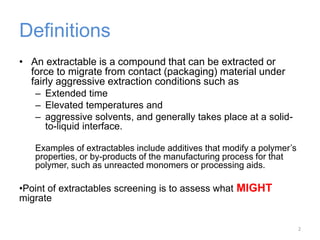
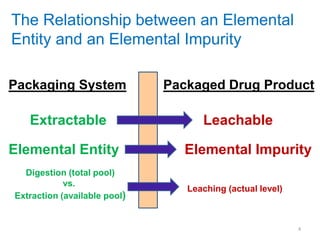
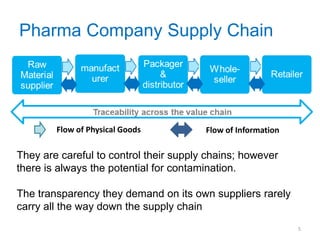
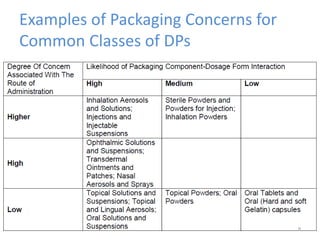
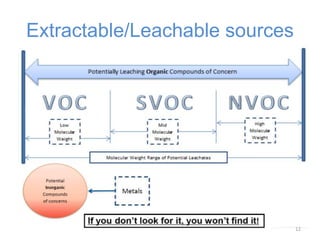
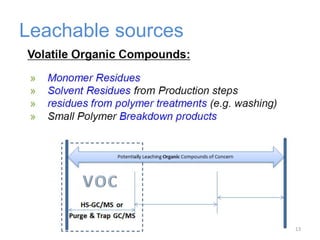
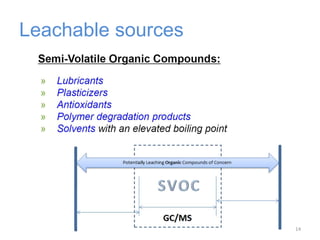
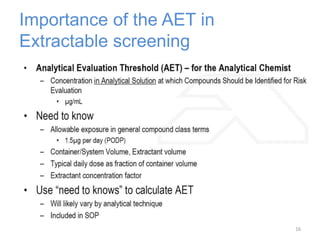
This document provides an introduction to extractables and leachables for pharmaceutical packaging. It defines extractables as compounds that can be extracted from packaging materials under aggressive extraction conditions, while leachables are those that migrate into drugs under normal conditions. The relationship between extractables, as the total potential pool of migrating compounds, and leachables, as the actual level that leaches into drugs, is explained. Key aspects of extractable and leachable screening covered include extraction/leaching conditions, regulatory guidelines, packaging material composition, and real examples of issues that have occurred.