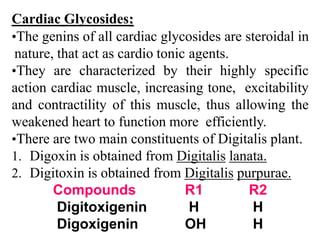
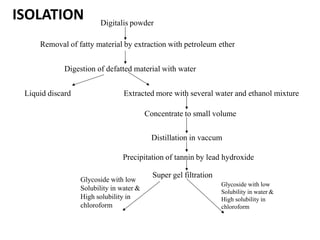
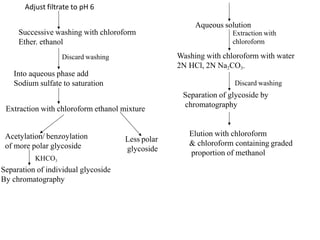
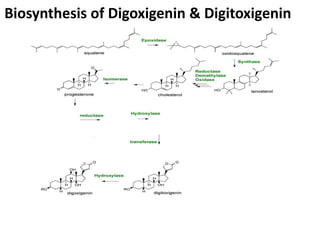
This document summarizes the biological evaluation of plant-derived drug molecules digoxin and digitoxin. It discusses that biological evaluation is used when drugs cannot be fully evaluated by chemical and physical methods alone. The response of a test drug is compared to a standard preparation using living systems, and activity is measured in International Units. Digoxin and digitoxin are cardiac glycosides obtained from Digitalis plants that act as cardio-tonic agents, increasing heart muscle tone, excitability and contractility. Their isolation, biosynthesis, structure-activity relationships, and uses are described.