This document provides an overview of non-relational databases and MongoDB. It discusses the advantages of non-SQL databases like scalability and flexibility compared to RDBMS. It also covers MongoDB features like document-oriented data structure, dynamic queries, indexing, replication and sharding. The document demonstrates basic MongoDB operations in Ruby like connecting to a database, inserting and querying documents.












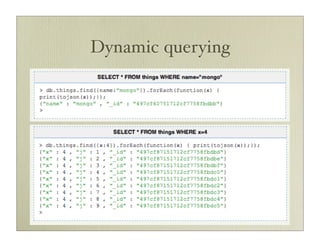
![Storage (BSON)
{ author: 'joe',
created: Date('03-28-2009'),
title: 'Yet another blog post',
text: 'Here is the text...',
tags: [ 'example', 'joe' ],
comments: [ { author: 'jim', comment: 'I disagree' },
{ author: 'nancy', comment: 'Good post' }
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbmy-091019010509-phpapp01/85/MongoDB-15-320.jpg)
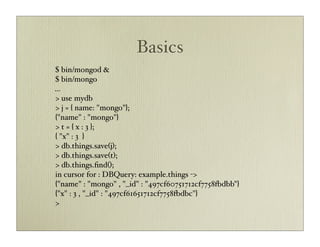

![Querying 2
• $in, $nin, $all, $ne, $gt, $gte, $lt, $lte, $size, $where
• :fields (like :select in active record)
• :limit, :offset for pagination
• :sort ascending or descending [[‘foo’, 1], [‘bar’, -1]]
• count and group (uses map/reduce)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbmy-091019010509-phpapp01/85/MongoDB-18-320.jpg)