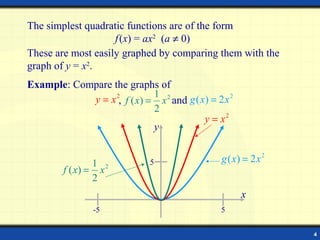
1) A quadratic function is an equation of the form f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0. Its graph is a parabola.
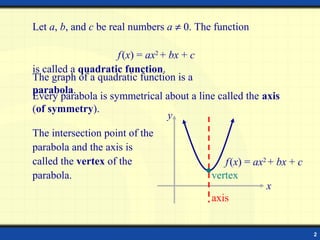
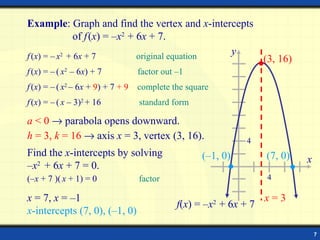
2) The vertex of a parabola is the point where it intersects its axis of symmetry. If a > 0, the parabola opens upward and the vertex is a minimum. If a < 0, it opens downward and the vertex is a maximum.
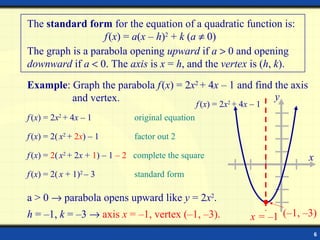
3) The standard form of a quadratic equation is f(x) = a(x - h)^2 + k, where the vertex is (h, k) and the axis of symmetry is x = h.