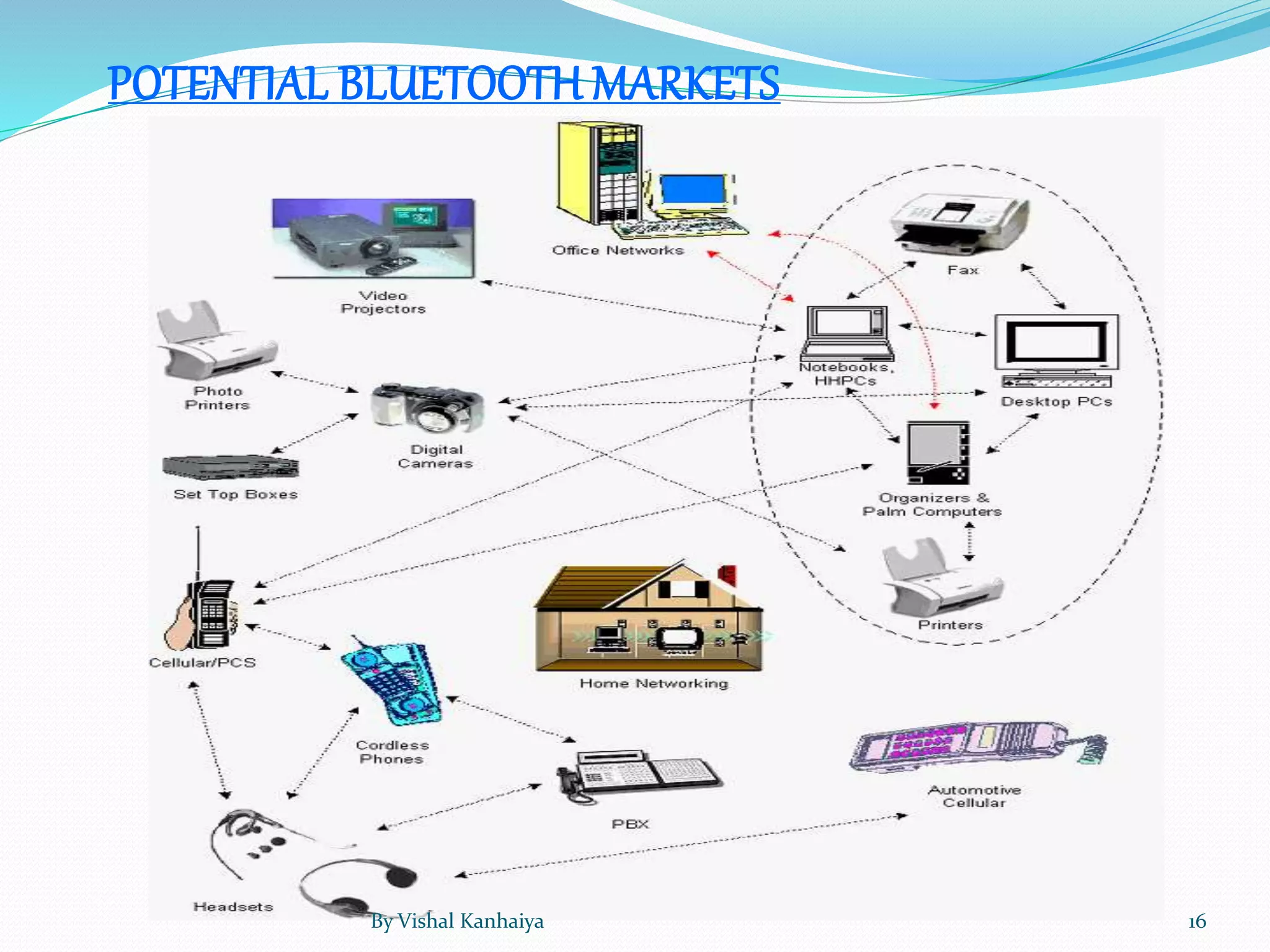
Bluetooth was created in 1994 by Ericsson to provide a wireless alternative to RS-232 cables. It uses short-wavelength radio waves to exchange data over short distances between devices. The name Bluetooth is derived from the Danish King Harald Bluetooth who united Denmark and Norway in the 10th century. The Bluetooth logo represents the merging of the runic letters H and B to represent the connection between devices. Bluetooth allows devices within 30 feet to connect and exchange information without cables.