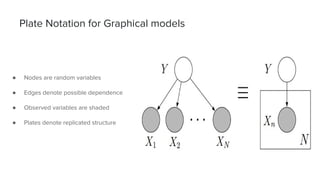
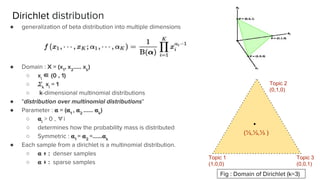
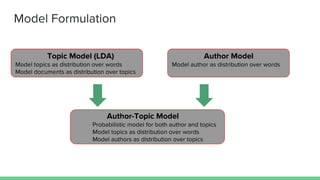
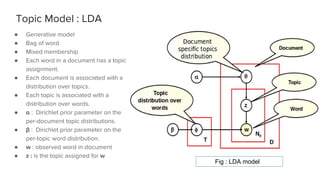
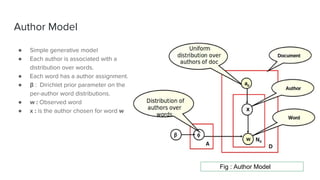
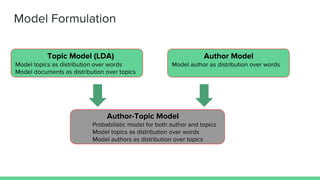
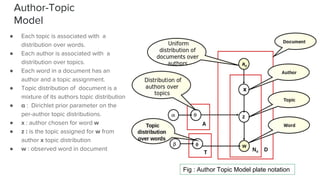
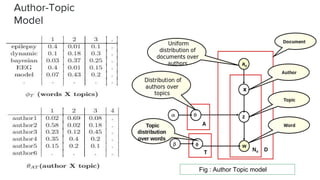
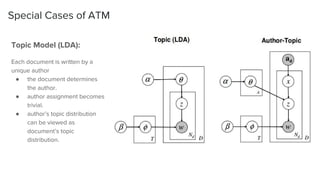
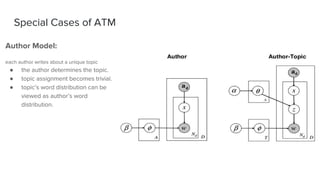
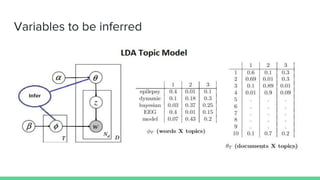
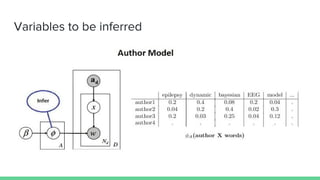
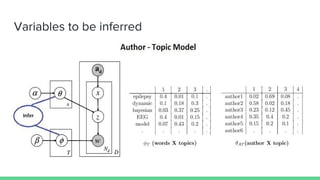
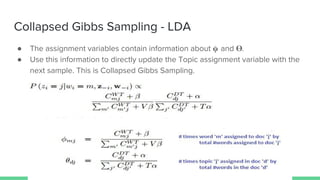
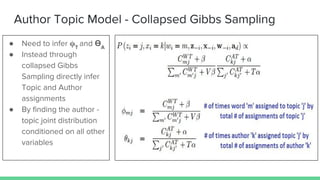
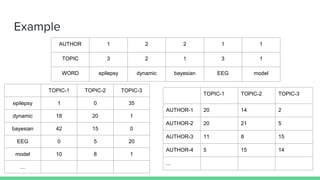
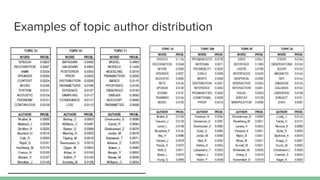
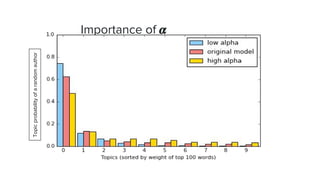
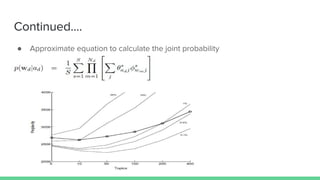
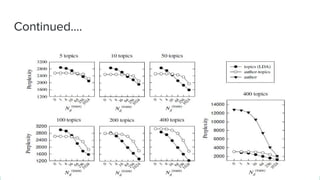
The document presents an overview of the author-topic model introduced by Darshan Ramakant Bhat and others, which simultaneously models document content and author interests. It includes model formulation, parameter estimation using Gibbs sampling, and evaluations on datasets like NIPS and Citeseer. The model's applications include automatic reviewer recommendation for academic papers, showcasing its predictive power and utility in authorship analysis.



![Notations
● Vocabulary set size : V
● Total unique authors : A
● Document d is identified as (wd
, ad
)
● Nd
: number of words in Document d.
● wd
: Vector of Nd
words (subset of vocabulary)
wd
= [w1d
w2d
…….. wNd d
]
● wid
: ith
word in document d
● Ad
: number of authors of Document d
● ad
: Vector of Ad
authors (subset of authors)
ad
= [a1d
a2d
…….. aAd d
]
● Corpus : Collection D documents
= { (w1
, a1
) , (w2
, a2
) ……. (wD
, aD
) }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/authortopicmodels-161122170039/85/Author-Topic-Model-4-320.jpg)