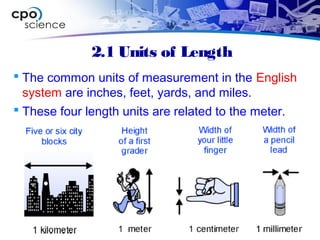
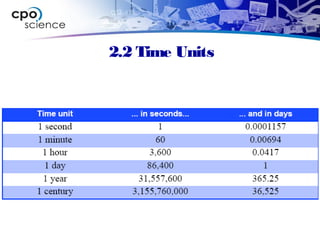
This document outlines the key concepts and objectives covered in Chapter 2 of the CPO Science Foundations of Physics textbook. The chapter focuses on measurement and units, including length, time, and mass. It describes the metric and English measurement systems, how to convert between units, and accurately measure distances, time intervals, and mass. Mass is explained at the atomic level, including atoms, molecules, and the three common states of matter. The objectives are to learn measurement skills and understand scientific concepts like distance, time, mass, and the structure of matter.