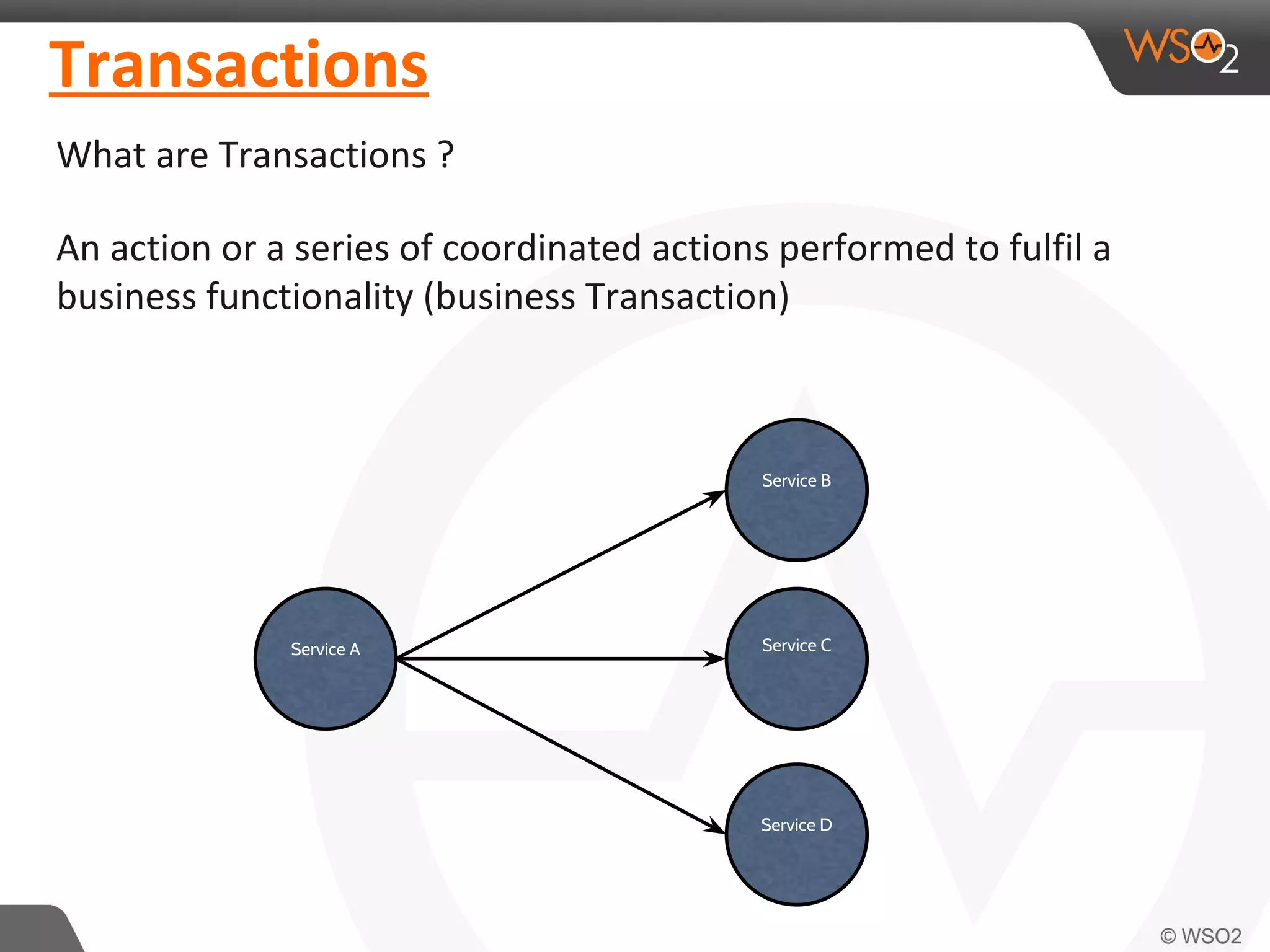
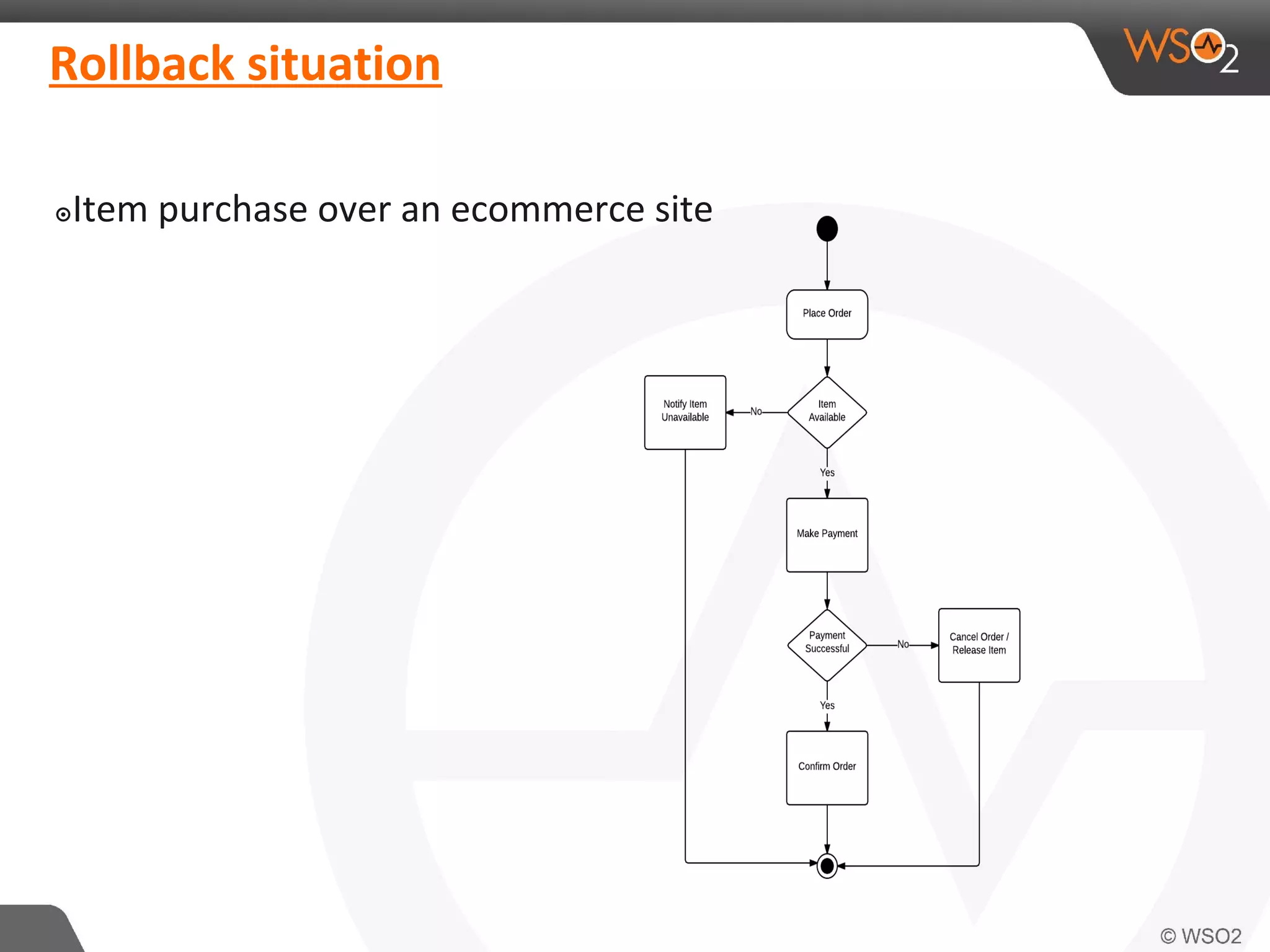
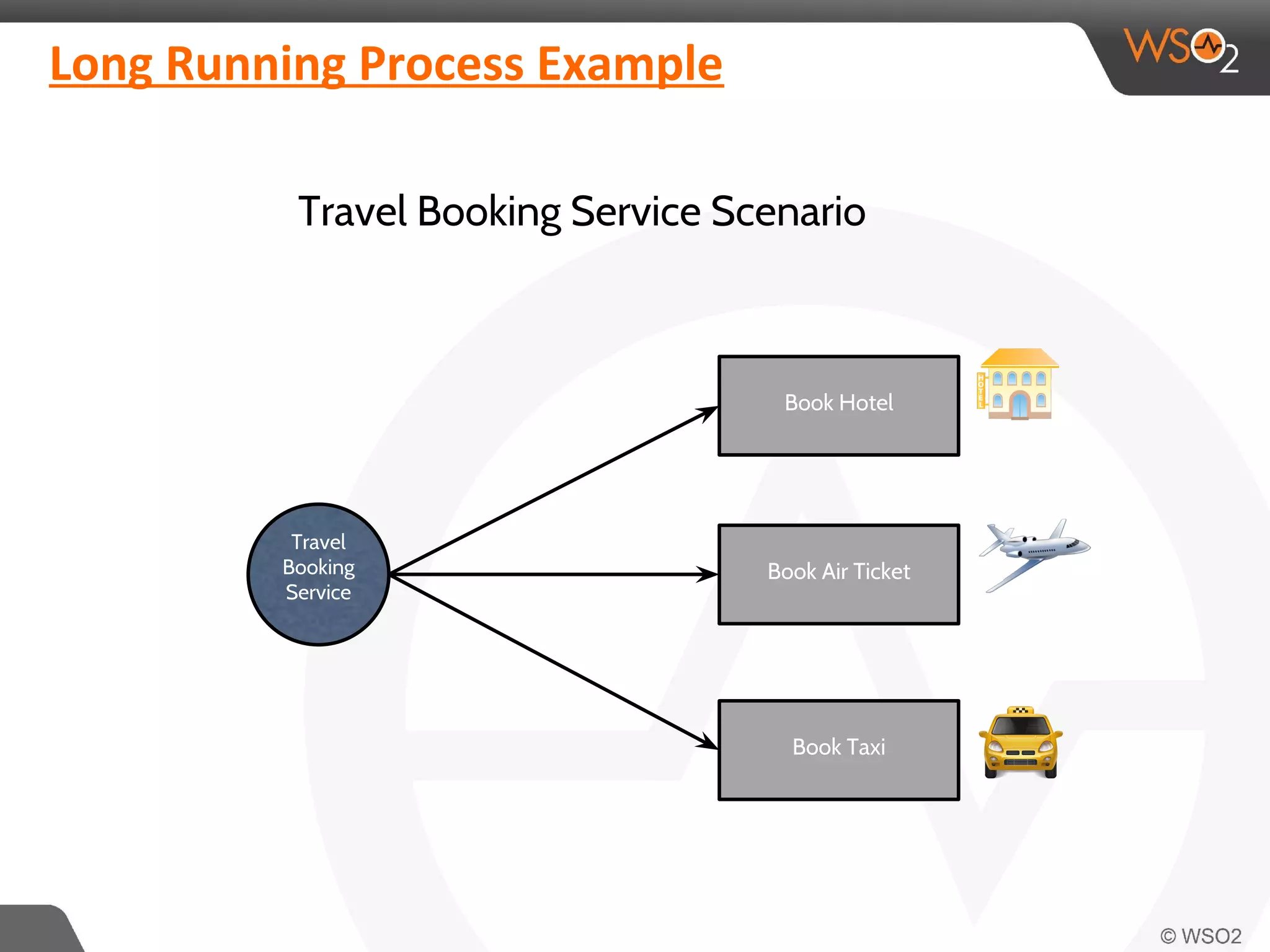
