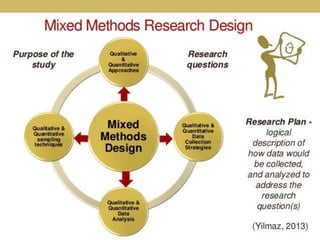
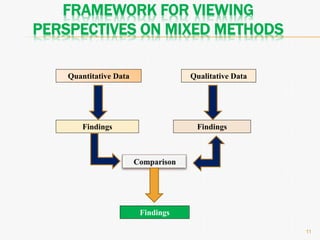
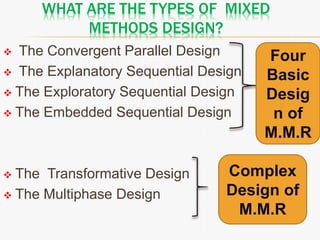
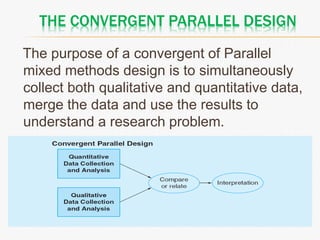
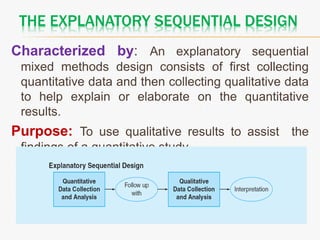
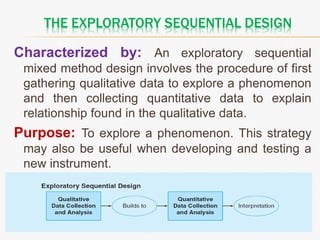
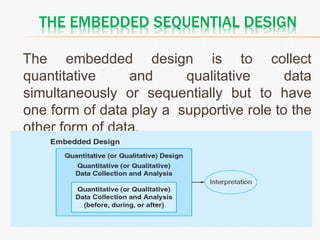
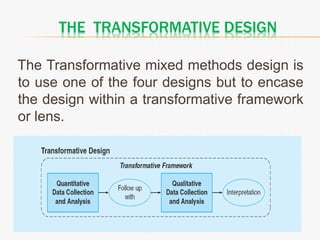
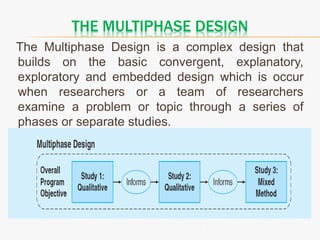
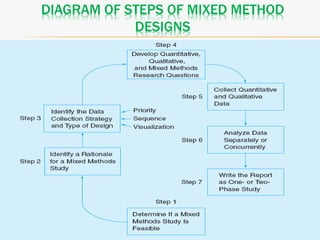
This document discusses mixed method research design. It defines mixed methods research as collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data within a single or series of studies. It outlines the basic characteristics of mixed methods research, including collecting both types of data, considering priority and sequence, and matching analysis to design. The document then discusses various aspects of mixed methods research such as when to conduct it, reasons for using it, types of designs, steps to carry out a mixed methods study, and criteria for evaluating it. It also notes some strengths as being able to describe findings easily but some weaknesses as taking more time.