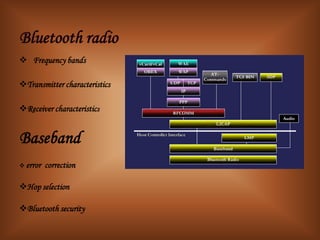
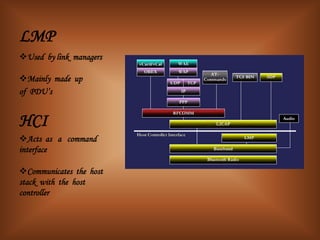
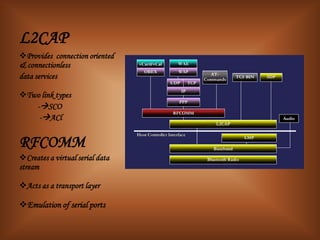
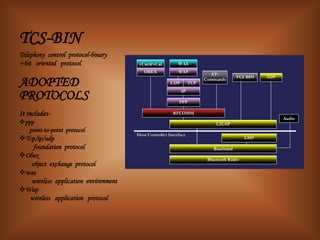
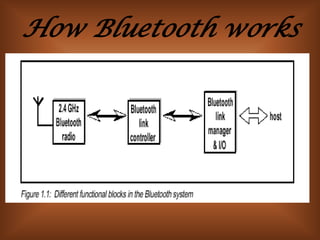
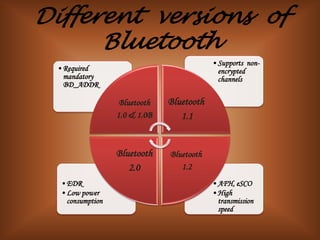
The document summarizes Bluetooth technology. It discusses how Bluetooth simplifies wireless data synchronization using short-range radio technology. It then describes the Bluetooth protocol stack including layers like the baseband, LMP, HCI, and various adopted protocols. The document outlines Bluetooth profiles and how they describe implementation of user models. It also provides an overview of Bluetooth modes of operation, versions, applications, advantages, security issues, and disadvantages.