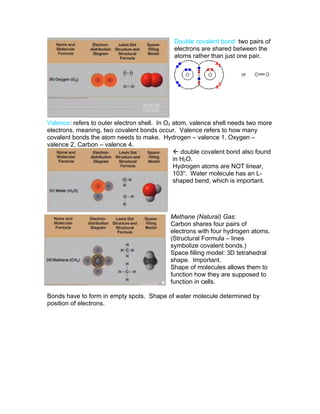
The document discusses the formation of chemical elements from hydrogen through nuclear fusion in stars, and how elements like carbon and oxygen that make up living things were created in stellar explosions. It then explains different types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds formed through electron transfer, covalent bonds where electrons are shared, and hydrogen bonds which are weak attractions between polar molecules. Molecular shapes determined by bonding allow compounds to function as required in living cells.