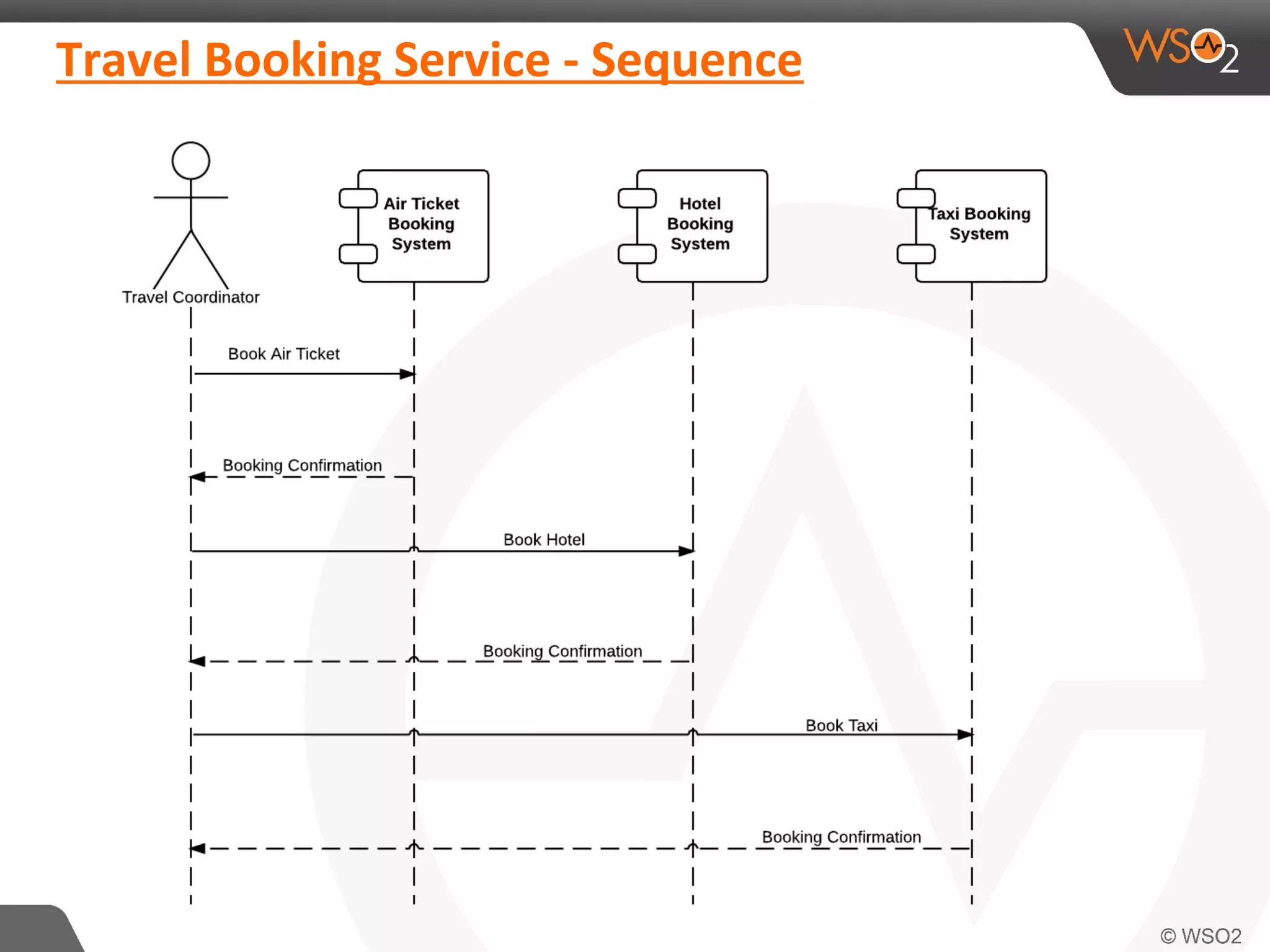
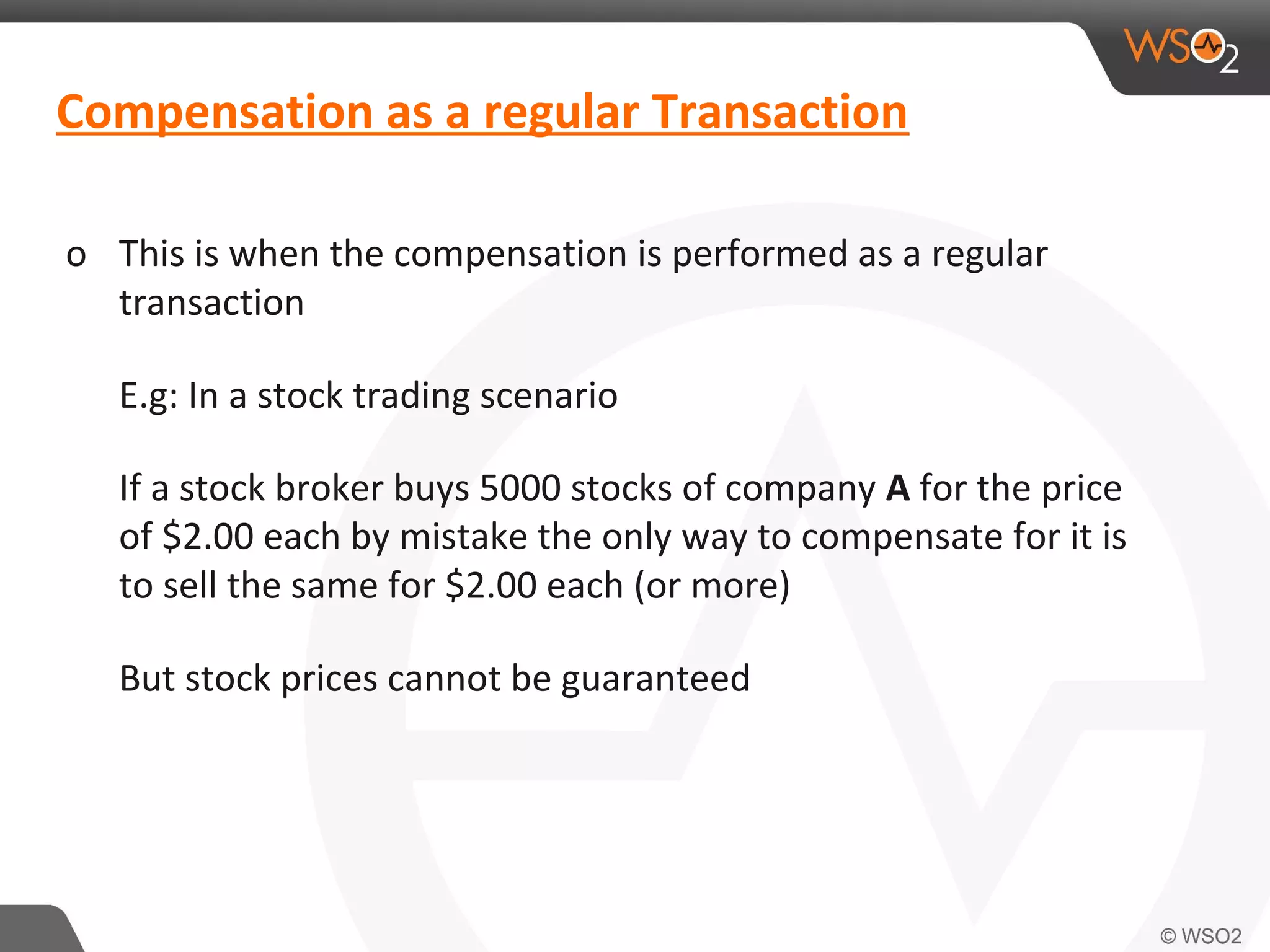
