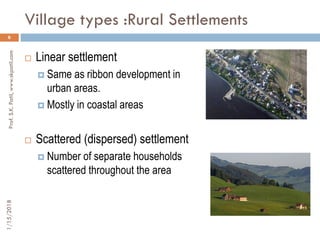
The document discusses the necessity of village planning in India, highlighting that a significant portion of the population lives in rural areas. It contrasts rural and urban living conditions, village types, and outlines principles for effective village planning, emphasizing accessibility and community hubs. The material is presented by Prof. S.K. Patil and is licensed for community use under a Creative Commons license.