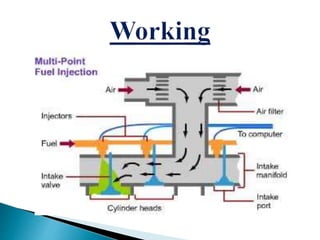
The document discusses multi-point fuel injection (MPFI) systems. It describes the components of an MPFI system, including the air intake system, pressure regulator system, control system, fuel pump control system, and functional divisions. An MPFI system injects fuel into individual cylinders based on commands from the engine control module. This provides faster throttle response and higher output under varying driving conditions compared to carburetor systems. The MPFI system can be divided into three main components: the electronic control unit, fuel system, and air induction system.