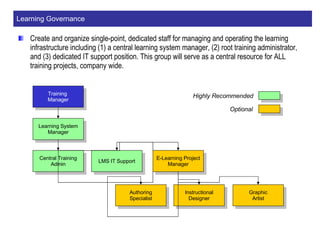
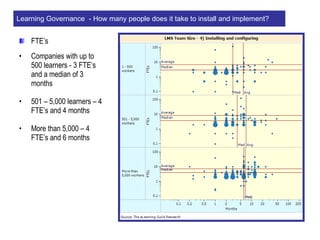
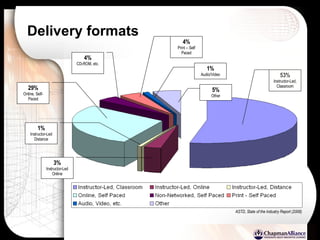
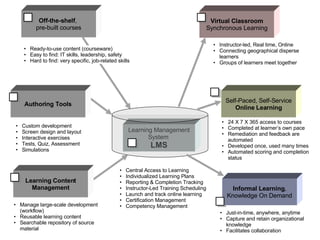
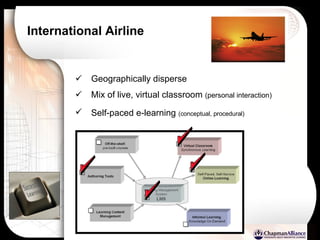
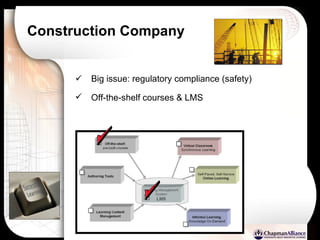
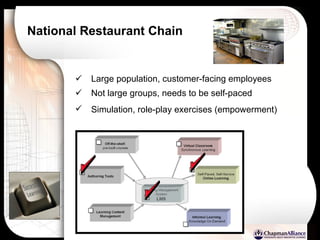
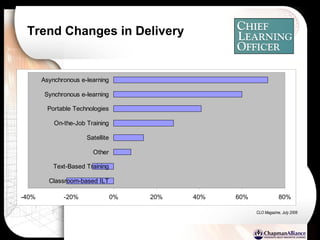
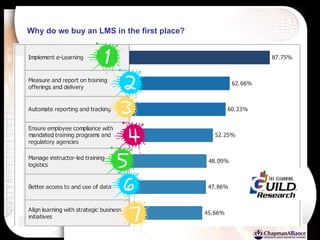
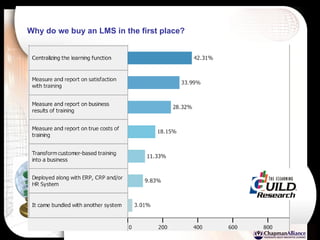
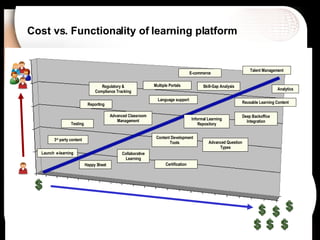
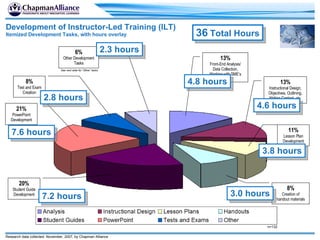
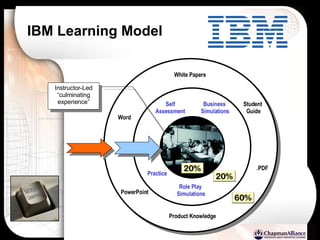
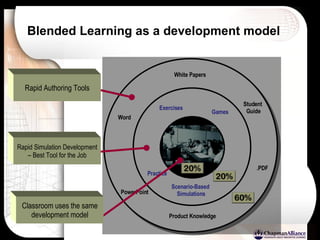
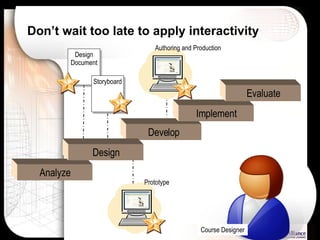
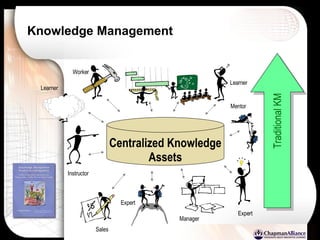
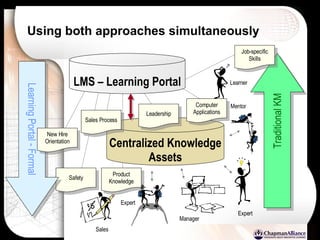
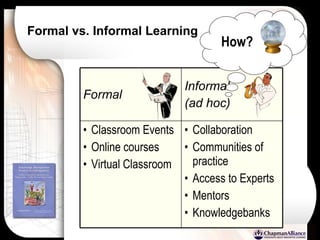
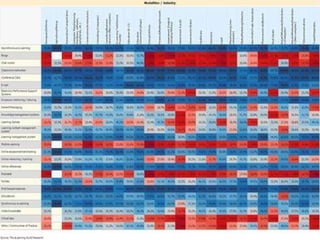
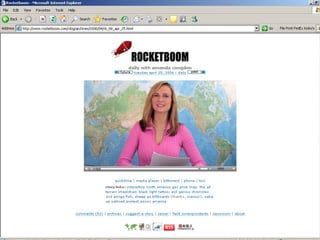
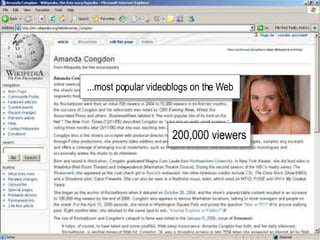