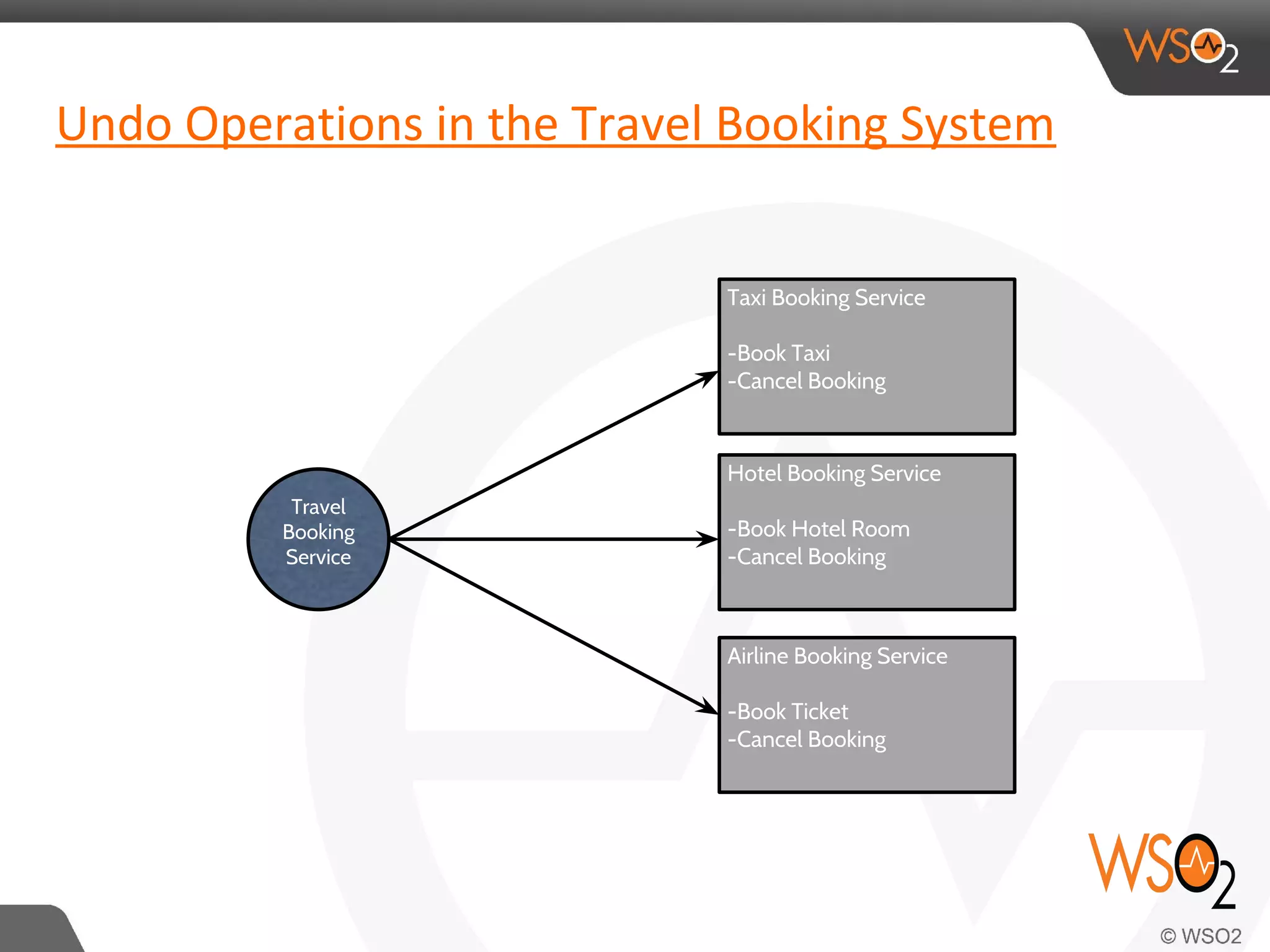
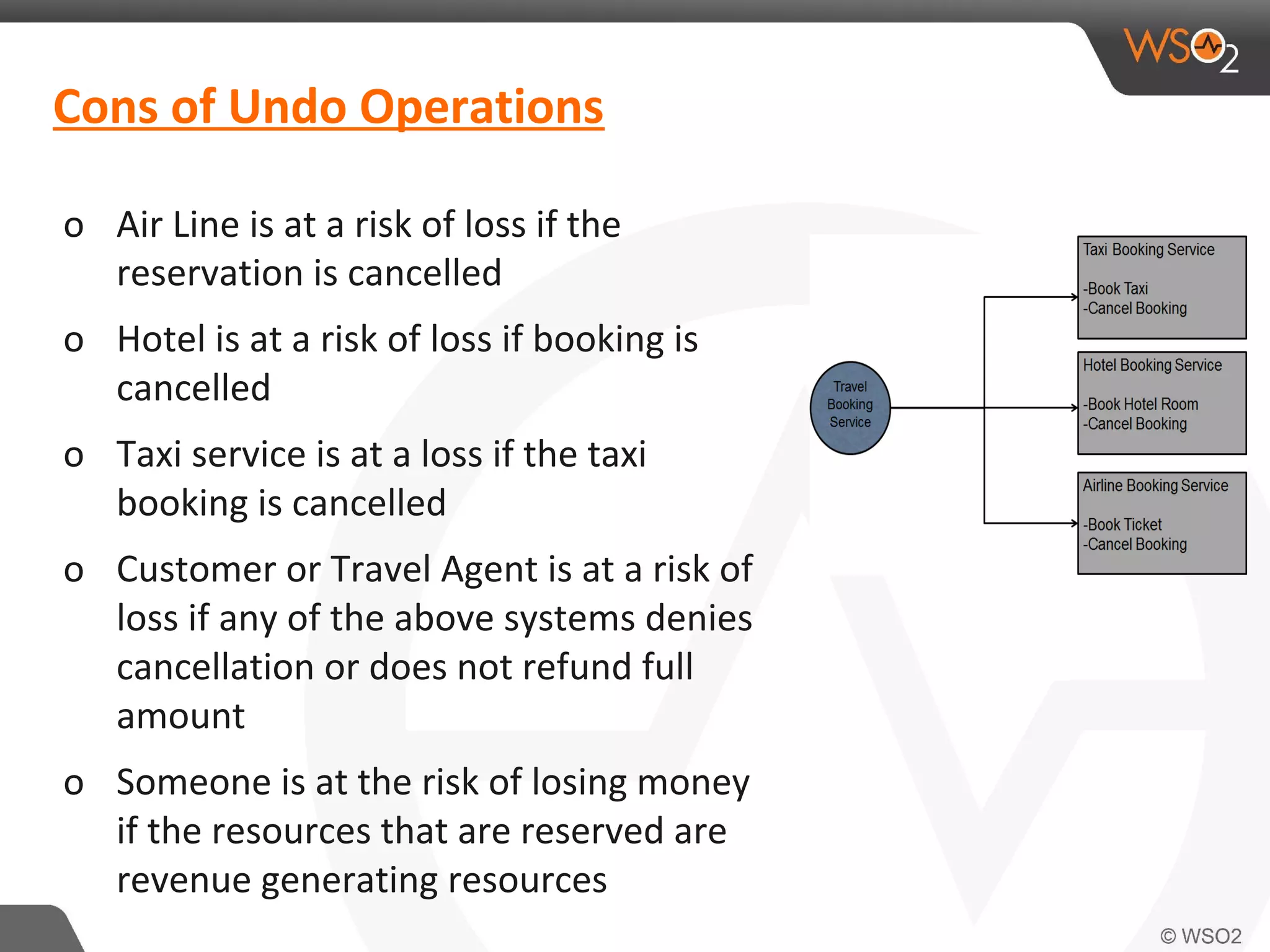
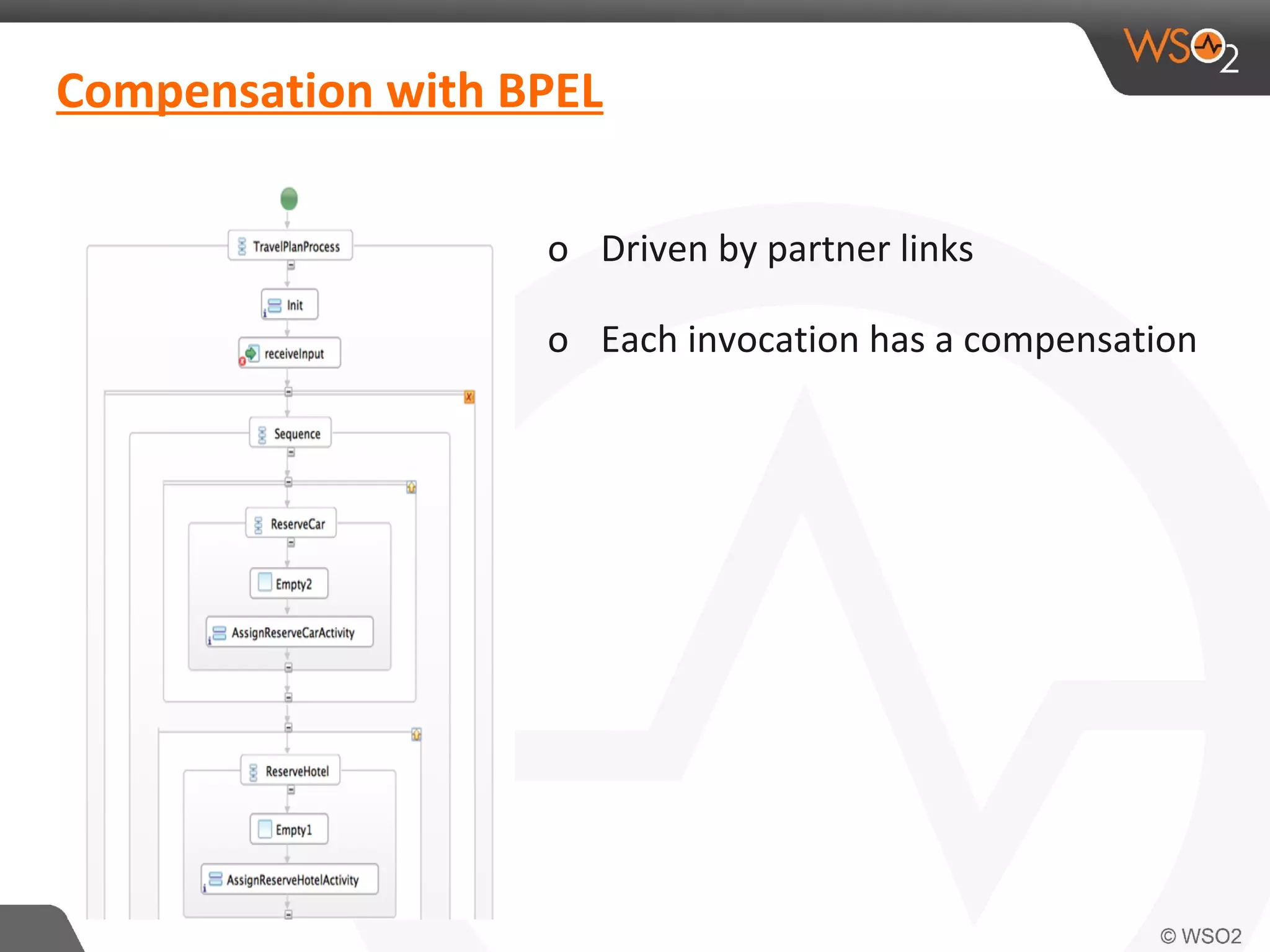
