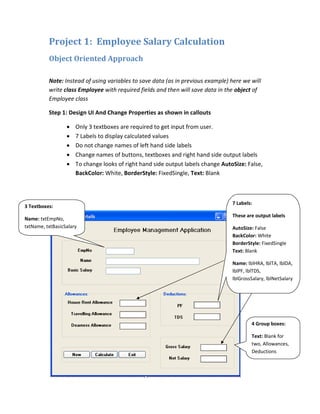
The document outlines a tutorial for creating an employee salary calculation application using Windows Forms and an object-oriented approach. It includes steps for designing the user interface, creating an employee class with salary calculation logic, and coding event handlers for user interaction. The final goal is to convert an existing student progress report project using the same object-oriented principles.