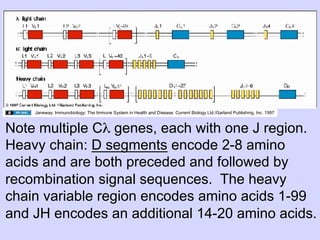
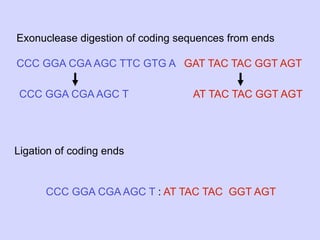
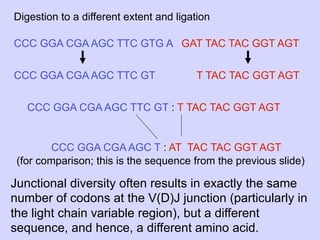
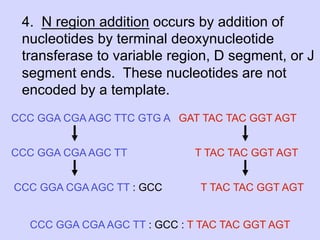
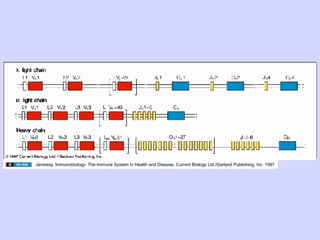
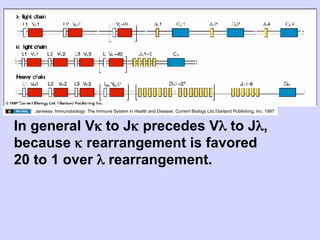
1. Diversity in the germline is expanded by DNA rearrangement in B cells through combinatorial diversity from joining variable, diversity and joining gene segments, as well as junctional diversity from variations in rearrangement.
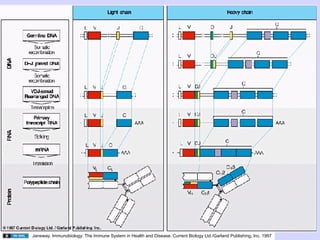
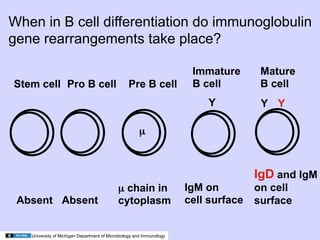
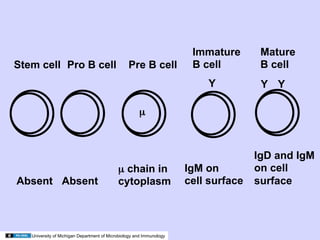
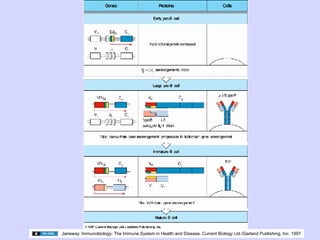
2. During antigen-independent B cell differentiation, immunoglobulin gene rearrangement begins with D-J joining, followed by V-DJ joining and light chain rearrangement, culminating in expression of IgM on the cell surface.
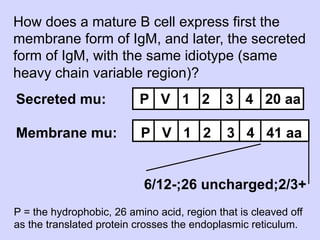
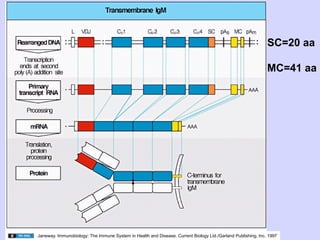
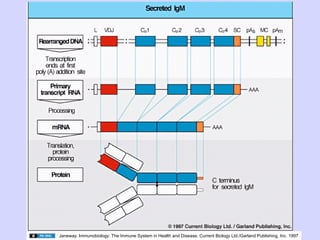
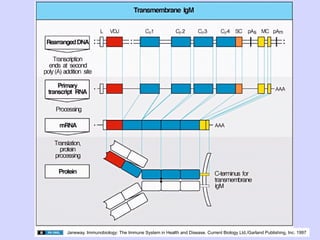
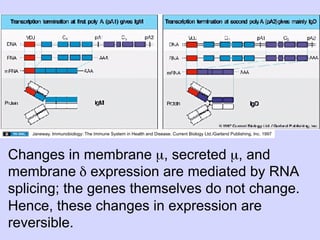
3. Mature B cells can express both IgM and IgD through alternative RNA splicing of primary gene transcripts for membrane and secreted forms of both antibodies.