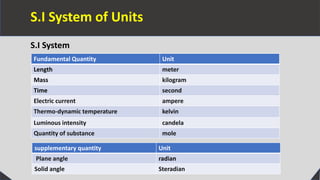
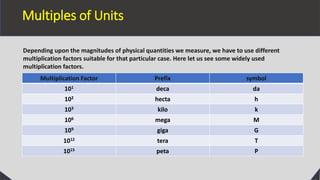
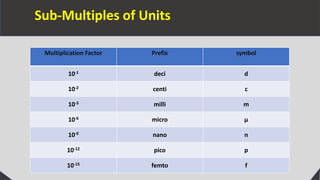
Units are necessary in physics to measure physical quantities and enable consistent comparisons. There are two types of units - fundamental units which measure fundamental quantities like length, mass, and time, and derived units which measure derived quantities like area, speed, and force. The International System of Units (SI) defines seven base units, including the meter, kilogram, and second. Units are also defined for other physical quantities using prefixes to indicate multiples or submultiples of the base units, enabling measurement of a wide range of quantities. Proper choice of units allows for convenient measurement depending on the magnitude of the physical quantity.