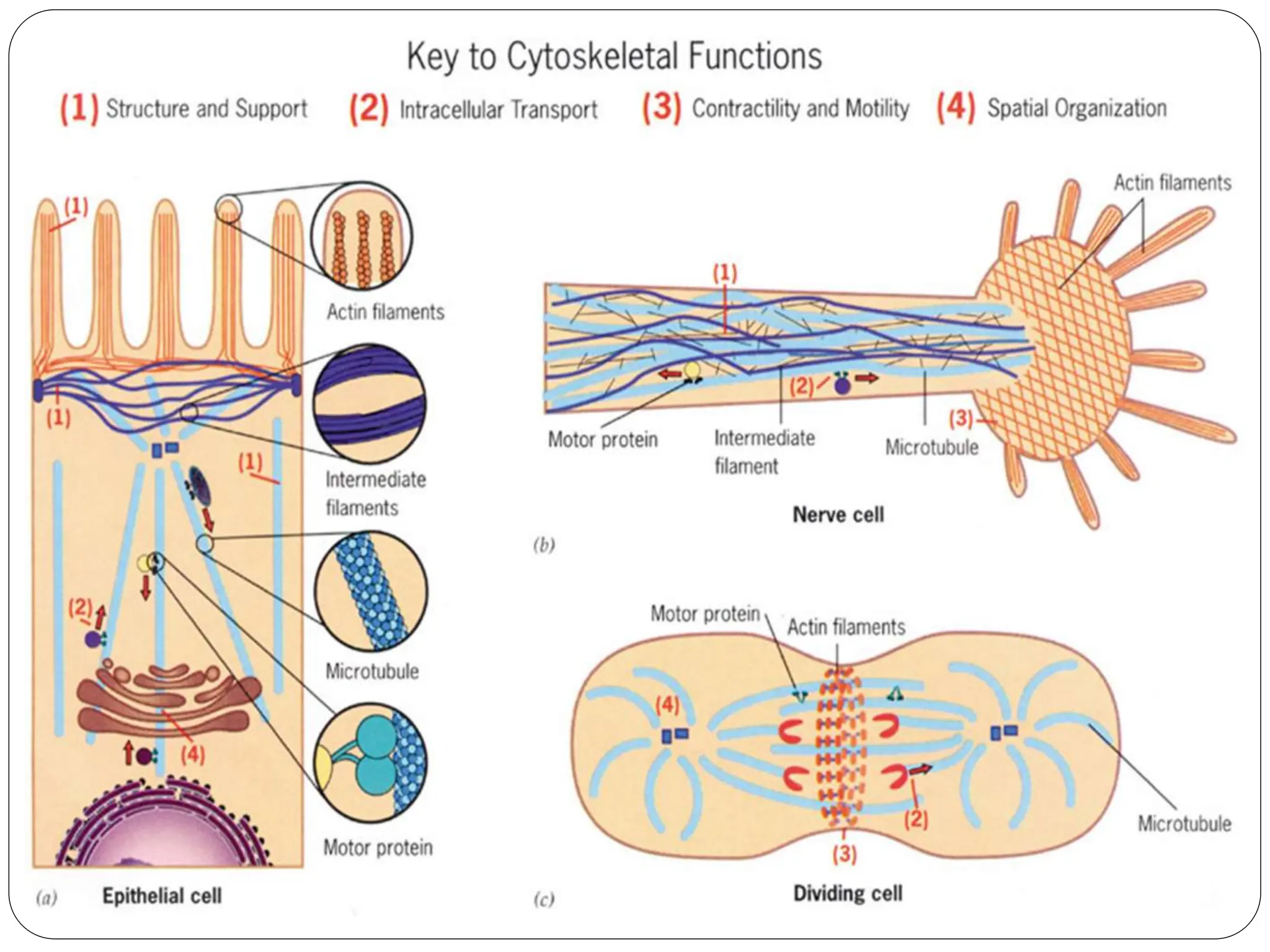
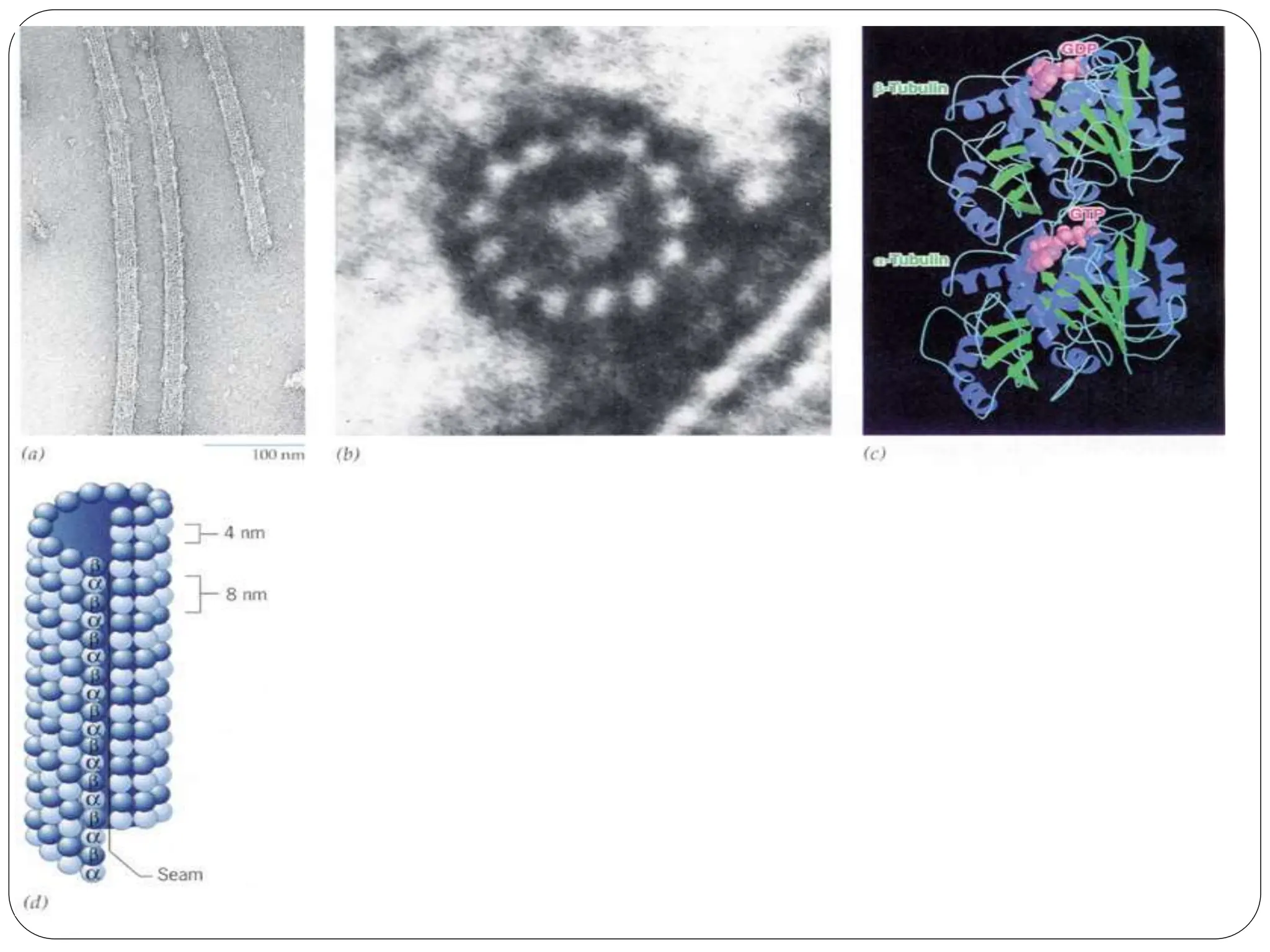
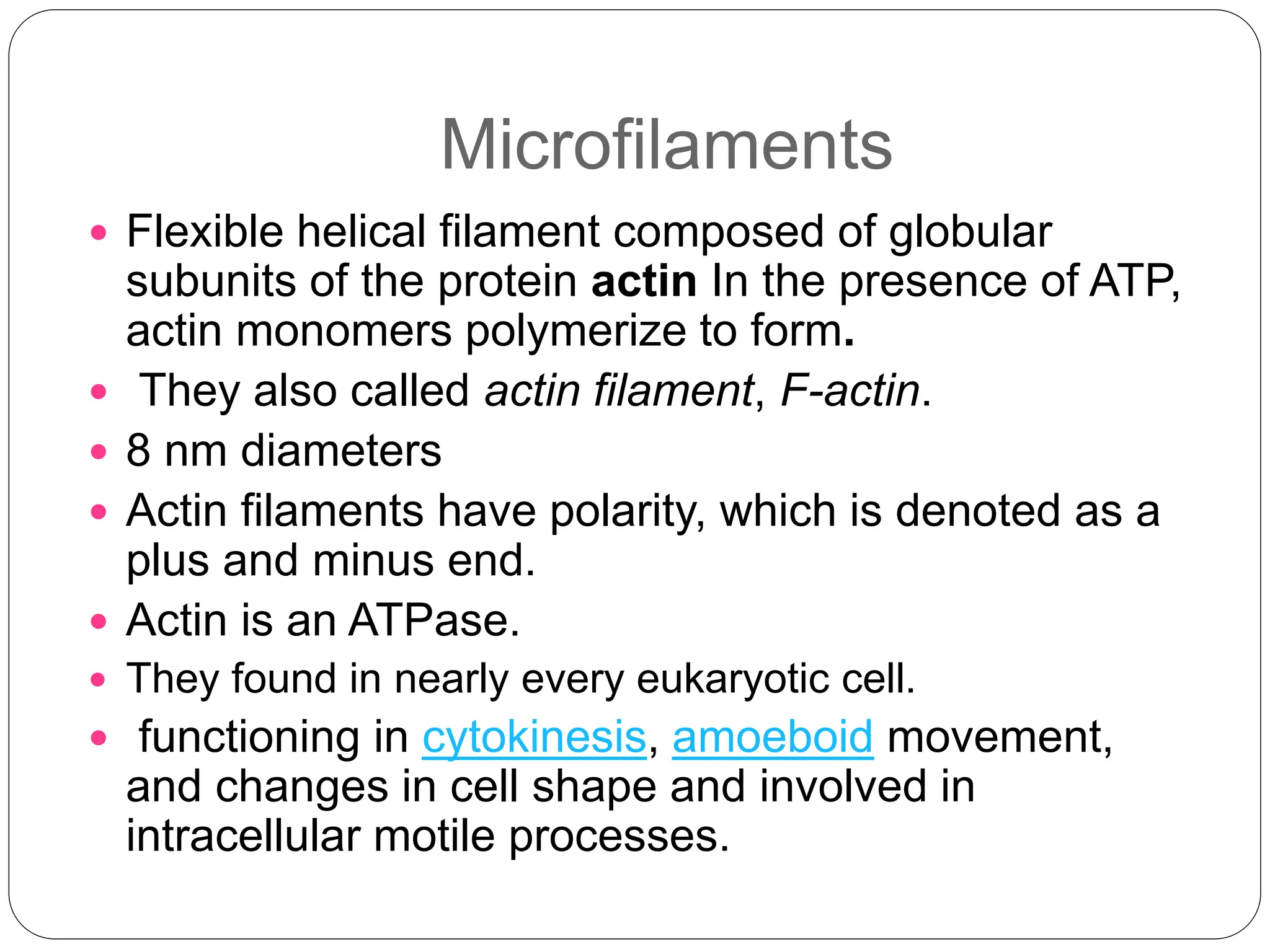
