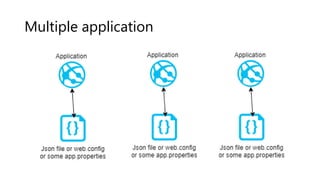
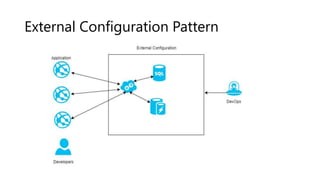
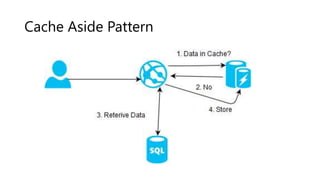
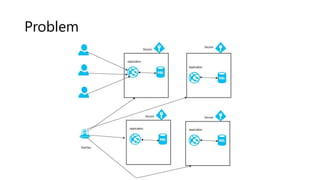
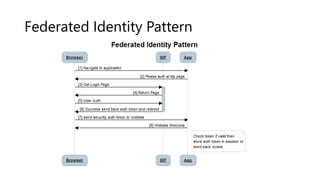
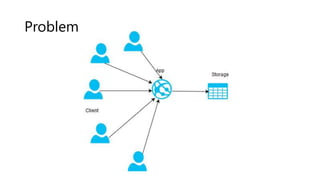
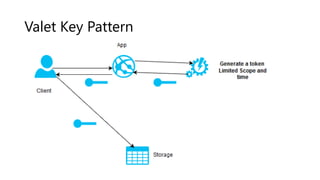
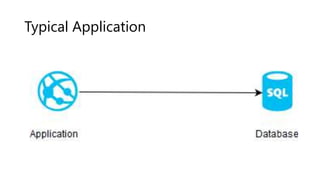
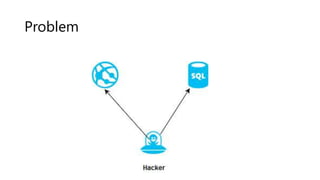
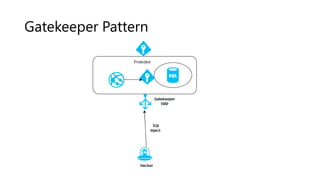
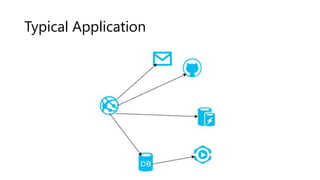
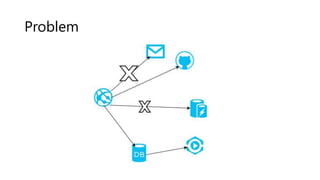
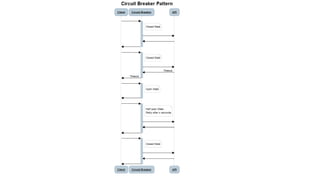
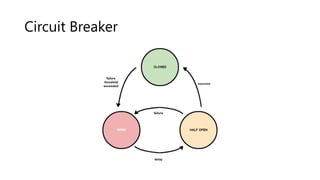
The document outlines several software design patterns including the external configuration, cache aside, federated identity, valet key, gatekeeper, and circuit breaker patterns, which aim to provide reusable solutions for common software problems. Each pattern describes its purpose, application scenarios, advantages, and potential drawbacks, along with relevant cloud offerings. These patterns facilitate better management, performance, security, and user experience in software development.