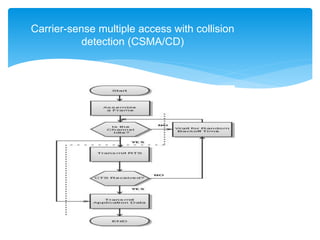
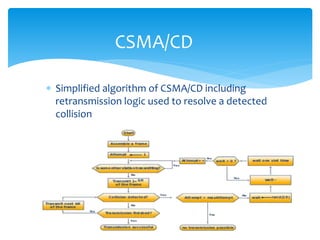
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is a media access control method used in early Ethernet technology. It uses carrier sensing to defer transmissions until no other stations are transmitting. When a collision is detected during transmission, the station stops transmitting and waits a random time before retrying. Stations first listen to ensure the network media is idle before transmitting. If a carrier signal is detected, the station must wait until the media is idle to transmit.