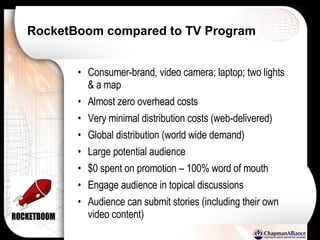
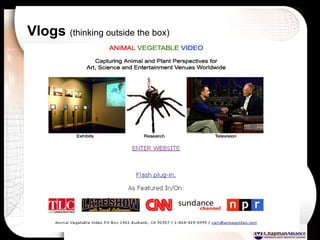
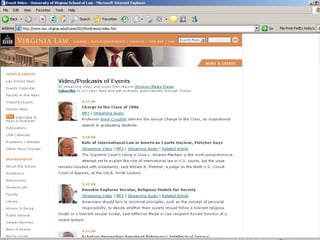
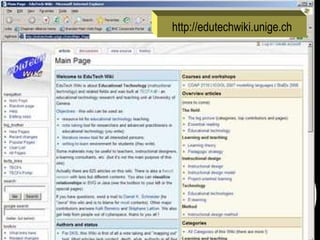
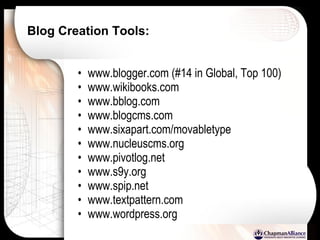
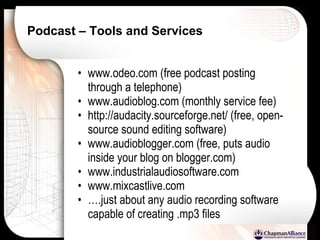
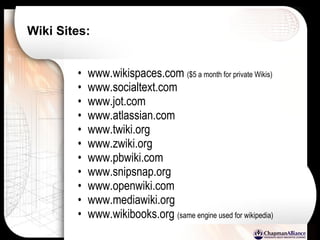
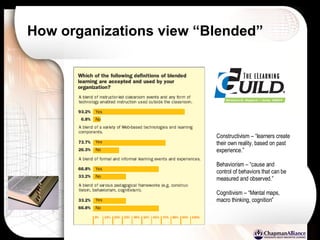
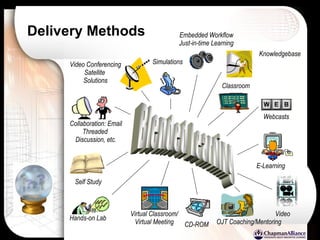
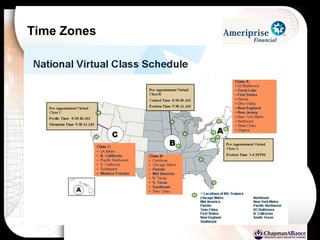
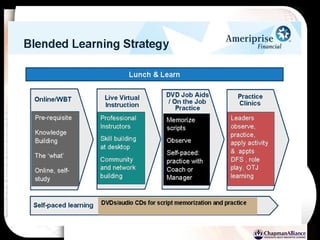
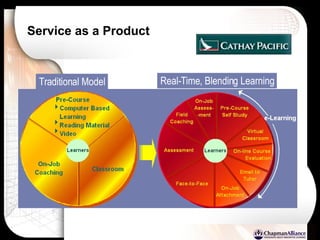
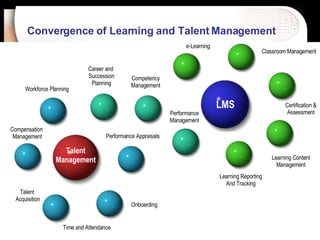
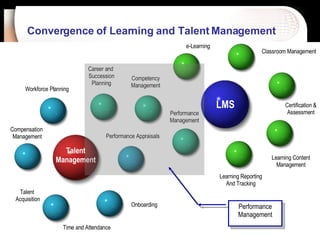
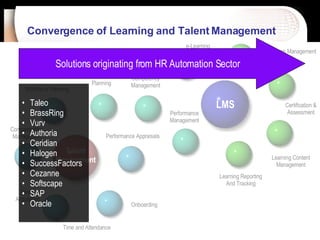
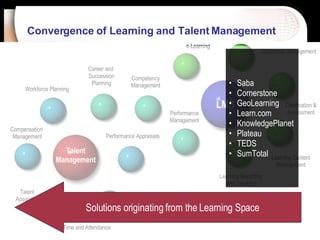
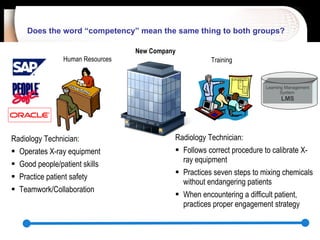
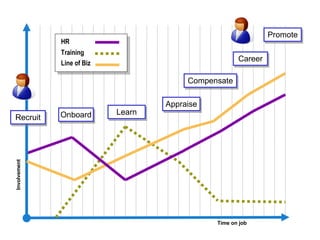
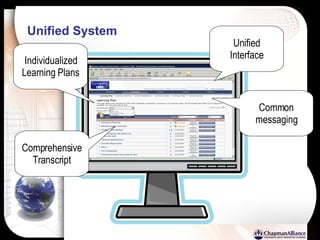
The document discusses a learning benchmarking forum agenda that includes benchmarking learning infrastructure alignment, content development, use of web 2.0 technologies, blended learning, and talent/performance management practices. It provides examples of how different organizations implement blended learning and informal learning strategies. Delivery formats and trends in the industry are also benchmarked.
![Learning Benchmarking Forum Facilitator: Bryan Chapman Chief Learning Strategist Chapman Alliance [email_address] 24x7 Learning presents](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-handout-version-1209975433312986-8/75/01-Handout-Version-1-2048.jpg)













































![Questions??? Facilitator: Bryan Chapman Chief Learning Strategist Chapman Alliance [email_address] Hosted by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-handout-version-1209975433312986-8/85/01-Handout-Version-108-320.jpg)