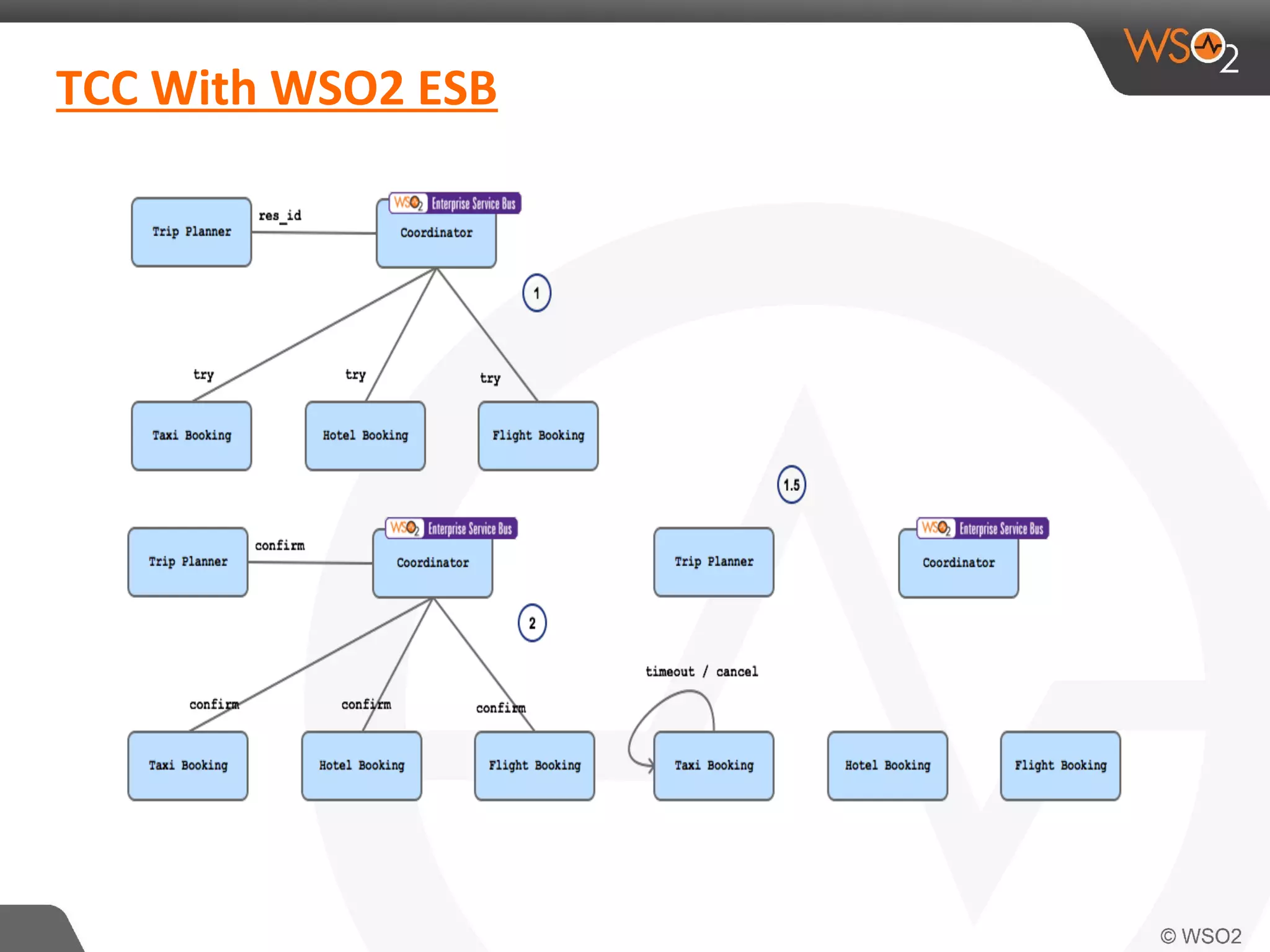
This document discusses compensating transactions in service-oriented architectures. It begins by defining transactions and describing stateful and stateless transactions. It then discusses challenges with long-running processes and rollbacks. Compensation is introduced as a way to restore systems after errors through undo operations or tentative reservations. The document outlines a Try-Confirm-Cancel model and shows how it can be implemented using BPEL and WSO2 ESB to handle compensation in long-running processes.