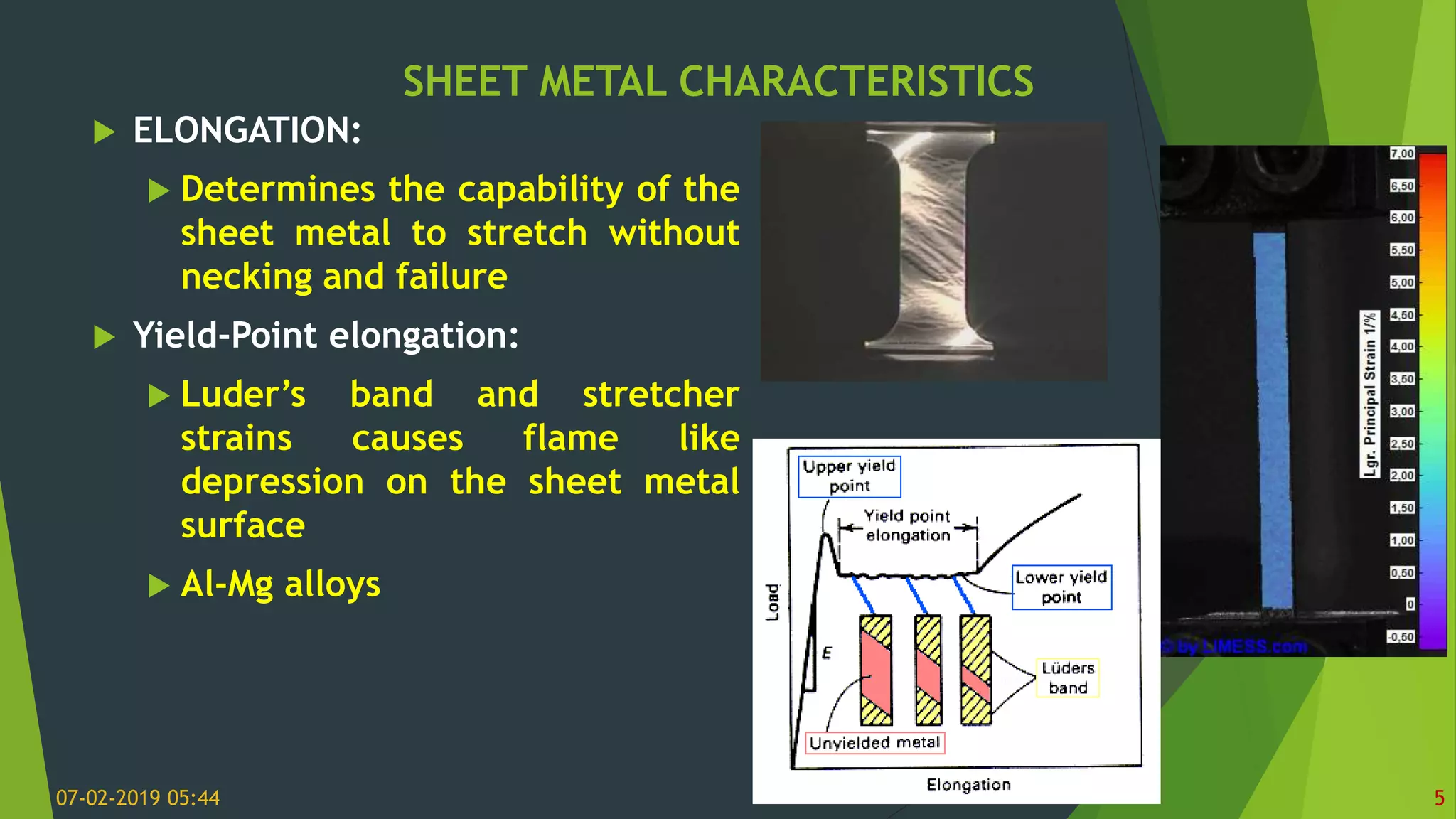
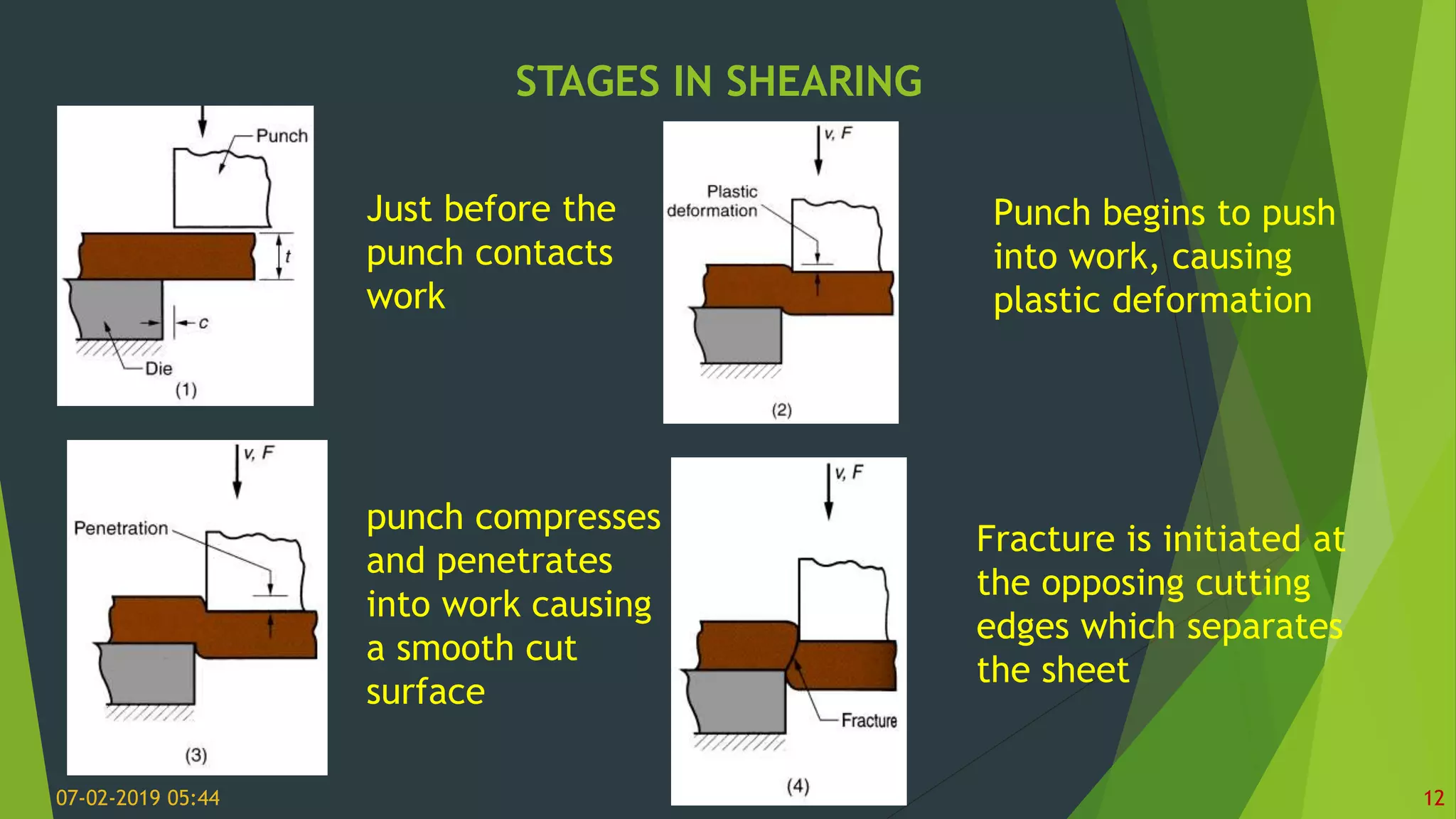
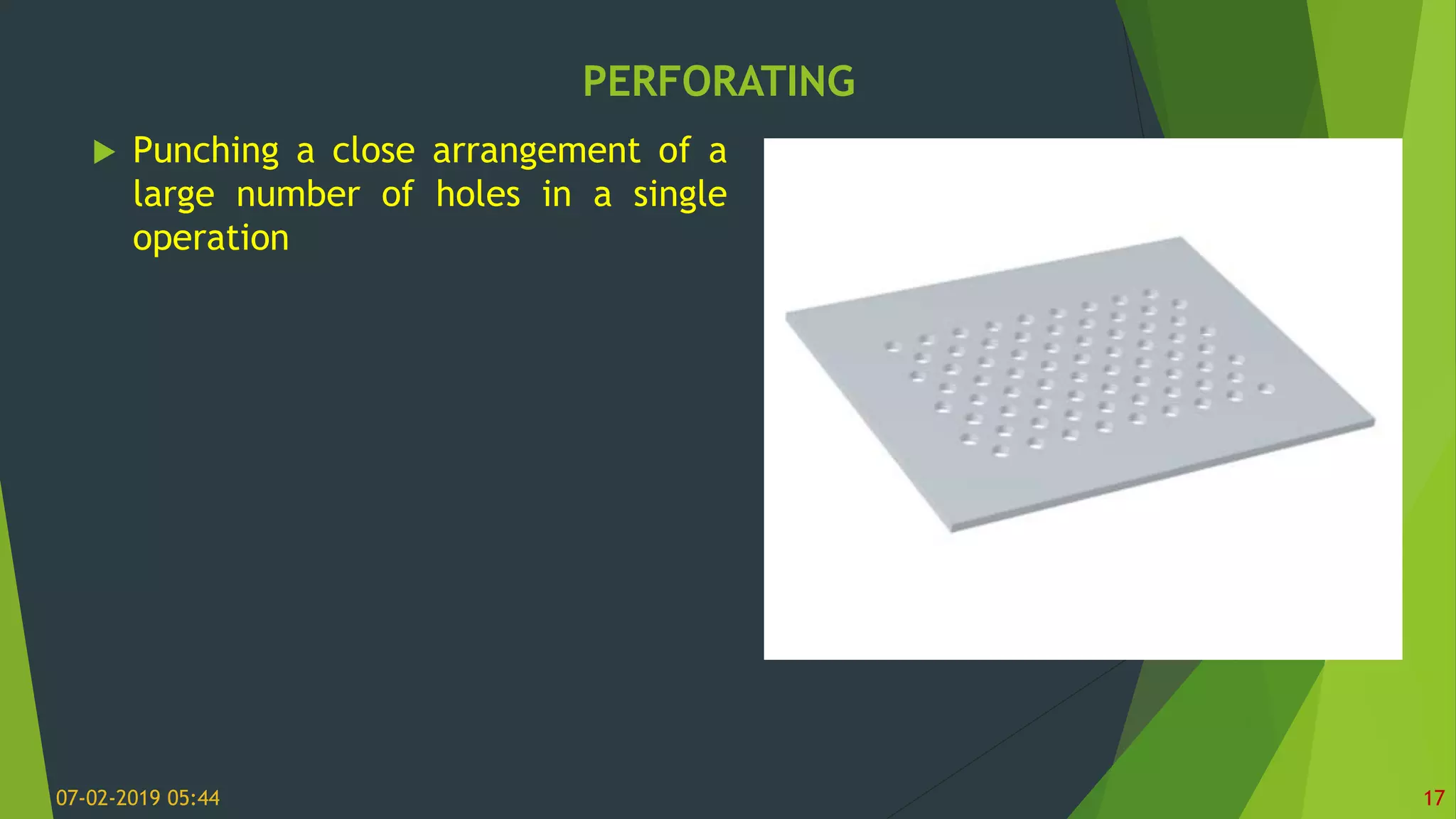
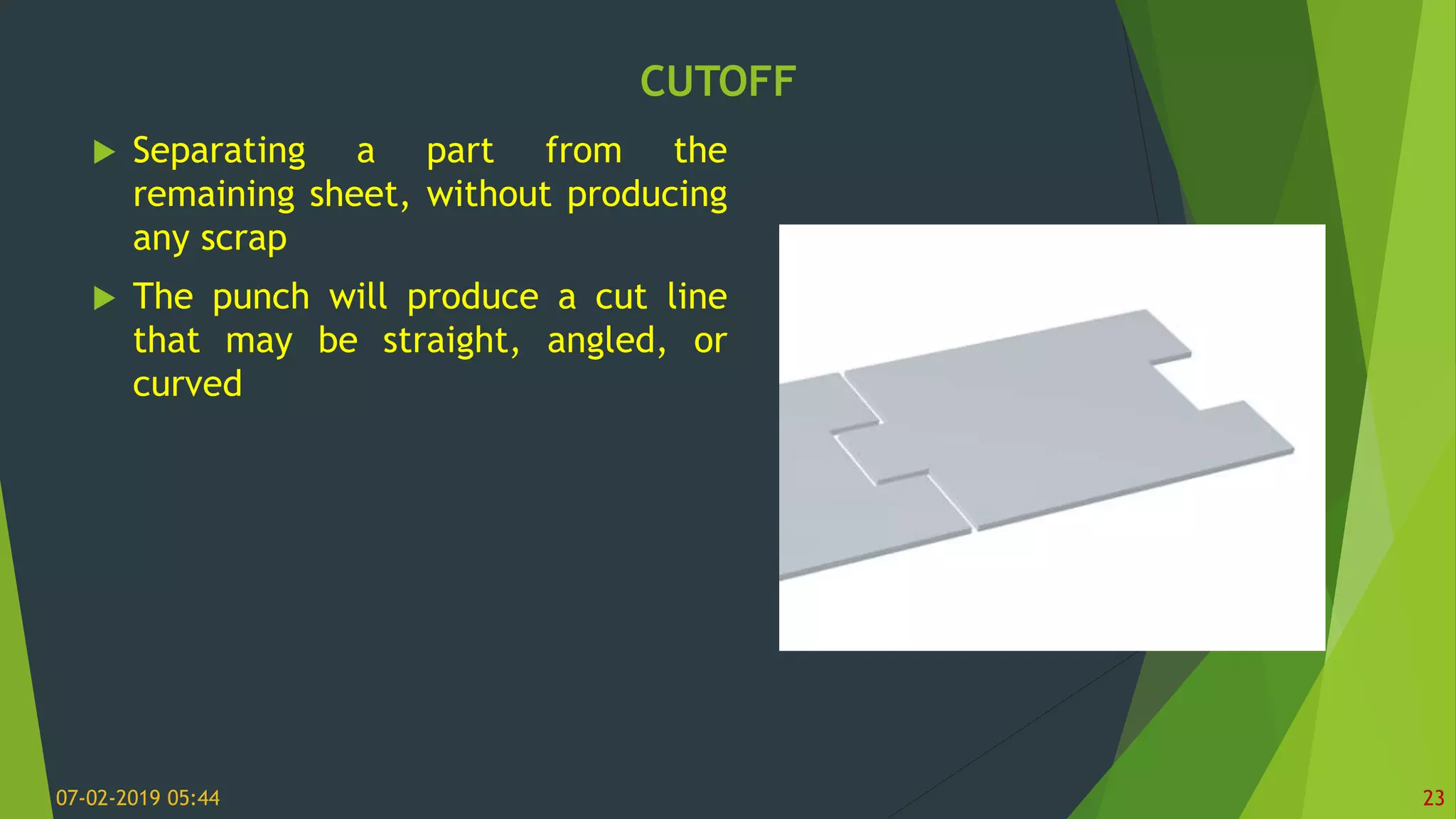
This document discusses sheet metal processes and operations. Sheet metal is metal formed into thin, flat pieces that can be cut and bent into various shapes. Common materials for sheet metal include steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals. Key sheet metal operations covered include shearing, blanking/punching, bending, drawing, deep drawing, stamping, and others. Factors that influence these operations such as punch and die design, clearance, and lubrication are also addressed.