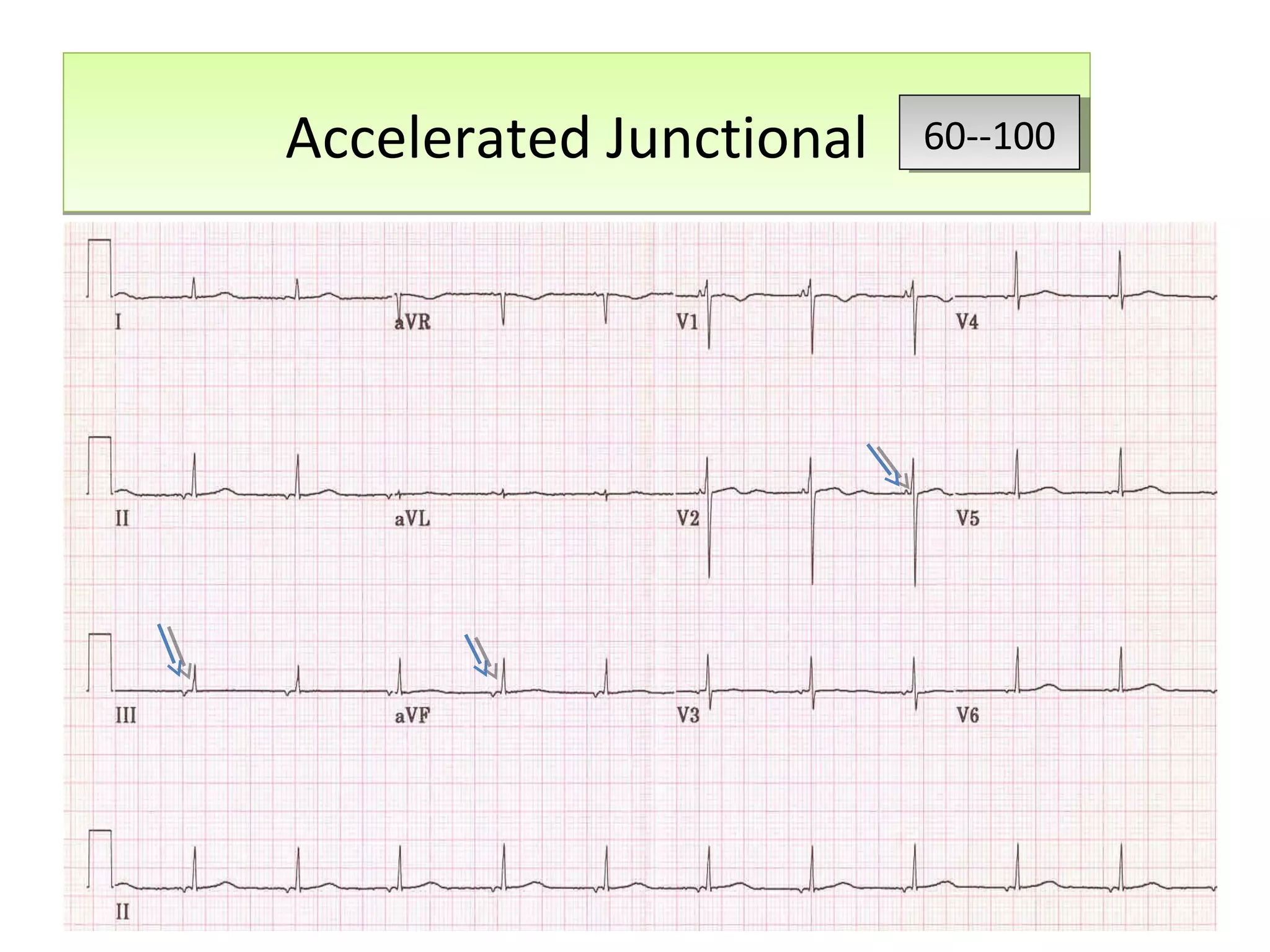
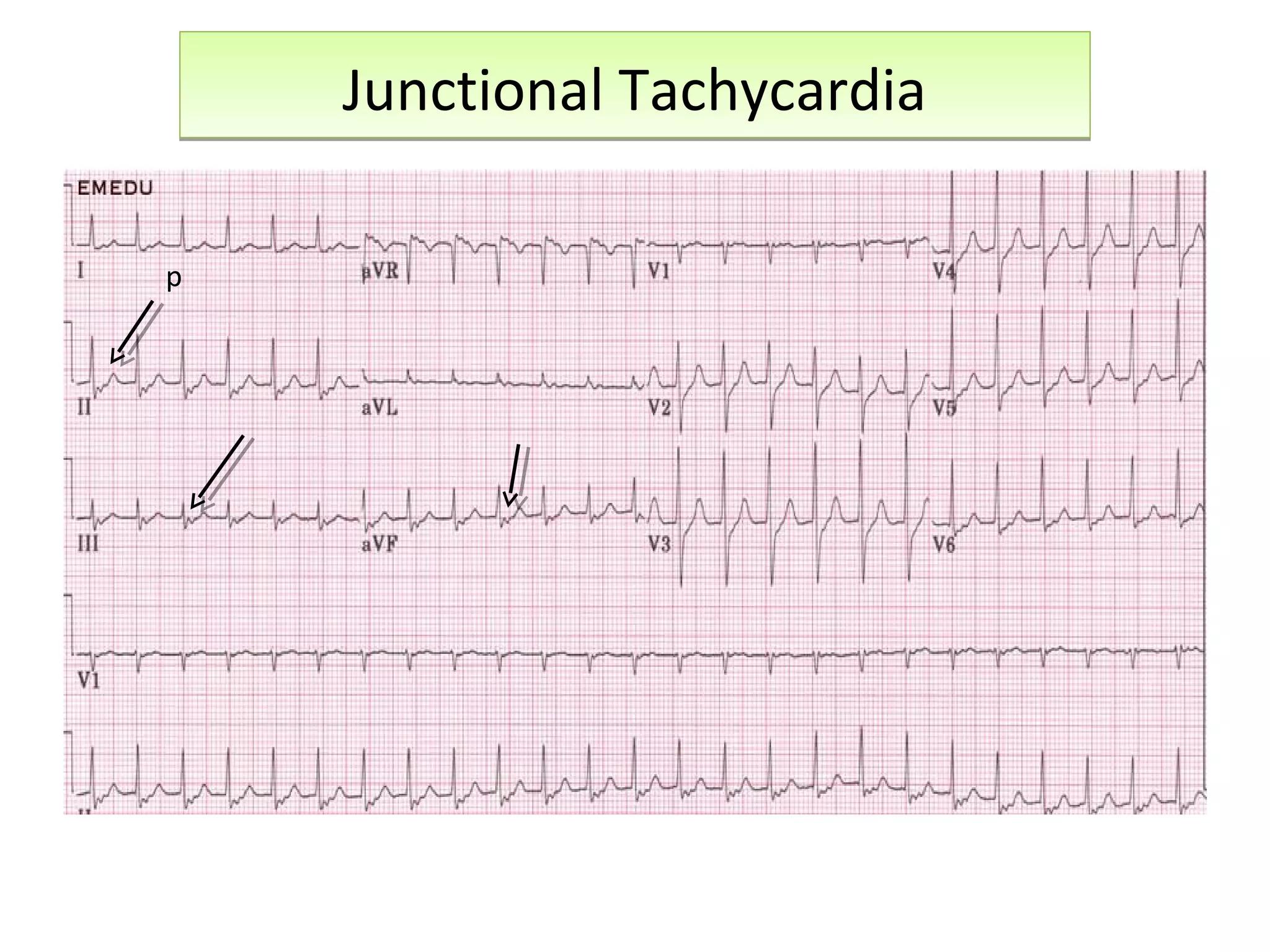
This document discusses various types of atrial and junctional dysrhythmias seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs), including atrial fibrillation, flutter, tachycardia, and premature atrial contractions as well as junctional rhythms, accelerated junctional rhythms, tachycardias, and premature junctional contractions. Mechanisms and treatments for supraventricular tachycardia are explained, including catheter ablation procedures to treat conditions like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.