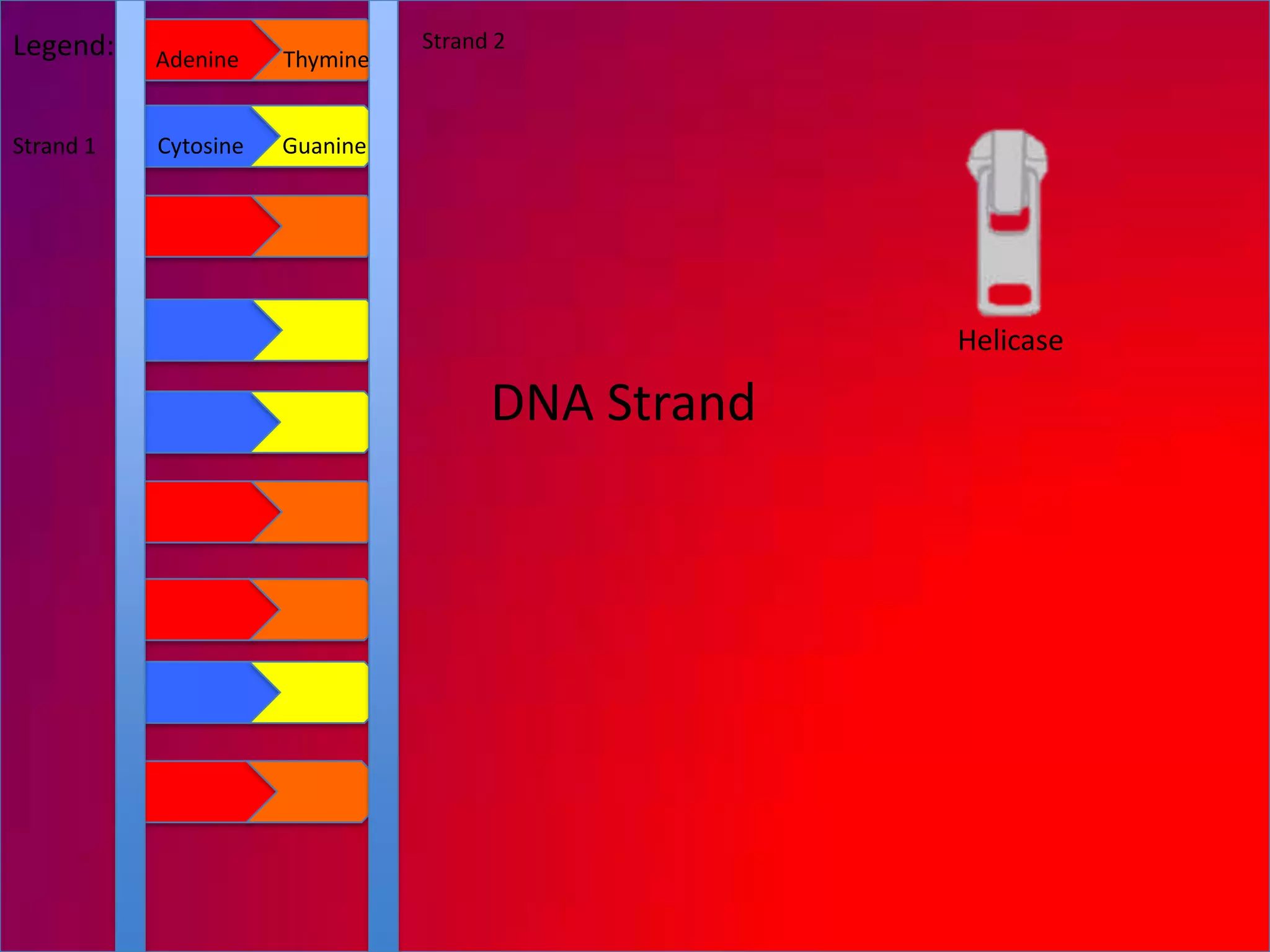
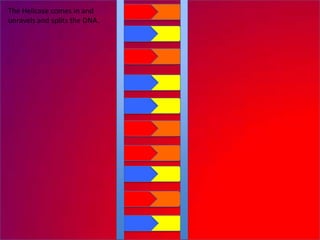
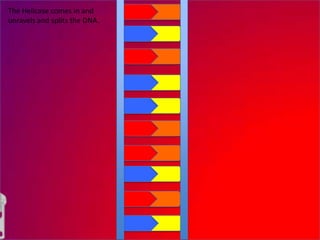
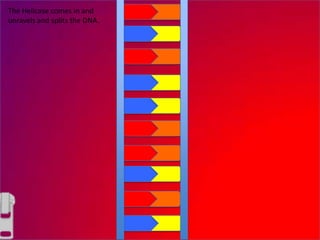
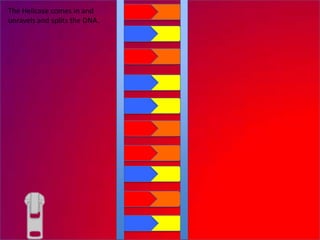
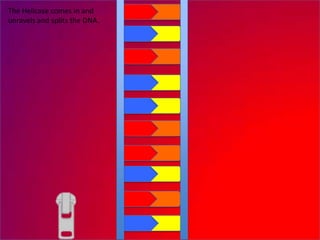
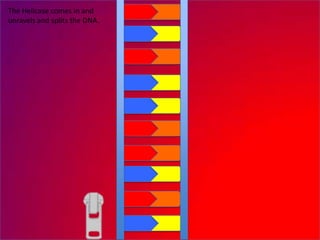
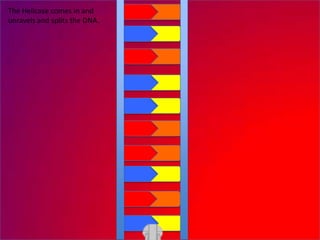
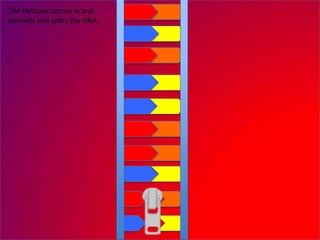
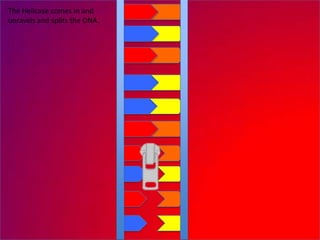
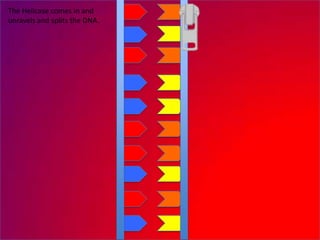
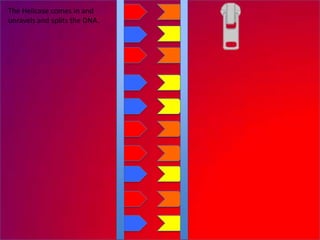
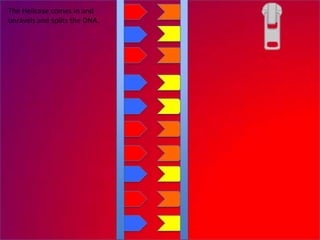
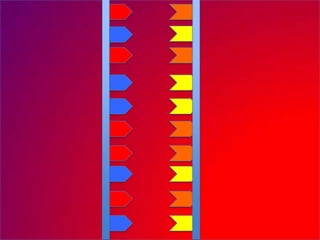
