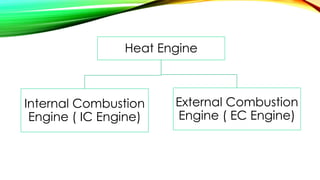
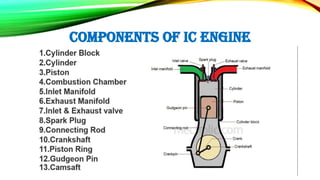
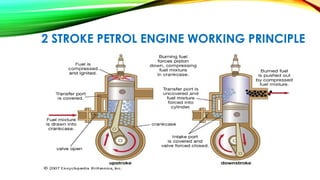
The document is a presentation on internal combustion (IC) engines, detailing their classification, working principles, and advantages and disadvantages. It explains the different types of IC engines based on thermodynamic cycles, fuel type, strokes, and ignition methods. The presentation highlights the pros and cons of both petrol and diesel engines.