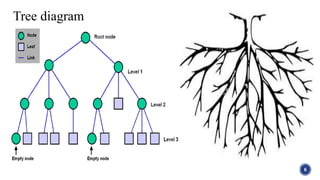
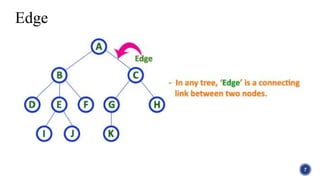
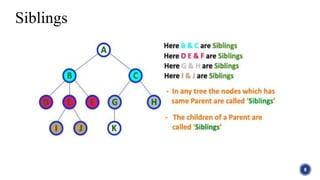
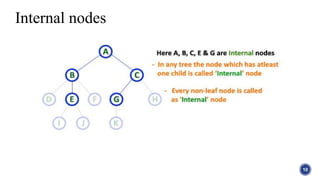
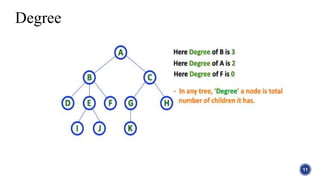
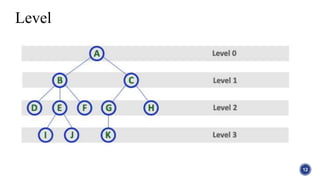
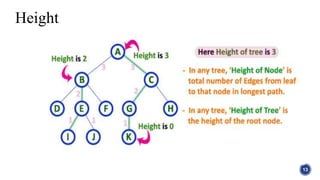
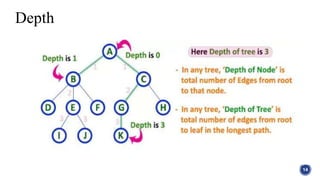
This document introduces tree structures in graph theory, emphasizing their importance as data structures composed of nodes and edges without cycles. It covers key terminologies related to trees, such as root, leaf, and height, and discusses various applications of trees in real life, including organizational hierarchies and computer algorithms. Additionally, it provides references for further reading on the topic.