1.1 Cell Injury and Cell Death.pptx
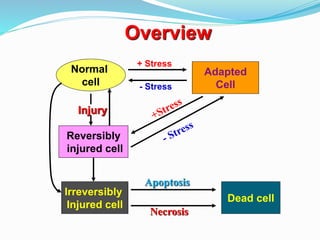
- 1. Adapted Cell + Stress Injury Normal cell Reversibly injured cell Irreversibly Injured cell Dead cell Apoptosis Necrosis - Stress Overview
- 4. Cell injury If the limits of adaptive responses are exceeded or if cells are exposed to injurious agents or stress, deprived of essential nutrients or become compromised by mutations that affect essential cellular constituents a sequence of events follows that is termed cell injury
- 5. Causes of Cell Injury...... Oxygen Deprivation Physical Agents Chemical Agents and Drugs Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Derangements Nutritional Imbalances
- 6. Oxygen Deprivation Hypoxia – deficiency of oxygen Ischemia – loss of blood supply (arterial flow or reduced venous drainage) Causes of Cell Injury
- 7. Physical Agents Mechanical trauma Extremes of temperature – burns, deep cold Radiation Electric shock Causes of Cell Injury
- 8. Chemical Agents and Drugs Hypertonic concentration of salt – deranging electrolyte homeostasis Poisons – arsenic, cyanide, or mercuric salts Insecticides and Herbicides Air pollutant – carbon monoxide Occupational hazard – asbestos Alcohol and Narcotic drugs Causes of Cell Injury
- 10. Immunologic Reactions Anaphylactic reaction to foreign protein or drug Reactions to endogenous self-antigens – autoimmune diseases Causes of Cell Injury
- 11. Genetics Derangements Congenital malformation – Down syndrome Decreased life of red blood cell – Thalassemia, Sickle cell anemia Inborn errors of metabolism Causes of Cell Injury
- 12. Nutritional Imbalances Protein-calorie deficiencies Vitamin deficiencies Anorexia nervosa Excesses of lipids – Obesity, Atherosclerosis Metabolic diseases – Diabetes Causes of Cell Injury
- 13. Mechanisms of Cell Injury Depletion of ATP Mitochondrial Damage Influx of Intracellular Calcium and Loss of Calcium Homeostasis Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived free radical (Oxidative stress) Defects in Membrane Permeability Damage to DNA and Proteins
- 14. Mechanisms of Cell Injury Depletion of ATP Na+K+ATPase (Na-pump) Ca2+Mg2+ATPases (Ca-pump) Causes Hypoxia, Ischemia Chemical Injury Membrane transport Protein synthesis, Lipogenesis etc ATP
- 15. Na + K+ Ca2+ Mechanisms of Cell Injury Depletion of ATP
- 16. Mitochondrial Damage Mechanisms of Cell Injury Causes Hypoxia, Toxins Cytosolic Ca2+ Oxidative stress (ROS)
- 17. Mitochondrial Damage Mechanisms of Cell Injury • Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (formation of high-conductance channel) • Leakage of Cytochrome c into cytosol •Abnormal oxidative phosphorylation and ROS formation. ATP production Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation
- 18. Mechanisms of Cell Injury Mitochondrial Damage
- 19. Influx of Intracellular Calcium and Loss of Calcium Homeostasis Mechanisms of Cell Injury Opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and failure of ATP generation. Activation of many enzymes with potentially deleterious effects on cells. Induction of apoptosis by direct activation of caspases and by increasing mitochondrial permeability.
- 20. Mechanisms of Cell Injury
- 21. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) The Oxidation-Reduction reaction (normal metabolic processes) -superoxide anion (O2 , ONE ELECTRON) -hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, TWO ELECTRON) -hydroxyl ion (OH ,Three electrons) Mechanisms of Cell Injury
- 22. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) Absorption of radiant energy (ultraviolet light, X-ray) Mechanisms of Cell Injury H20 Ionizing radiation OH H
- 23. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) Transition Metals – iron, copper Mechanisms of Cell Injury H202 OH- OH Fe3+ Fe2+ “Fenton reaction”
- 24. Continue…… Rapid brust of ROS production in activated leukocytes during inflammation. Enzymatic metabolism of exogenous chemicals or drugs generate free radicals. (ccl4 generate .ccl3 ) Nitric oxide can act as free radical which generated by macrophages, endothelial cells, neurons.
