This document discusses advanced PowerShell concepts including functions, modules, comment-based help, accepting pipeline input, and creating PowerShell objects. It highlights three important cmdlets for discovery (Get-Help, Get-Command, Get-Member) and how to create reusable functions and modules with functions. It also covers how to accept pipeline input into functions and create PowerShell objects to output from functions.



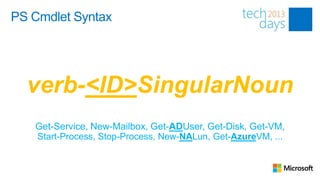
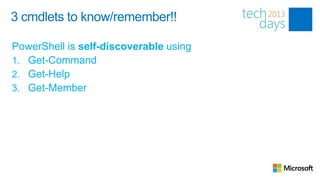






![Creating Functions
function Get-OS
{
param(
[string[]]$ComputerName = $env:COMPUTERNAME
)
gwmi Win32_OperatingSystem -ComputerName $ComputerName
}
PS C:> Get-OS -ComputerName “MyClient1”, ”MyClient2”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03itproroom9thepowerofpowershellkurtroggen85-130313120816-phpapp01/85/The-Power-of-PowerShell-Advanced-12-320.jpg)
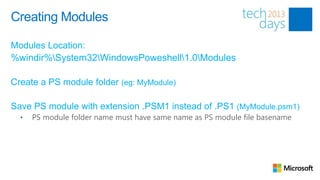

![Comment Based Help
Function Get-OS
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
<toktok>
.DESCRIPTION
<toktok>
.PARAMETER ComputerName
<toktok>
.EXAMPLE
Get-OS
.LINK
http://mysite.com/get-os/
#>
Param (
[string]$ComputerName,
[switch]$Details
)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03itproroom9thepowerofpowershellkurtroggen85-130313120816-phpapp01/85/The-Power-of-PowerShell-Advanced-15-320.jpg)

![Accepting Pipeline Input
function Get-OS
{
param(
[Parameter(ValueFromPipeLine=$true)]
[string[]]$ComputerName = $env:COMPUTERNAME
)
PROCESS
{
<blabla>
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03itproroom9thepowerofpowershellkurtroggen85-130313120816-phpapp01/85/The-Power-of-PowerShell-Advanced-17-320.jpg)



