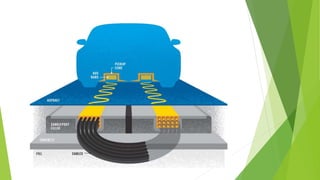
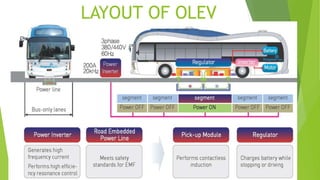
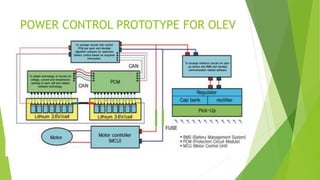
The document discusses Online Electric Vehicles (OLEV), which are powered through electromagnetic induction from electrical strips buried under roads, rather than through onboard batteries. Researchers from KAIST launched a public transport system using this technology in 2010. OLEV vehicles are equipped with regulators and inverters that are compatible with the 20kHz frequencies generated in the buried power strips to provide electricity for propulsion and battery charging. The technology offers advantages like lower operating costs than gas vehicles and zero tailpipe emissions, but implementing supporting infrastructure would be costly.