- 25. Effects of the free radicals on cell injury Lipid peroxidation of Membranes - Plasma membrane - Organellar membrane Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) Mechanisms of Cell Injury Double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids membrane damage
- 26. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) Mechanisms of Cell Injury Effects of the free radicals Oxidative modification of proteins -Oxidation of amino acid side chains Protein-protein cross-linkages -Oxidation of the protein backbone Protein fragmentation Damage active sites of enzymes Disrupts structural conformation of proteins Enhances protein degradation
- 27. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) Mechanisms of Cell Injury Effects of the free radicals Lesions in DNA DNA single and double-strand break Cross linking of DNA strand DNA fragmentation
- 31. Defects in Membrane Permeability Decreased phospholipid synthesis Mitochondrial dysfunction or hypoxia Increased phospholipid breakdown by phospholipases Cytoskeletal abnormalities by proteases activation Reactive oxygen species Lipid peroxidaton Mechanisms of Cell Injury Mechanism of Membrane damage
- 32. Cellular and biochemical sites of damage in cell injury
- 33. Cell Injury Cell Injury – Reversible – Irreversible Cell Death – Necrosis – Apoptosis
- 34. Morphology of Cell Injury Plasma membrane alteration Mitochondrial Changes Dilation of Endoplasmic reticulum Nuclear Alteration Reversible Injury Cellular swelling Fatty change
- 36. Cellular swelling Normal Liver cells Swollen Liver cells
- 37. Necrosis Necrosis refers to a spectrum of morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue largely resulting from the denaturation of intracellular proteins and enzymatic digestion of lethally injured cell.
- 38. Morphology of Necrotic Cells Increased Eosinophilia - loss of RNA (basophilia) - denatured cytoplasmic protein Nuclear Changes - Pyknosis - Karyorrhexis - Karyolysis Myelin figure : From damaged cell membrane – large, whorled phospholipid mass
- 39. Nuclear change Karyolysis: Basophilia of chromatin fade due to loss of DNA. Pyknosis : Nuclear shrinkage and increased basophilia. Karyorrhexis: Fragmentation of pyknotic nucleus.
- 40. Morphologic pattern of Necrotic Cell Coagulative necrosis Liquefactive necrosis Gangrenous necrosis Caseous necrosis Fat necrosis Fibrinoid necrosis
- 41. Morphologic pattern of Necrotic Cell Coagulative Necrosis: Architecture of dead tissue preserved. – protein denatures – proteolysis inhibited Esonophilic , anucleated cells persists. Example: Ischaemia leads to coagulative necrosis in all organs except brain.
- 42. This is an example of coagulative necrosis. This is the typical pattern with ischemia and infarction (loss of blood supply and resultant tissue anoxia). Here, there is a wedge-shaped pale area of coagulative necrosis (infarction) in the renal cortex of the kidney.
- 43. Ischemic necrosis of the myocardium A, Normal myocardium. B, Myocardium with coagulation necrosis
- 44. Morphologic pattern of Necrotic Cell Liquefactive Necrosis : Digestion of dead cells and transformation of tissue into liquid viscous mass. Focal bacterial (or fungal) infections Accumulation of inflammatory cells and enzymes liberation necrotic materials is creamy yellow called PUS. Hypoxic death of cells within CNS
- 45. The liver shows a small abscess here filled with many neutrophils. This abscess is an example of localized liquefactive necrosis
- 46. Coagulative and Liquefactive necrosis A, Kidney infarct exhibiting coagulative necrosis B, A focus of liquefactive necrosis in the kidney
- 47. Morphologic Pattern of Necrotic Cell Caseous necrosis: Example: Tuberculous infection Gross appearance: cheese like ( friable white like) Microscopic – Structureless collection of lysed cells and amorphous granular debris enclosed within a inflammatory border GRANULOMA
- 48. A tuberculous lung with a large area of caseous necrosis
- 49. Tuberculous granuloma showing an area of central necrosis, epithelioid cells, multiple Langhans’-type giant cells, and lymphocytes.
- 50. Fat Necrosis Acute pancreatitis : Resulting from release of activated pancreatic lipases Lipase split TG into FA Fat saponification ( FA combines with calcium to produce chalky white areas)
- 51. Foci of fat necrosis with saponification in the mesentery
- 52. Gangrenous Necrosis Typically coagulative necrosis Generally occurs in lower limb due to ischaemia. Bacterial infection cause liquefactive necrosis called wet gangrene.
- 53. Fibrinoid Necrosis Special form of necrosis Occur in immune reactions involving blood vessels Immune complexs together with fibrin leaked out of vessels Bright pink amorphous appearance.