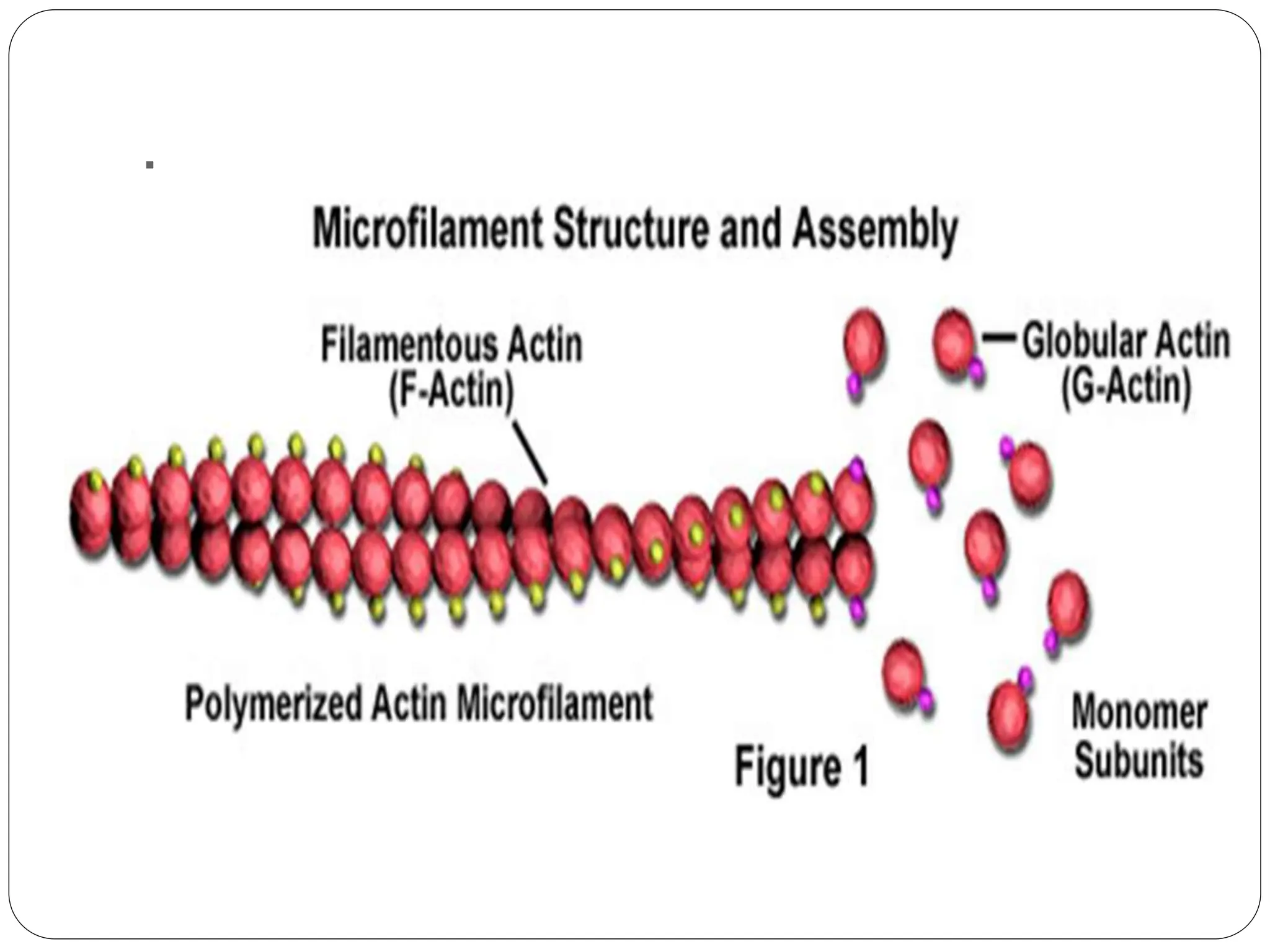
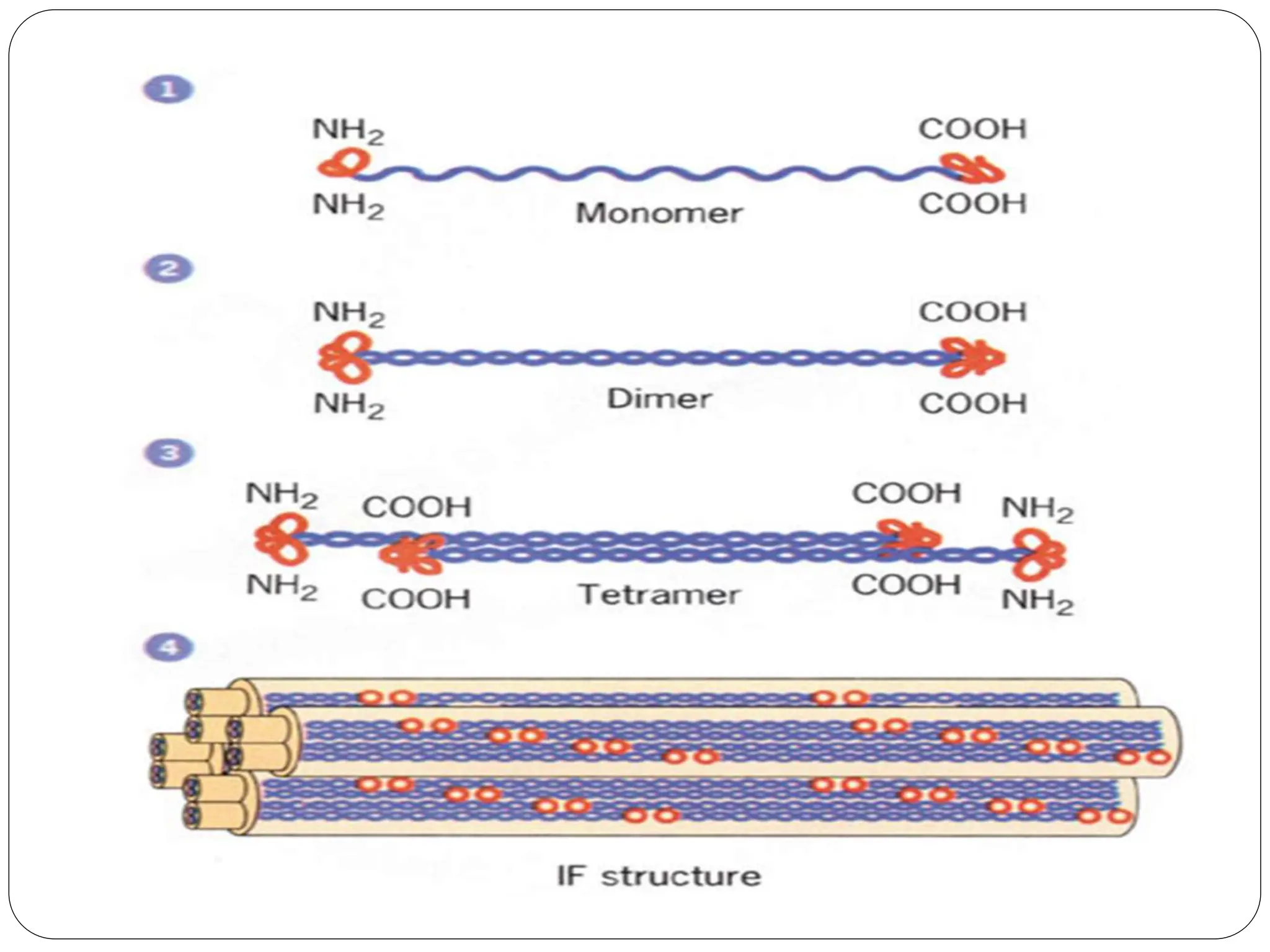
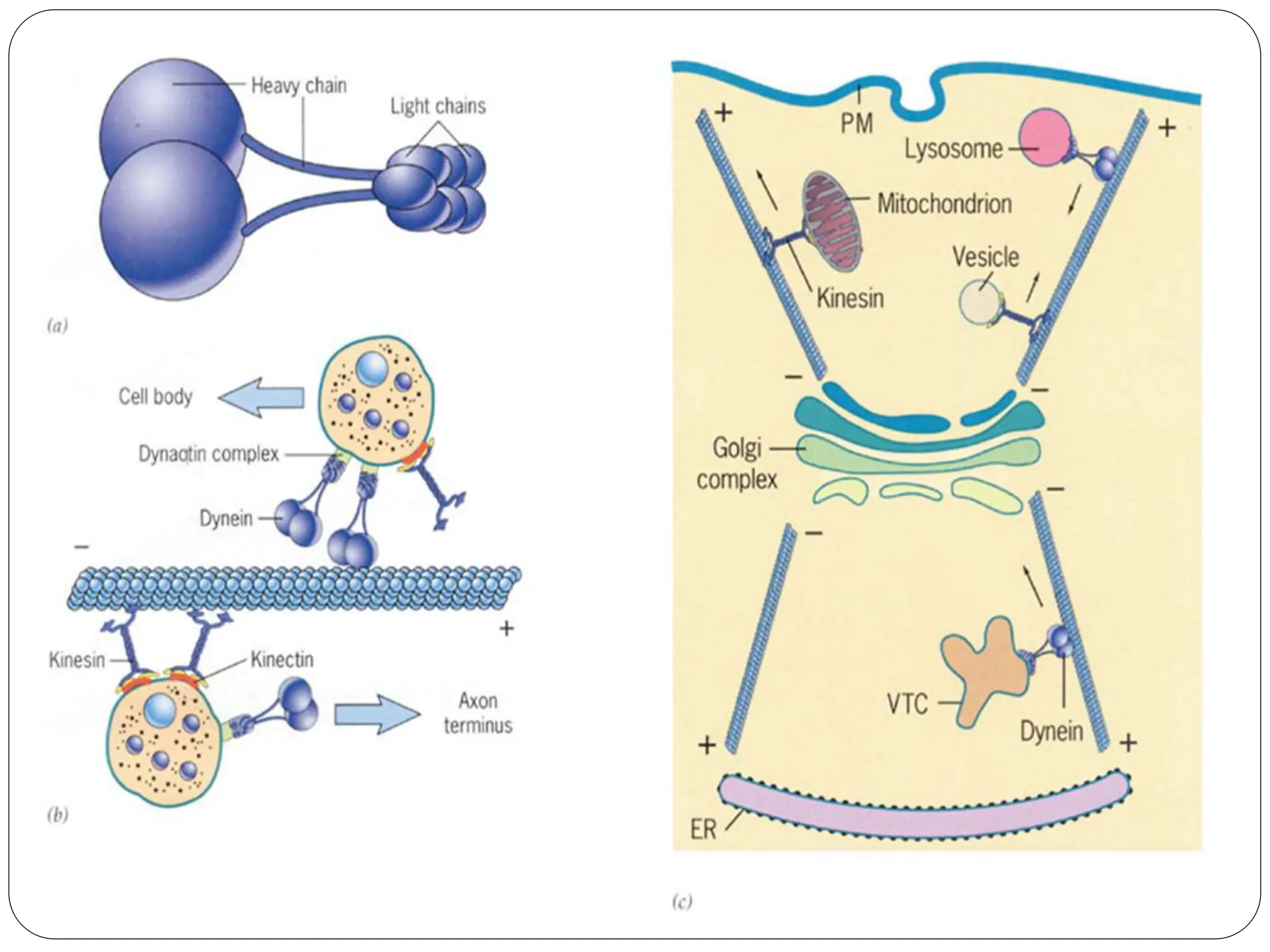
