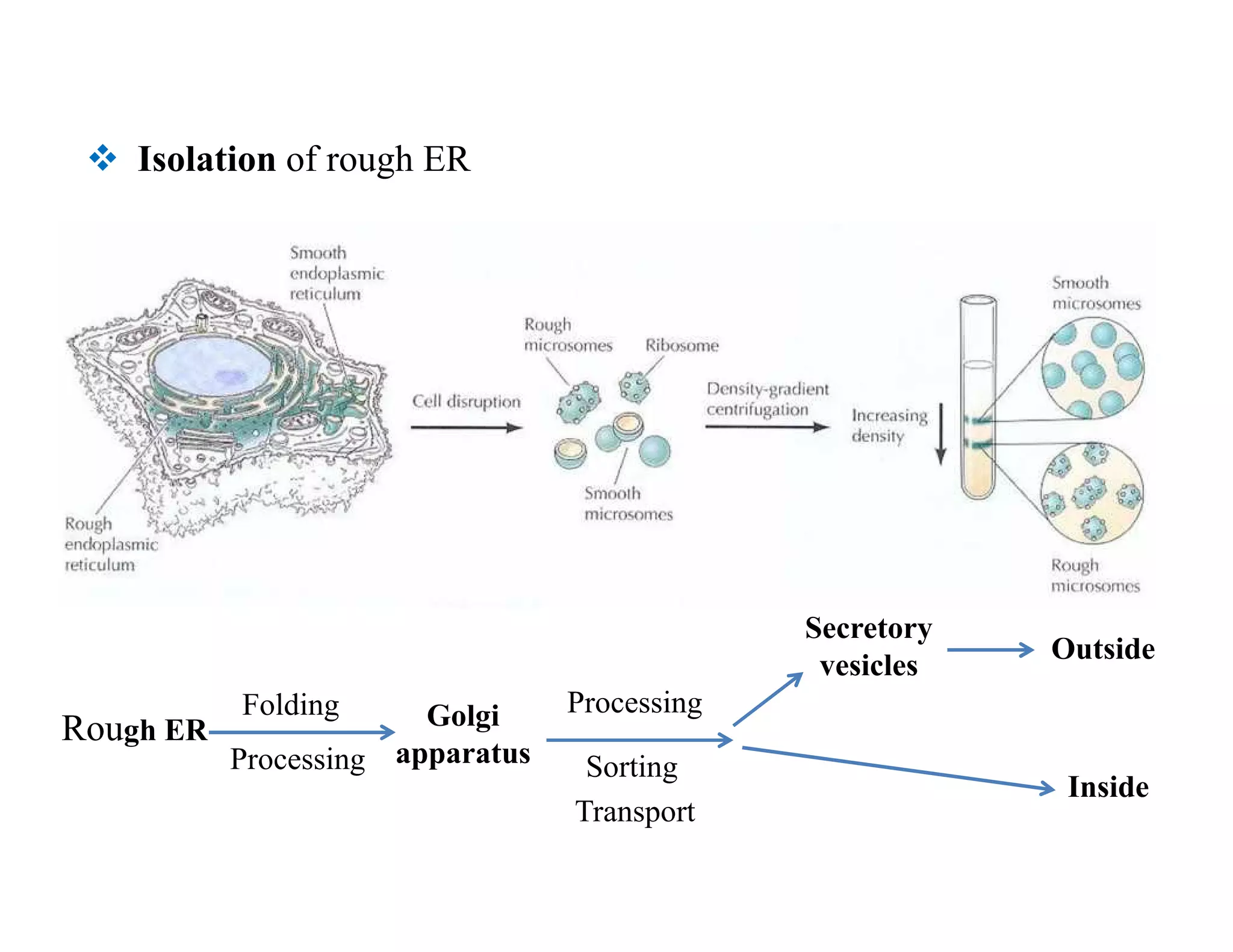
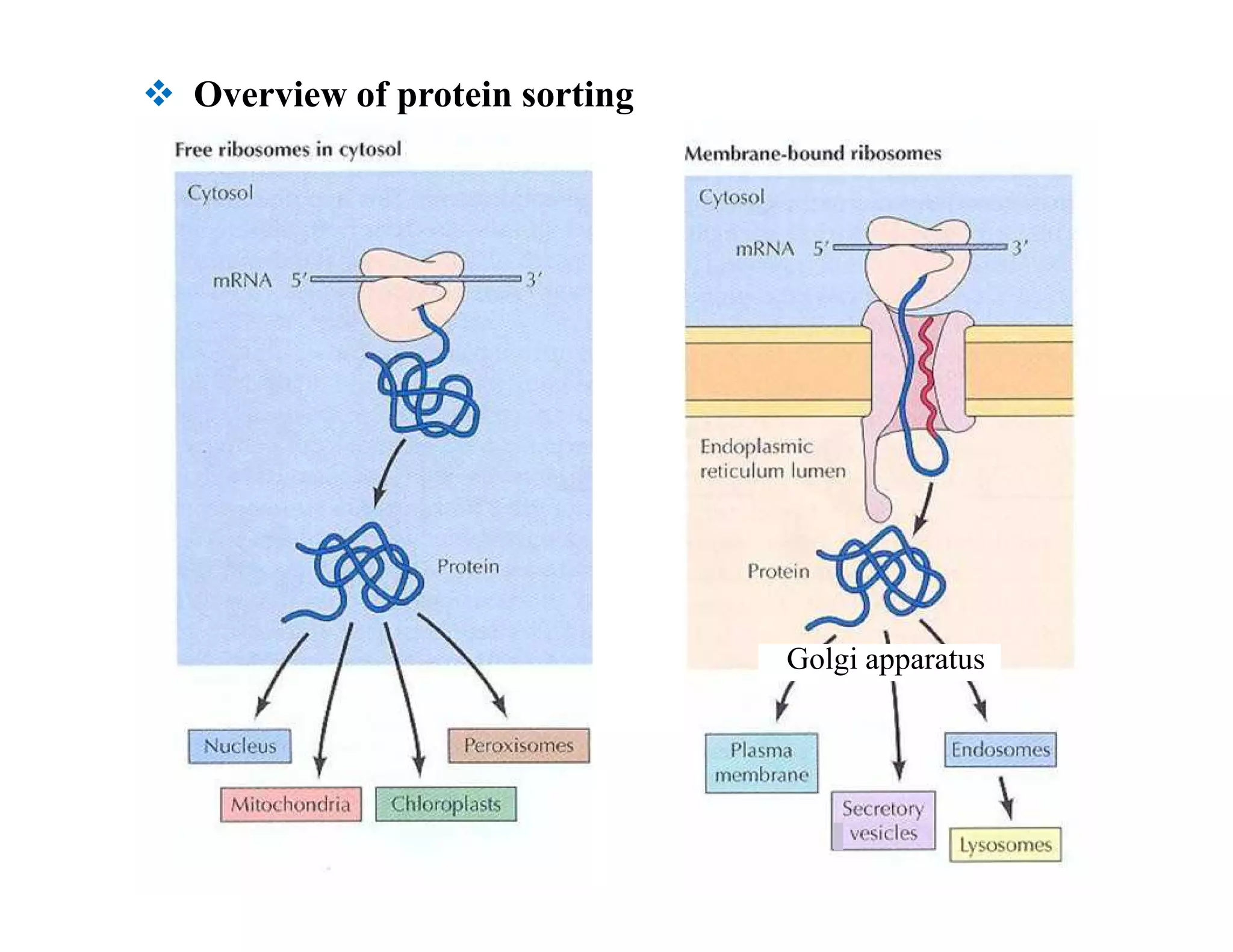
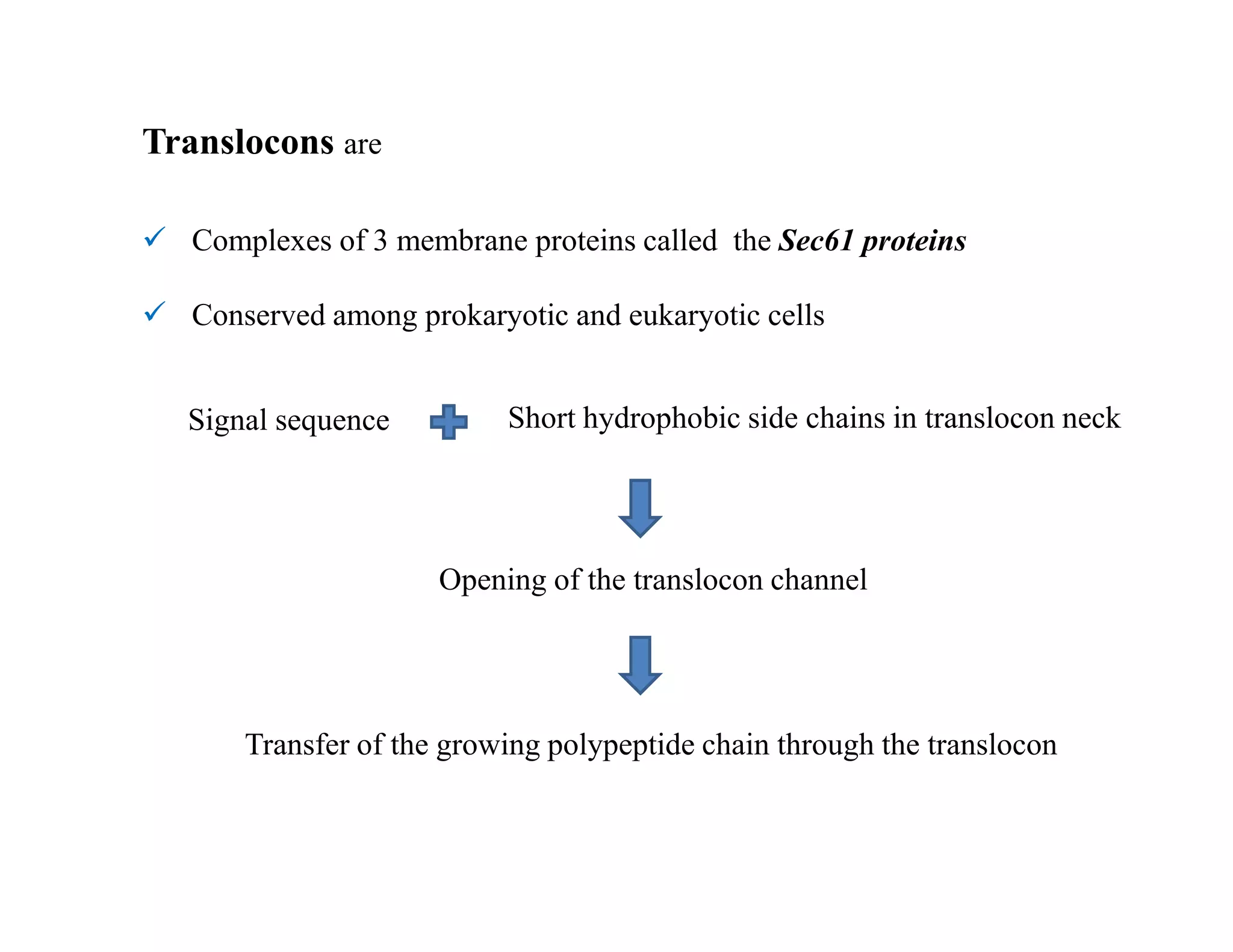
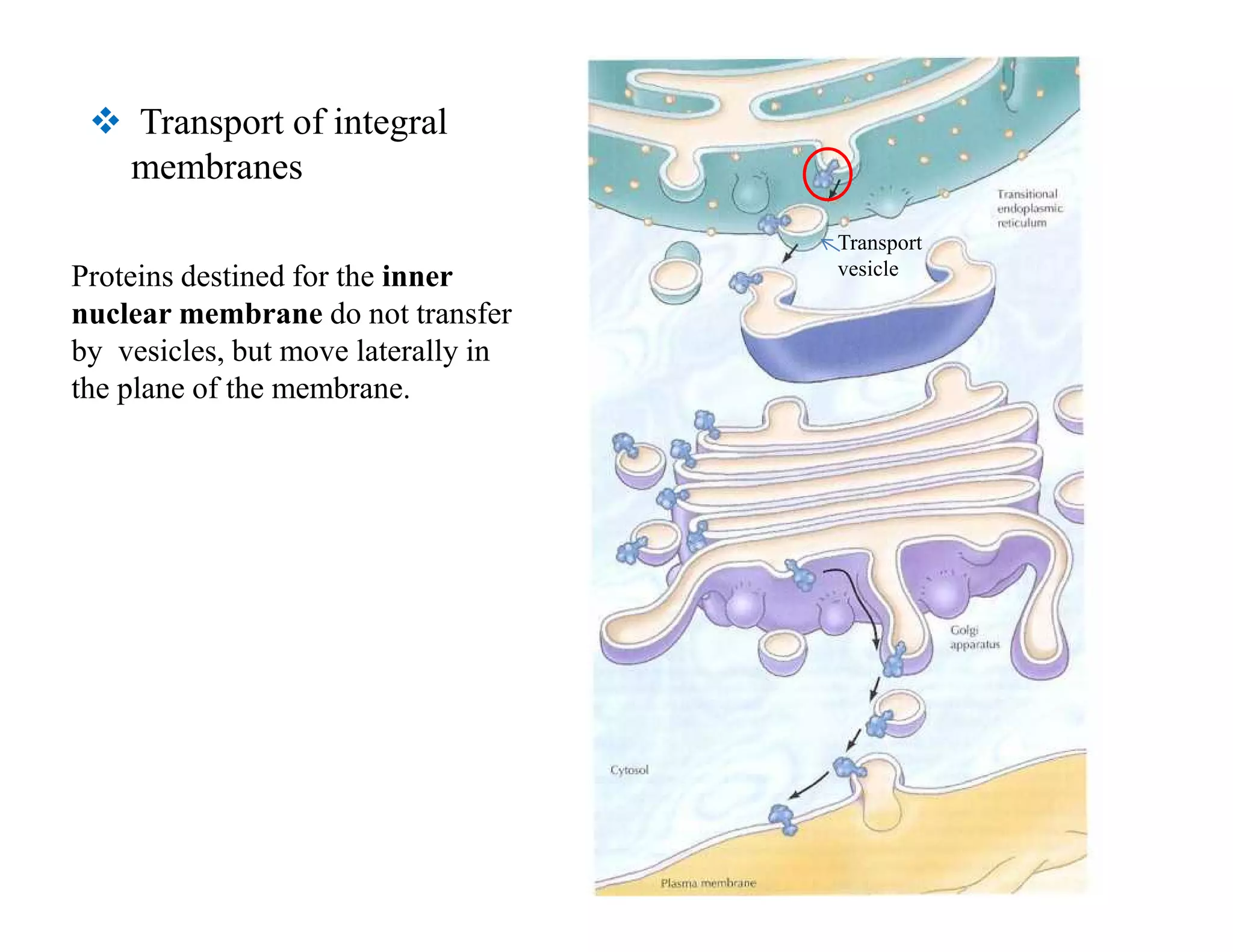
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large organelle that helps process and transport proteins within cells. It has two main domains: the rough ER, where proteins are synthesized, and the smooth ER, where lipids are produced. Newly synthesized proteins enter the ER through translocon channels in the membrane. In the ER, proteins undergo modifications like folding, disulfide bond formation, glycosylation, and lipid additions to help them mature and prepare for transport to other organelles like the Golgi apparatus via transport vesicles. Integral membrane proteins are inserted into the ER membrane through translocon complexes and can span the membrane multiple times. The ER plays a key role in protein sorting and transport within eukaryotic cells