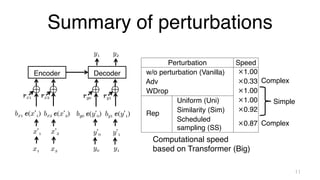
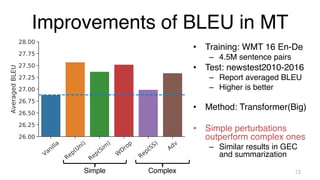
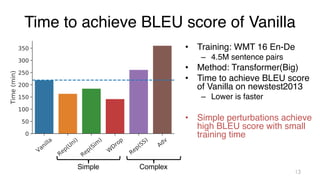
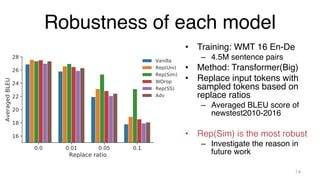
The document investigates time-efficient perturbation methods in sequence-to-sequence tasks, including machine translation, summarization, and grammatical error correction. It finds that simple perturbations, such as word dropout, can achieve comparable performance to complex methods like scheduled sampling while significantly reducing training time. The research emphasizes the utility of simple perturbations as a foundational approach for building strong models.


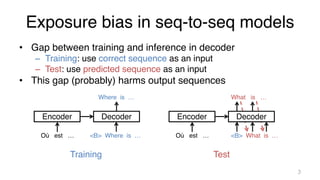
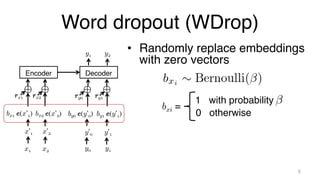
![Address exposure bias
• Scheduled sampling [Bengio+ 15]
– Probabilistically use predicted tokens during the training
• We can also add other noises to inputs
– Adversarial perturbations, word dropout, …
– Call such noises “perturbations” in this study
4
Encoder
What was you …
Où est ma … <B> What is you …
Correct
Predict
Where is my …
Decoder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naacl2021slide4slideshare-210511104820/85/Rethinking-Perturbations-in-Encoder-Decoders-for-Fast-Training-4-320.jpg)
![Perturbations are widely-used?
• There are various (complex) perturbations
• Researchers report (complex) perturbations are useful
– Scheduled sampling [Zhang+ 19] was awarded ACL Best paper
• However, perturbations are NOT widely-used
5
Recent WMT systems didn’t use perturbations.
We also didn’t use perturbations but achieved
the top score on WMT 2020 news translation!!!
(Re-)investigate the usefulness of perturbations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naacl2021slide4slideshare-210511104820/85/Rethinking-Perturbations-in-Encoder-Decoders-for-Fast-Training-5-320.jpg)

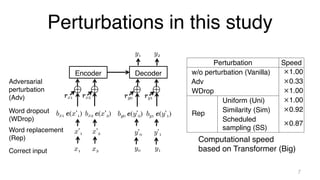
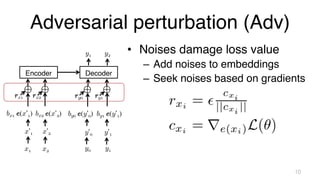
![Word replacement (Rep)
• Randomly replace words with sampled ones
– Where is my cat ? → What is my dog ?
• 3 distributions for samplings
– Uniform (Uni)
– Similarity (Sim)
• Based on embeddings:
– Conditional probability
= Scheduled sampling (SS)
• Prediction of a decoder:
8
Decoder
Encoder
y1 y2
x1
x’1
bx1 e(x’1)
rx1
x2
x’2
bx2 e(x’2)
rx2
y0
y’0
by0 e(y’0)
ry0
y1
y’1
by1 e(y’1)
ry1
め込み表現(次元数は 𝑑𝑥)を 𝑬𝑥 ∈ ℝ|
ン 𝑥𝑖 に対応する埋め込み表現を 𝒆(𝑥𝑖)
とき,次の確率分布を 𝑄𝑥𝑖 として用い
softmax(𝑬𝑥 𝒆(𝑥𝑖)),
ここで,softmax(.) はソフトマックス
すなわち,式(7)は 𝒆(𝑥𝑖) に似た埋め
い確率を付与する.言い換えれば,式(
考慮していない場合の,𝑥𝑖 の類似トー
率を付与する.デコーダ側についても
列および長さ 𝐽 の出力トークン列をそれぞ
𝒚1:𝐽 とすると,エンコーダ・デコーダは次
き確率を計算する:
𝑝(𝒀|𝑿) =
𝐽+1
!
𝑗=1
𝑝(𝑦𝑗 |𝒚0:𝑗−1, 𝑿), (1)
𝑦0 および 𝑦𝐽+1 はそれぞれ文頭,文末を示す
ークンとし,𝑿 = 𝒙1:𝐼 ,𝒀 = 𝒚1:𝐽+1 とする.
おいては,訓練データにおける負の対数尤
化するパラメータ 𝜽 を探す.𝑿𝑛 と 𝒀𝑛 とい
する系列のペアを含む訓練データを D と
なわち,D = {(𝑿𝑛,𝒀𝑛)}|D|
𝑛=1 とすると,次の
を最小化するように学習を行う.
L(𝜽) = −
1 "
log 𝑝(𝒀|𝑿; 𝜽). (2)
ここで,𝑞 と 𝑘 はハイパーパラメータで
の式により,𝛼𝑡 は 1 から 𝑞 まで,学習ス
依存して減少していく.この 𝛼𝑡 を各ス
ける 𝛼 として用いる.
分布 𝑄𝑥𝑖 については,条件付き確率,
類似度の 3 種類を用いる.
条件付き確率: Rep(SS) Bengio ら [9]
推論時における差異に対処するため,ス
ドサンプリングを提案した.スケジュー
リングは次の条件付き確率を 𝑄𝑦𝑖 として
𝑝( ˆ
𝑦𝑖 |𝒚!
0:𝑖−1, 𝑿).
スケジュールドサンプリングはデコーダ
計算する手法であり,𝑄𝑥𝑖 に対応する関](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naacl2021slide4slideshare-210511104820/85/Rethinking-Perturbations-in-Encoder-Decoders-for-Fast-Training-8-320.jpg)