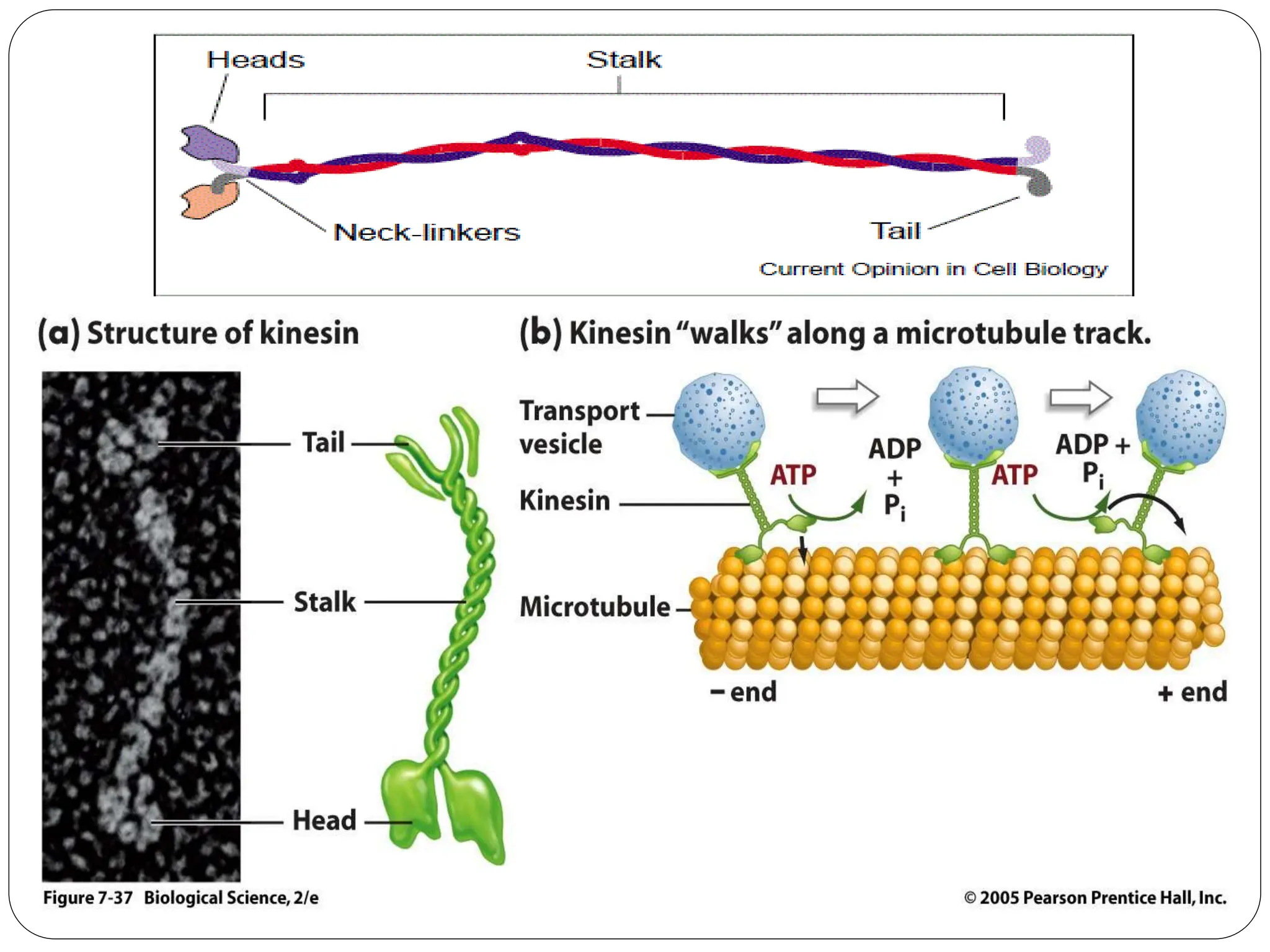
The cytoskeleton of the cell consists of three main filamentous structures: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which provide structural support, organelle positioning, and intracellular motility. Microtubules are hollow structures made of tubulin, microfilaments are flexible actin filaments, and intermediate filaments are robust polypeptides providing mechanical strength. Motor proteins, including kinesins and dyneins, facilitate the movement of cellular cargo along these cytoskeletal elements.