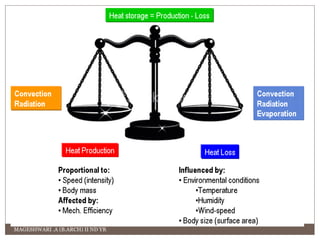
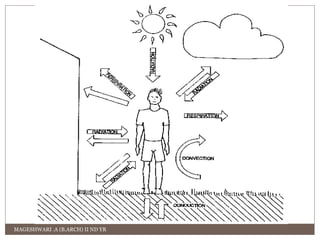
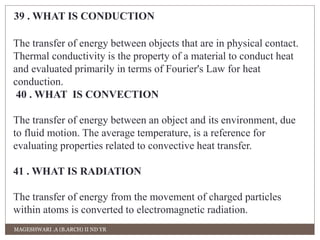
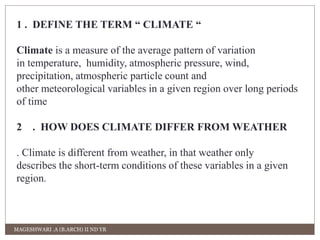
This document contains definitions and explanations of various climatic and meteorological concepts. It discusses factors that determine climate like temperature, precipitation, altitude, latitude, winds and more. It also defines terms like weather, humidity, wind, atmospheric pressure and how they impact human thermal comfort and building design. Key climatic classifications and methods to assess human comfort like effective temperature and clothing insulation are also summarized.










![17 . DEFINE RELATIVE HUMIDITY
The relative humidity of an air-water mixture is defined as the ratio of the partial pressure of
water vapor (H2O) in the mixture to the saturated vapor pressure of water at a
given temperature. Thus the relative humidity of air is a function of both water content and
temperature.
Relative humidity is normally expressed as a percentage and is calculated by using the following
equation:[4]
MAGESHWARI .A (B.ARCH) II ND YR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climateandbuilt-141119024841-conversion-gate01/85/Climate-and-built-environment-12-320.jpg)




![• 25 .DEFINE ACCLIMATIZATION
• acclimatization is the process in which an individual organism
adjusts to a gradual change in its environment (such as a change
in temperature, humidity, photoperiod, or pH), allowing it to
maintain performance across a range of environmental
conditions.
• Acclimatization occurs in a short period of time (days to weeks),
and within the organism's lifetime (compare to adaptation).
• 26 .WHAT IS PERSPIRATION
• Perspiration (sweating, transpiration, or diaphoresis) is the
production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin
ofmammals.[1]
• MAGESHWARI Two types .A (B.ARCH) of sweat II ND YR
glands can be found in humans: eccrine
glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climateandbuilt-141119024841-conversion-gate01/85/Climate-and-built-environment-17-320.jpg)