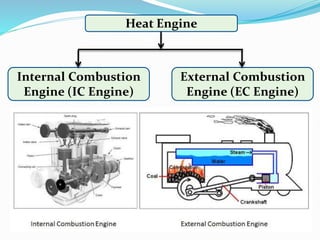
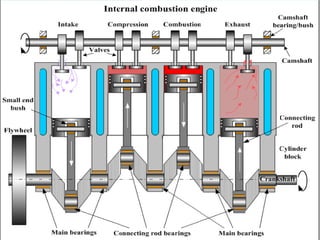
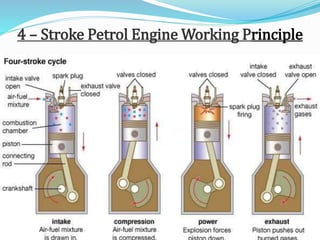
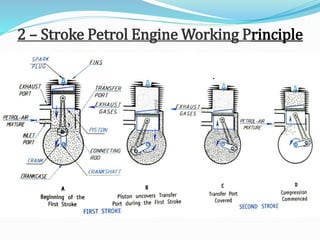
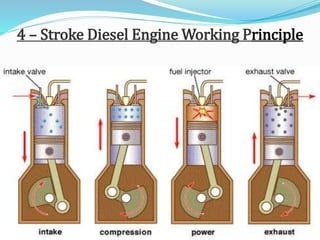
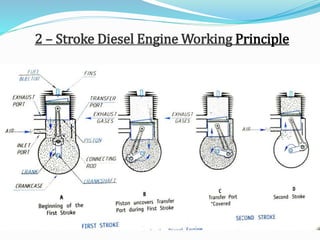
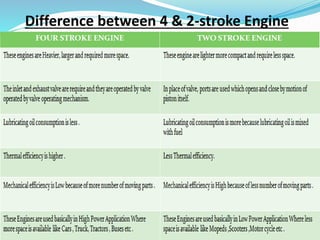
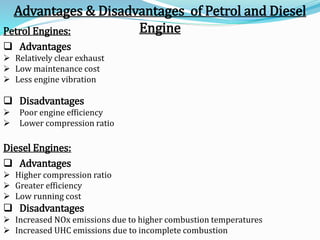
The document provides an overview of internal combustion (IC) engines, including their classification based on thermodynamic cycles, fuel type, ignition type, and other characteristics. It details the working principles of 4-stroke and 2-stroke petrol and diesel engines, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. The content is structured to explain the components and operational differences between various engine types.