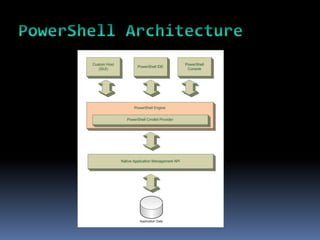
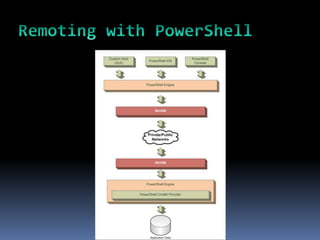
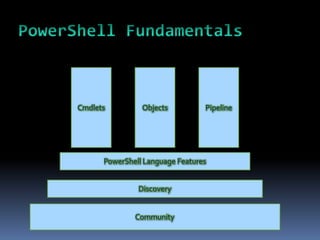
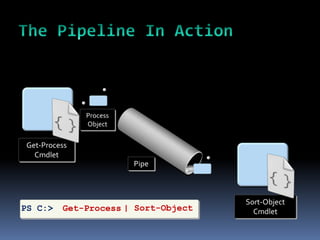
This document provides an introduction to PowerShell, including what it is, its core components like cmdlets and objects, and how it can be used for automation and management. PowerShell combines a command-line shell and a scripting language that allows users to discover, query, and manipulate systems through a .NET object model. It includes cmdlets for common system tasks and can be extended with additional cmdlets. PowerShell is included with Windows 7/Server 2008 R2 and later or can be installed on earlier versions, and will be important for IT professionals to learn as it replaces traditional shells.















![ Array variables contain multiple values/objects
Array members addressed with [], e.g. $a[0]
$a[0] is first item in array
$a[-1] is last item
Use .GetType()
$myfoo = LS c:foo
$myfoo.gettype()
Array members can be one or multiple types
LS c: | Get-Member
Arrays used with loops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psh101-111030131451-phpapp02/85/PowerShell-101-20-320.jpg)



![ Variables can be implicitly typed
PowerShell works it out by default
$I=42;$i.gettype()
Variables can be explicitly typed
[int64] $i = 42
$i.gettype()
Typing an expression
$i = [int64] (55 – 13); $i.gettype()
$i = [int64] 55 – [int32] 13; $i.gettype()
$i = [int32] 55 – [int64] 13; $i.gettype()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psh101-111030131451-phpapp02/85/PowerShell-101-24-320.jpg)










![ Set up prompt
Function prompt {“Psh`[$(pwd)]: “}
Add personal aliases
Set-Alias gh get-help
Create PSDrives
New-PsDrive demo file e:pshdemo
Set size/title of of PowerShell console
$host.ui.rawui.WindowTitle = "PowerShell Rocks!!!"
$host.ui.rawui.buffersize.width=120
$host.ui.rawui.buffersize.height=9999
$host.ui.rawui.windowsize.width=120
$host.ui.rawui.windowsize.height=42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psh101-111030131451-phpapp02/85/PowerShell-101-36-320.jpg)






