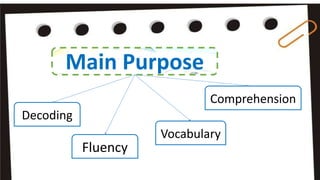
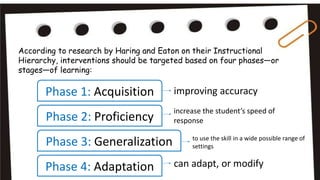
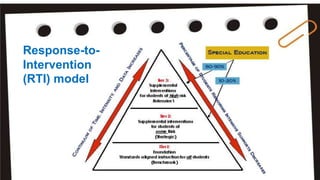
Reading intervention programs aim to prevent or address reading failure by targeting students' specific needs. Effective interventions identify whether a student struggles with decoding, fluency, comprehension, or vocabulary and provide instruction tailored to their phase of learning. The response to intervention model uses increasingly intensive tiers of support. Tier 1 involves core instruction, Tier 2 adds more time and intensity, and Tier 3 provides individualized intervention. Successful programs explicitly teach phonics, include reading with comprehension, and can be implemented in small groups or by paraprofessionals especially in early grades. Evaluating programs ensures they adapt to student needs and include alphabetic knowledge, phonemic awareness, vocabulary and text reading.