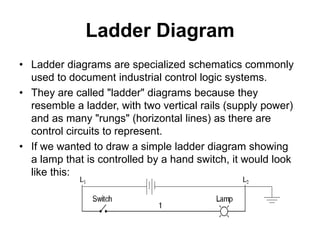
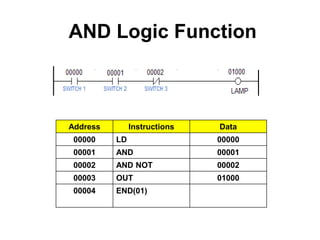
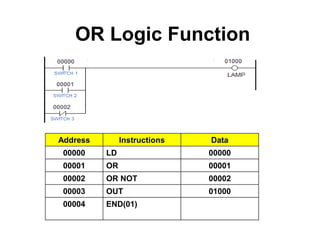
This document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and ladder logic programming. It discusses how PLC programs are loaded into microprocessor-based systems using machine code. The IEC 61131-3 standard defines common PLC programming languages like ladder diagrams and function block diagrams. Ladder diagrams resemble electrical ladder diagrams and are read from left to right. They use contacts to represent inputs and coils to represent outputs. Basic logic functions like AND, OR, and NOT are used to write simple PLC programs in ladder logic.