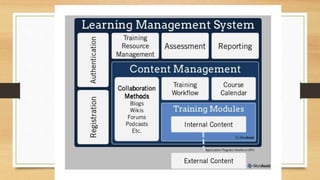
This document discusses learning management systems (LMS) and how they can be used for online education and employee training. It begins by explaining that LMS tools are used by schools and companies to track student/employee progress and ensure skills and processes are up to date. The rest of the document outlines key aspects of setting up and implementing an LMS, including: components like content hosting, reporting, and communication tools; use cases like onboarding, training, and knowledge retention; and options for hosted or open-source systems. It emphasizes using data from LMS to identify training needs and high/low performers, and provides examples of how libraries can implement LMS for staff and patron training.