- 55. Ischemic injury
- 56. Mechanisms of Cell Injury Ischemic injury
- 57. Figure: Sequence of events leading to fatty change and cell necrosis in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) toxicity. RER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; SER, smoothendoplasmic reticulum. Downloaded from: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (on 19 October 2005 05:23 PM) © 2005 Elsevier Chemical injury
- 58. Ischemic- Reperfusion injury How it occurs? Oxidative stress: Generation of ROS Intracellular calcium overload Inflammation : Cytokines release Complement activation
- 59. Apoptosis Pathway of Cell death that is induced by a tightly regulated suicide program in which cells destined to die activate intrinsic enzymes that degrade cells own nuclear DNA and nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. “Programmed Cell Death” Causes of Apoptosis - Physiologic situations - Pathologic conditions
- 60. Morphology of Apoptosis Cell shrinkage Chromosome condensation Formation of cytoplasmic blebs and apoptotic bodies Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells or cell bodies
- 61. Apoptosis in Physiologic Situations Programmed destruction of cell during embryogenesis Hormone-dependent involution - endometrial cells (menstrual cycle) Cell deletion in proliferating cell population Death of host cells - neutrophils Elimination of self reactive lymphocyte
- 62. Apoptosis in Pathologic Conditions Cell death produced by injurious stimuli – radiation, cytotoxic drug Accumulation of misfolded proteins ER stress Cell injury in certain viral diseases – viral hepatitis Pathologic atrophy Cell death in tumors, transplants rejection
- 65. Dysregulated apoptosis Defective apoptosis and increased cell survival: Malignancy Autoimmune disorder Increased apoptosis and excessive cell death: Neurodegenerative diseases Ischemic injury Death of virus infected cells
- 66. Necroptosis Hybrid form of cell death that shares aspects of both necrosis and apoptosis. Morphologically resembles necrosis but mechanistically it is genetically programmed cell death. Programmed necrosis Caspase independent programmed cell death but dependent on RIP1 and RIP3 complex signaling.
- 67. Examples of necroptosis Formation of mammalian bone growth plate. Cell death in steatohepatitis, acute pancreatitis, reperfusion injury, neurodegenerative dieases. Host defense against certain virus: cytomegalovirus. Pyroptosis Another programmed cell death occurs in cells infected by microbes. Accompanied by release of fever inducing cytokine IL-1 and it bears some similarities with apoptosis. Activation of caspase-1 and generates IL-1 and cause cell death.
- 69. Intracellular Accumulations Manifestation of “metabolic derangements” characterized by intracellular accumulation of abnormal amounts of various substances that may be harmless or varying degrees of injury. Types: Normal cellular component: water, lipid, proteins,CHO. Abnormal substance: Exogenous: Minerals or infected agents products Endogenous: Abnormal metaboloic products.
- 70. Mechanisms of intracellular accumulations (1)abnormal metabolism (2)alterations in protein folding and transport (3)deficiency of critical enzymes (4)inability to degrade phagocytosed particles
- 71. Lipids Accumulation of Lipids - Triglycerides - Cholesterol/ Cholesterol ester - Phospholipid A. Steatosis (fatty change) Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within liver parenchymal cells – fatty liver in chronic alcoholism
- 72. Downloaded from: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (on 19 October 2005 05:51 PM) © 2005 Elsevier Lipid accumulation
- 73. Downloaded from: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (on 19 October 2005 05:51 PM) © 2005 Elsevier Fatty liver
- 74. Lipids B. Cholesterol and Cholesterol Esters: Atherosclerosis : Accumulation of cholesterol-laden macrophage (foam cell) and smooth muscle cells in the intima of aorta and arteries . Cholesterolosis : Accumulation of foam cells in the lamina propria of gallbladder. Xanthomas: Foam cells in subepithelial connective tissue of skin and tendons. Niemann-Pick diseases type –C: Choleserol accumulation in multiple organs.
- 75. Downloaded from: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (on 19 October 2005 05:51 PM) © 2005 Elsevier
- 76. Proteins Accumulation of protein droplets in proximal renal tubule : Renal disease Defective intracellular transport and secretion of protein : Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency. Accumulation of cytoskeletal proteins: Keratin, vimentin Abnormal proteins aggregation : Amyloidosis
- 77. Protein reabsorption droplets in the renal tubular epithelium. Downloaded from: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (on 19 October 2005 05:51 PM) © 2005 Elsevier
- 78. Glycogen “Patients with abnormal metabolism of glucose or glycogen” Diabetes mellitus: disorder of glucose metabolism - glycogen accumulate in epithelial cells of renal tubules, liver cells, beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans heart muscle cells
- 79. Glycogen storage disease (Glycogenosis) - genetic diseases - defect of enzymes in the synthesis or breakdown of glycogen accumulation cell injury death Glycogen
- 80. Pigments Exogenous pigments Carbon ( anthracosis) Coal dust ( pneumoconiosis) Tattooing: Localized exogenous pigmentation.
- 81. Pigments Endogenous pigment Lipofuscin – Insoluble pigment ,found in liver and heart of aging patients or severe malnutrition. Melanin – Brown black colour Hemosiderin – Golden yellow colour
- 82. Pathologic Calcification Abnormal tissue deposition of Calcium Salts Two forms 1. Dystrophic calcification 2. Metastatic calcification
- 83. Pathologic Calcification Dystrophic Calcification - Area of tissue necrosis - Aging or damage heart valve - Atherosclerosis
- 84. Metastatic Calcification Occur in normal tissue in “hypercalcemia” Site : Gastric mucosa, kidneys, lungs, systemic arteries, pulmonary veins. Pathologic Calcification Hypercalcemia • Hyperparathyroidism • Resorption of bone tissue • Renal failure •Vitamin D related disorder
- 85. THANK YOU