The document provides information on principles of first aid, including:
1) The definition of first aid and its aims which are to preserve life, prevent worsening of conditions, promote recovery, and ensure safe transportation for medical care.
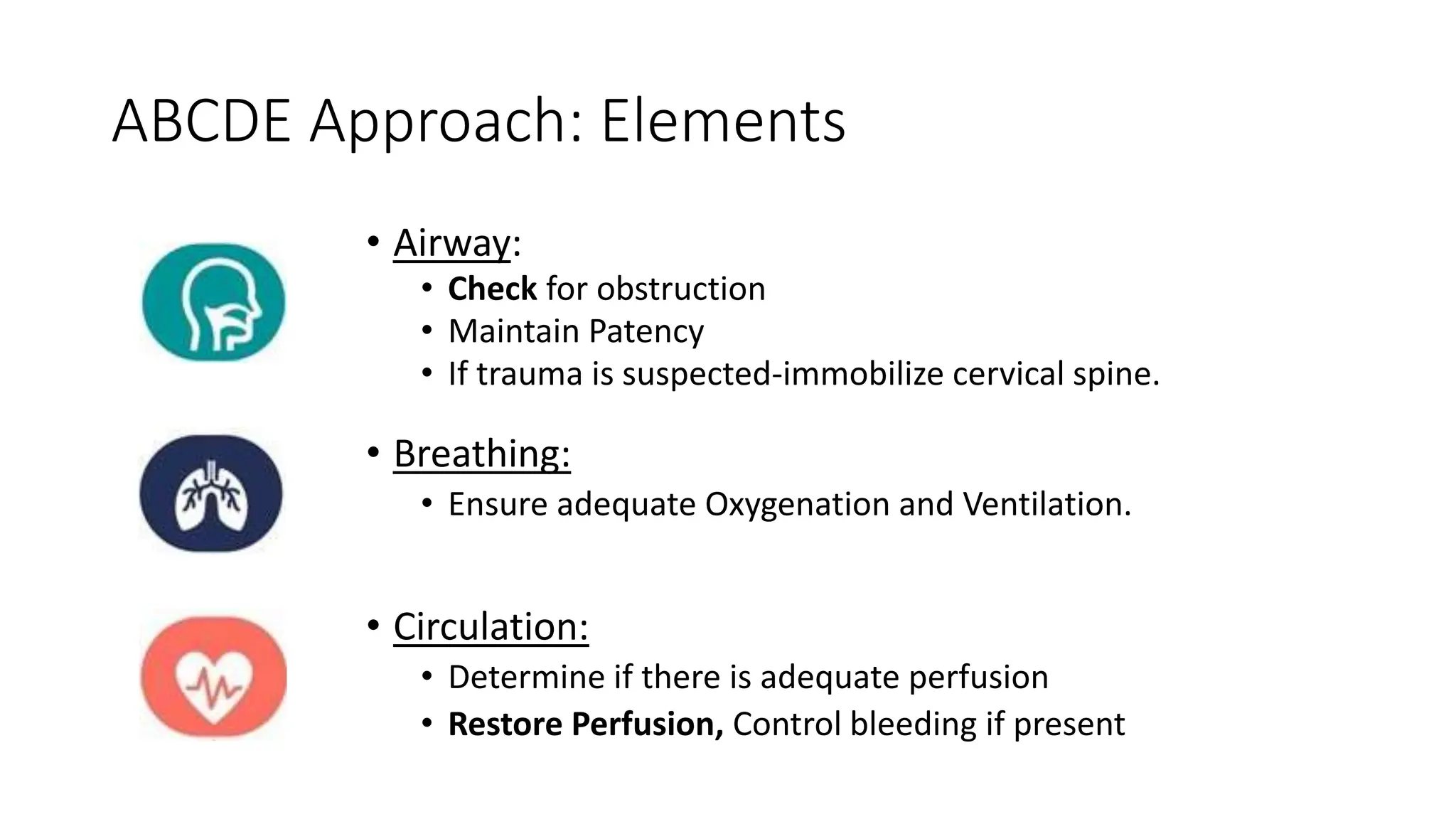
2) How to approach an emergency using the ABCDE approach - Assess the scene, call for help, perform first aid, reevaluate the patient, and provide ongoing care until emergency responders arrive.
3) The ABCDE approach prioritizes Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure to assess and treat life-threatening conditions first before moving on to less severe issues.