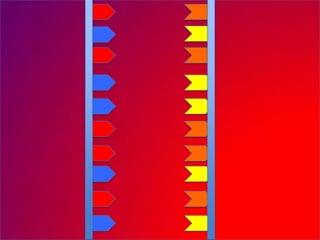
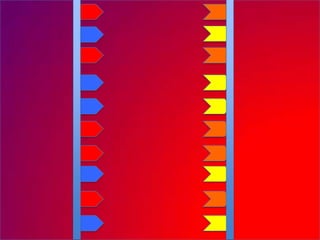
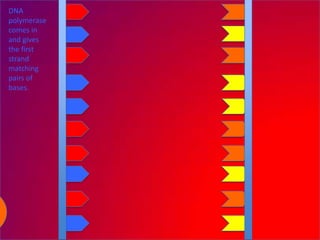
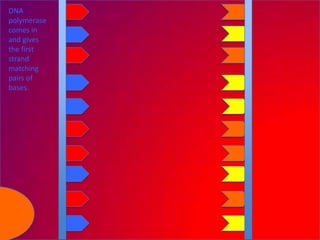
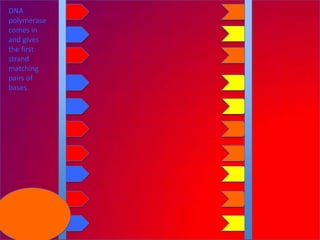
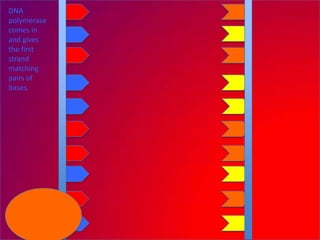
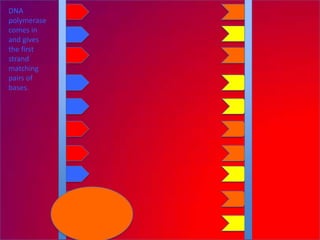
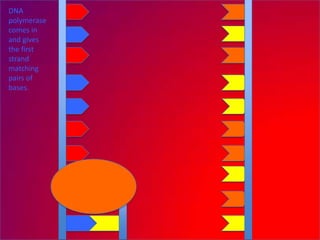
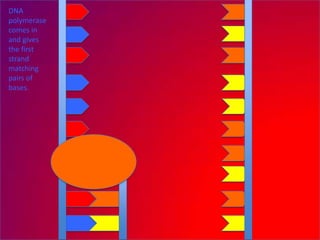
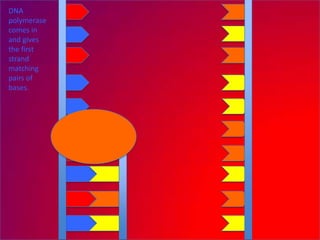
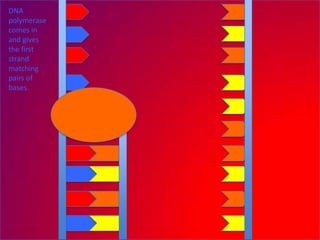
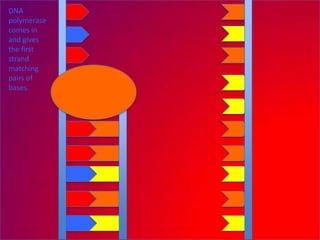
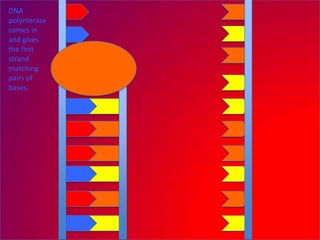
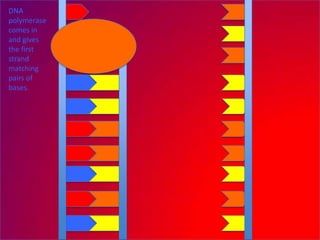
