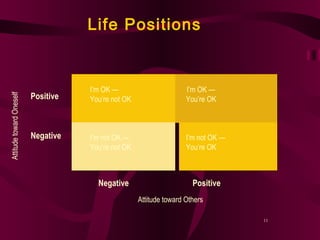
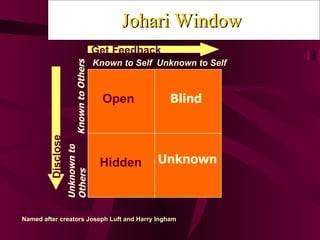
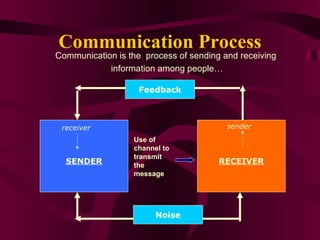
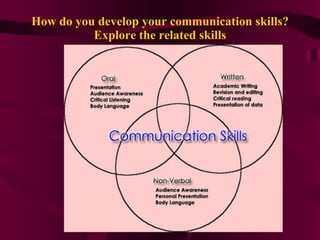
The document discusses various aspects of communication skills including types of communication, barriers to effective communication, and components of the communication process. It emphasizes that communication involves sending and receiving both verbal and nonverbal messages and highlights the importance of active listening, clarity, and establishing understanding between parties. Effective communication is described as a two-way process that utilizes feedback to convey information freely without stress or misunderstanding.










![Emotional Or Psychological Barriers Premature mindset[i am not ok,you are not ok] Inattention Loss of transmission & poor retention Undue reliance on the written word Distrust of communication Failure to communicate Over confidence[I am ok,you are not ok]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicationskillssdevelopment-100905101105-phpapp01/85/Communication-skills-development-13-320.jpg)
![Organization Barriers Organizational policy Organization rules & regulation Status relation[Power and position] Complexity in organization[Organisational structure]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicationskillssdevelopment-100905101105-phpapp01/85/Communication-skills-development-14-320.jpg)
































![Mr. Rajib Kumar jena Rajib kumar Campus : Shiksha Vihar, Baranga-Khurda Rd., Chandka, Bhubaneswar: 754 005 Phone: +91 674 2111204, 07, 08 Asian School of Business Management, Bhubaneswar e-mail : [email_address] : [email_address] Mobile : +91 9438412802 Developed for Business Communication by …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicationskillssdevelopment-100905101105-phpapp01/85/Communication-skills-development-50-320.jpg)