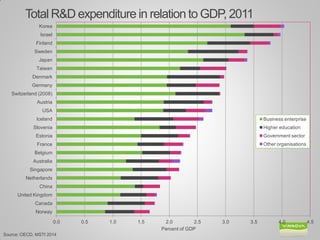
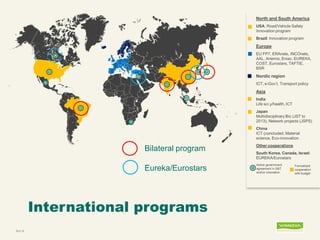
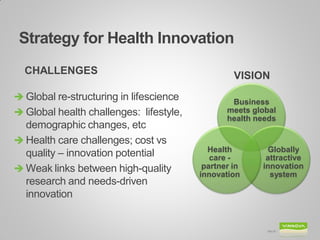
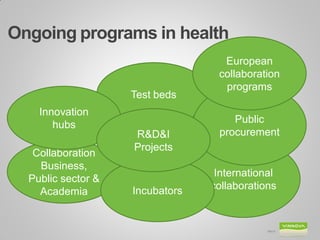
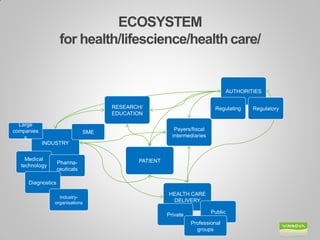
Johanna Adami is the director and head of health at VINNOVA, Sweden's innovation agency. She discusses Sweden's national innovation strategy and VINNOVA's role in funding research and innovation. VINNOVA aims to address grand challenges like health, the environment, and an aging population through collaborative projects bringing together researchers, industries, and other stakeholders both within Sweden and internationally. VINNOVA's health programs support personalized medicine, life sciences, and reforming healthcare to be more innovation-focused. The future roadmap involves stronger public-private partnerships and providing evidence of innovation outcomes.