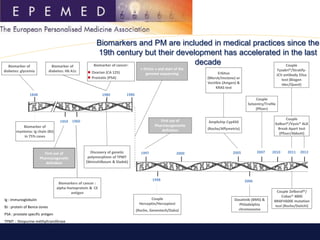
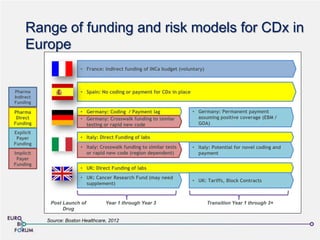
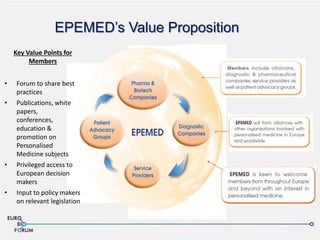
The Eurobioforum 2013 conference, led by Emmanuelle Benzimra of the European Personalized Medicine Association, discussed the evolution of biomarkers and personalized medicine, highlighting the regulatory and commercialization challenges faced in Europe. Despite advancements in biomarker development, only a small percentage of companion diagnostics have reached the market due to hurdles in validation, reimbursement, and regulatory requirements. The EPMP aims to facilitate collaboration and propose solutions to enhance the access and implementation of personalized medicine across European member states.