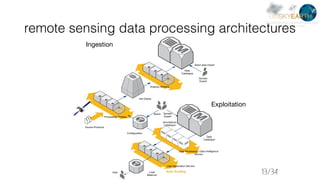
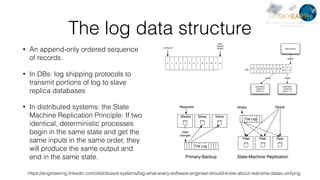
This document discusses image search and analysis techniques for remote sensing data. It describes an index management system that takes in data and indexes it using column-based databases. Images are analyzed to extract features that allow for image search based on compression in compressed streams. Queries can be performed on the indexed data to return similar images based on semantic labels and normalized distances from queries. Examples are provided using different remote sensing datasets, including GeoEye, DigitalGlobe, and TerraSAR-X images.

![Hadoop Cluster computing
[Lisa Vaas 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-3-320.jpg)
![Spark cluster computing
[Hitesh Dharmdasani, “Python and Bigdata - An Introduction to Spark (PySpark)”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-4-320.jpg)





![SQL vs NoSQL
[Lisa Vaas 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-11-320.jpg)










![iqcbm: geoeye
semantic label and these labels are stored into the database as part of the patch
information.
In the following, the results of different queries using the CBIR-FCD and TerraSAR-X
images are described.
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-22-320.jpg)
![23
iqcbm: digitalglobe
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-23-320.jpg)
![24
.76
.69
.79
.90
.95
.99
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]
normalized distance from query](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-24-320.jpg)
![25
iqcbm: terrasar-x
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-25-320.jpg)
![26
iqcbm: terrasar-x
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-26-320.jpg)

![iqcbm: terrasar-x
D3.1 KDD concepts and methods proposal: report & design recommendations 96
The patches were annotated with a semantic label by using the Search Engine based on
SVM tool and user supervision previously presented in section 5.1. The semantic labels
associated to the selected classes were previously described in Table 5.
In the following, we present some examples of retrieving TerraSAR-X structures using
both images. Table 11 displays the query images and the 20 top retrieved images. Some
quality metrics (Precision and Recall) were computed from these results and they are
summarized in Table 12.
Query
images
Retrieved images
Class9
Class6
Class7
Class36
TELEIOS FP7-257662
Class20
Class31
Class28
Class32
Table 11: Results of the queries based on image content using CBIR-FCD as data
mining tool.
Table 12 shows the precision and recall for the classes and the query time in seconds
needed for searching and retrieving the results.
Table 12: Precision and recall of the semantic classes using query based on content
and the query time.
Class Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
Query time
(sec)
Class1 5,36 5,17 0.32882
Class2 10,71 10,34 0.318238
Class3 5,36 5,17 0.235323
Class4 7,14 6,90 0.107209
TELEIOS FP7-257662
7. Applicable and Reference Documents
7.1. Applicable Documents
Document Title
Internal
Referenc
e
Katrin Molch et al., (2010). “Naming Convention for Image Patches”. [RI- 1]
N. Ritter and M. Ruth, (1995) “GeoTIFF Format Specification GeoTIFF”,
Revision 1.0, Version 1.8.1.
[RI- 2]
Robert M Haralick, K Shanmugam, Its'hak Dinstein (1973). "Textural Features
for Image Classification". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, SMC-3 (6): 610–621.
[RI- 3]
The GLCM Tutorial
http://www.fp.ucalgary.ca/mhallbey/tutorial.htm
[RI-4]
H.G. Feichtinger, Th. Strohmer (1998). "Gabor Analysis and Algorithms",
Birkhäuser.
[RI-5]
B.S. Manjunath, W.Y. Ma (1996). “Texture features for browsing and retrieval
of image data”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 18 (8): 837–842.
[RI-6]
A. Popescu, I. Gavat, M. Datcu (2008). "Complex SAR image characterization
using space variant spectral analysis". IEEE Radar Conference, 1-4.
[RI-7]
T. Li, M. Ogihara (2006). “Towards Intelligent Music Information Retrieval”.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 8(3), 564-574.
[RI-8]
A. Croisier, D. Esteban, C. Galand (1976). "Perfect channel splitting by use of
interpolation / decimation / tree decomposition techniques". International Conf.
on information Science and Systems, Patras, Greece: 443-446.
[RI-9]
P.P Vaidyananthan (1987). “Quadrature Mirror Filter Banks, M-Band
Extensions and Perfect-Reconstruction Techniques”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 4
(3): 4-20.
[RI-10]
TELEIOS KDD concepts and methods proposal: report & design recommendations
Corneliu Octavian Dumitru, Daniela Espinoza Molina, Shiyong Cui, Jagmal Singh, Marco Quartulli, Mihai Datcu
2011, FP7 TELEIOS Tech Report](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l8gxmuaorxgmm1xs2ozr-signature-a67e94e385b0f51ee716eaa6622e12490992bac90a7a1bf9ae2be66c7fac4b82-poli-160812071230/85/07-data-structures_and_representations-28-320.jpg)
