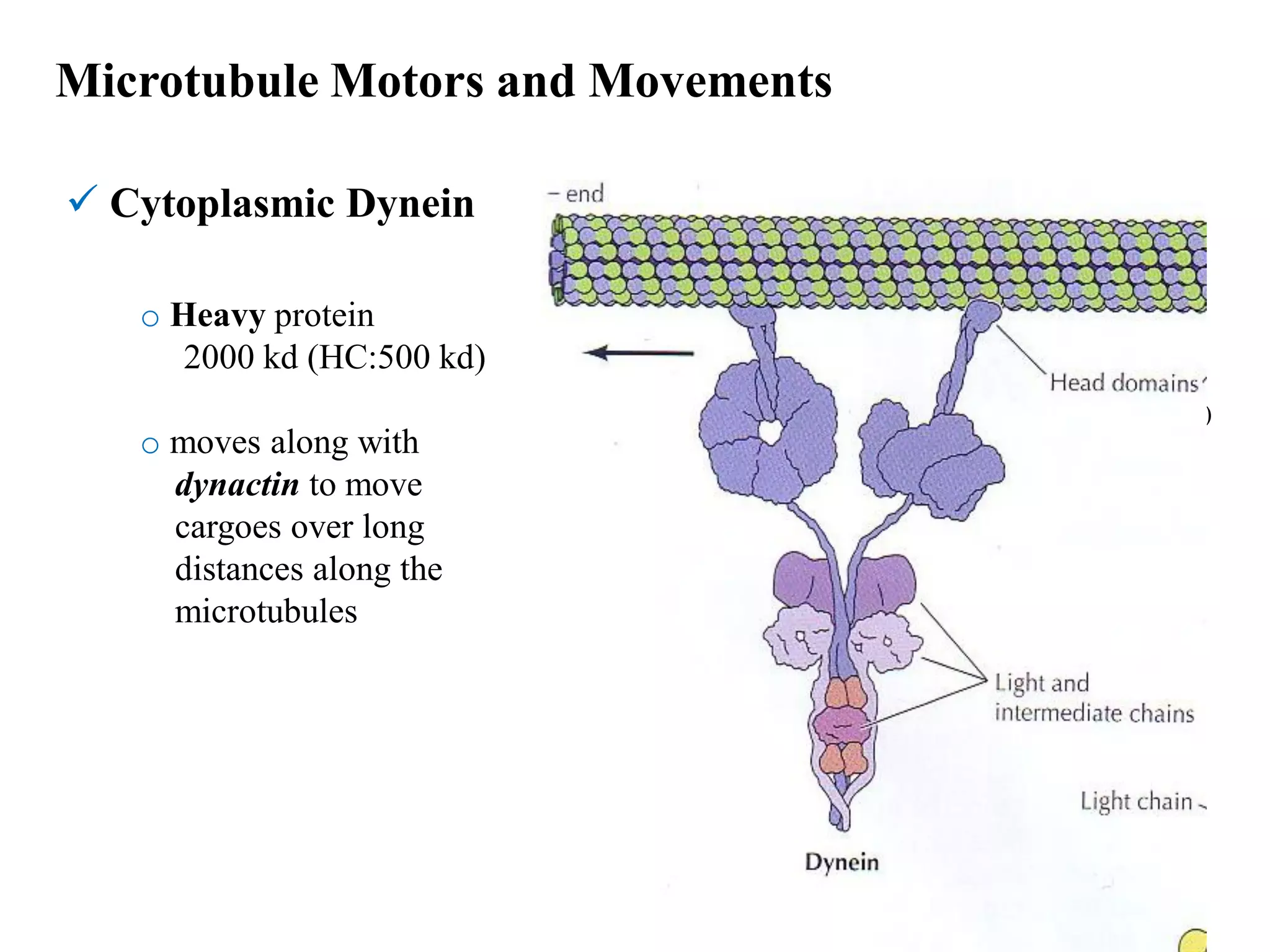
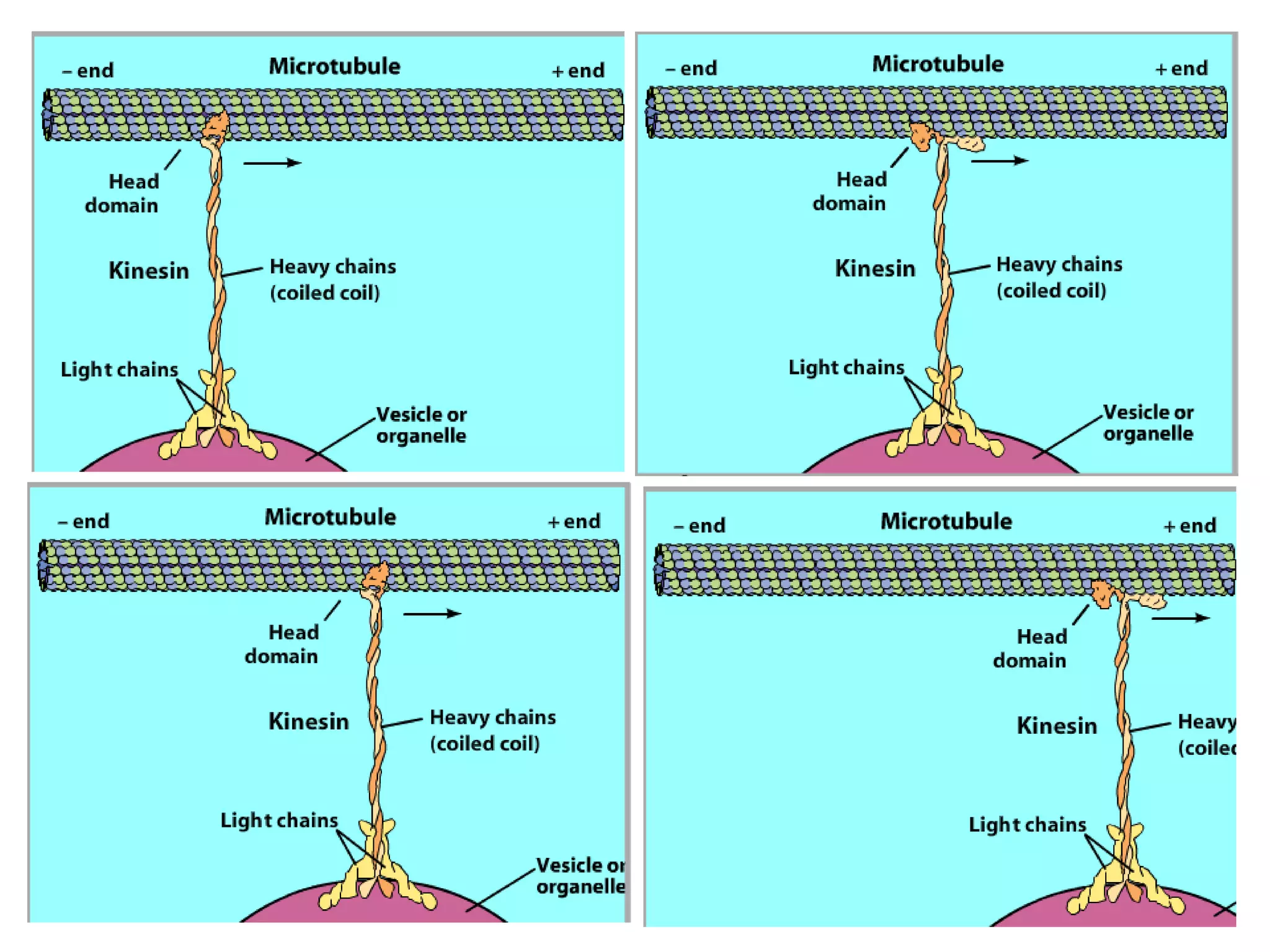
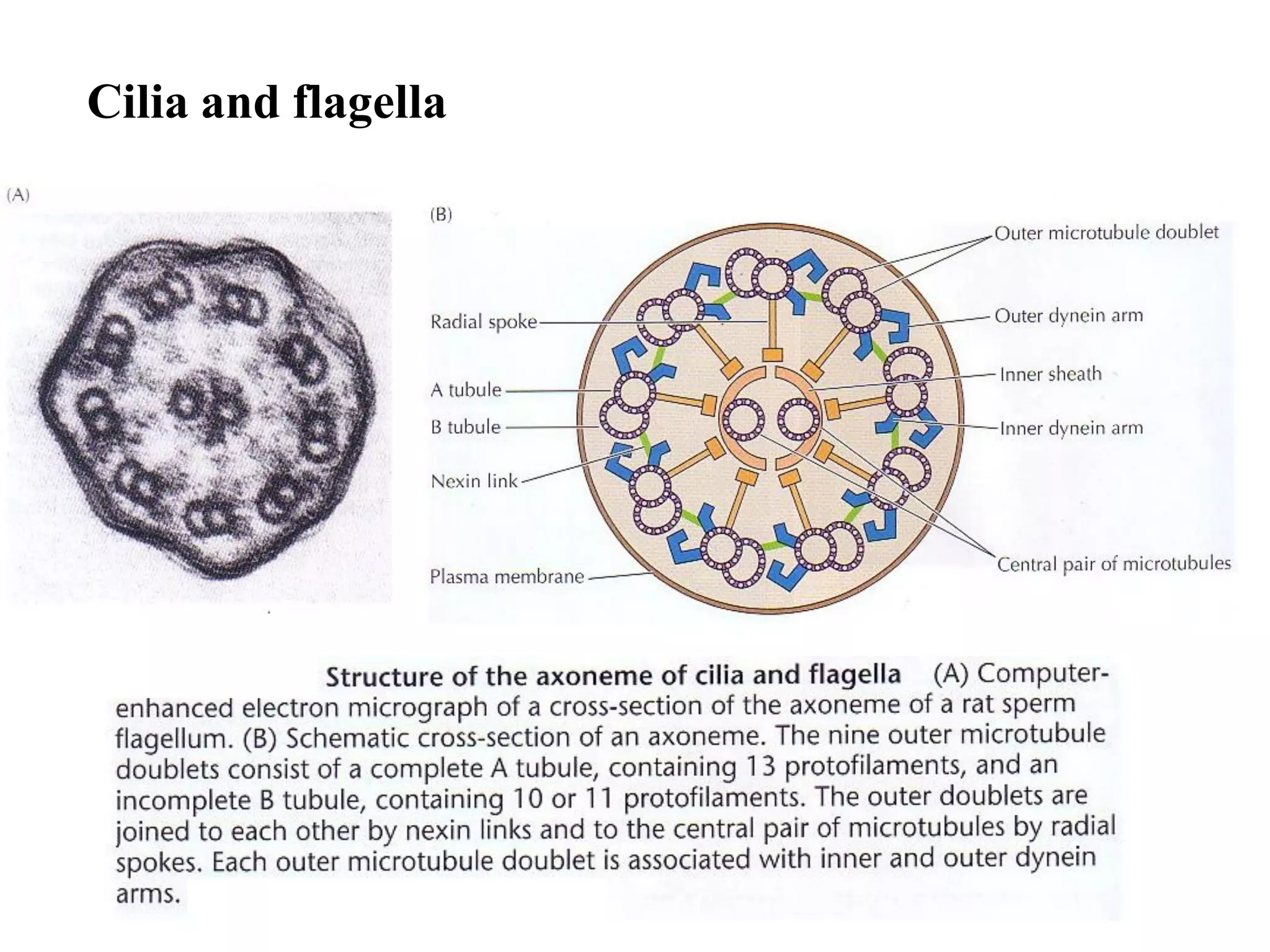
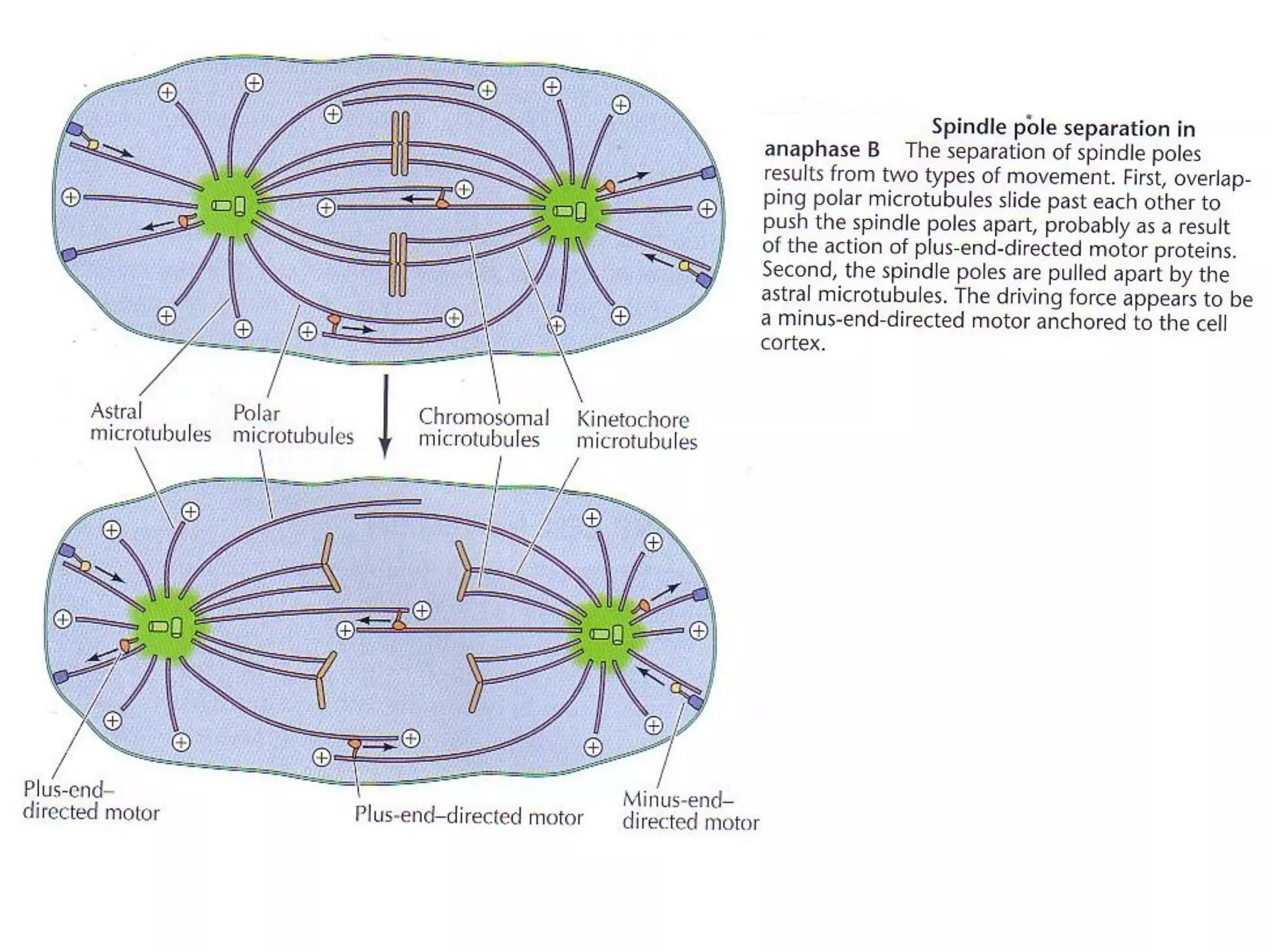
This document discusses microtubules and their role in cell movement. It describes how vincristine and vinblastine inhibit microtubule polymerization and cell division in rapidly dividing cells. It also discusses dynamic instability in microtubule growth and shrinkage cycles. The document outlines how microtubules extend from the centrosome in animal cells and form the mitotic spindle. It describes the structure of the centrosome and centrioles, and how gamma-tubulin nucleates microtubule assembly. Finally, it briefly summarizes microtubule organization in cells and their role in processes like cargo transport, cilia/flagella movement, and chromosome movement during mitosis.