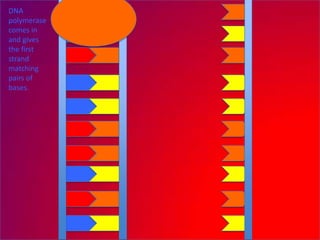
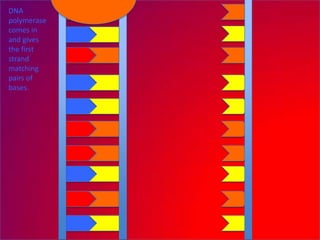
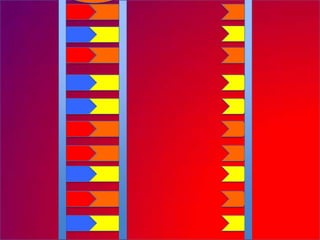
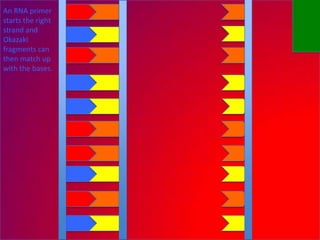
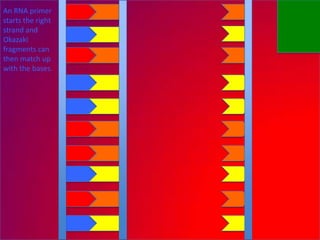
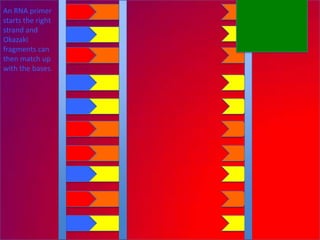
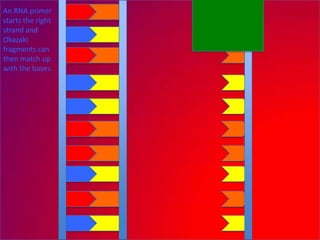
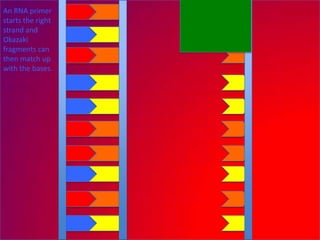
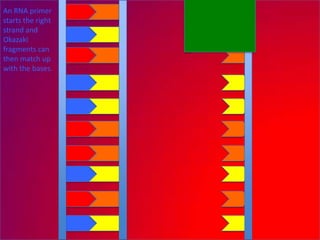
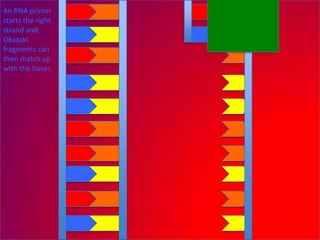
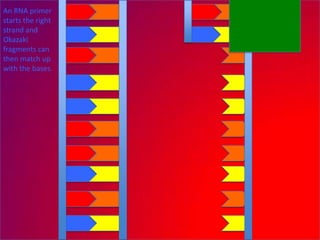
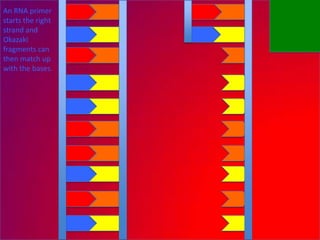
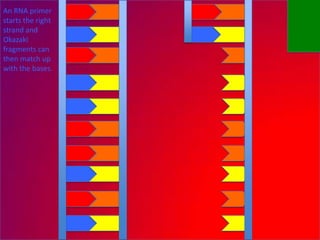
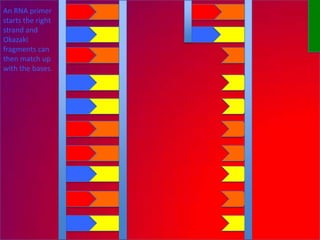
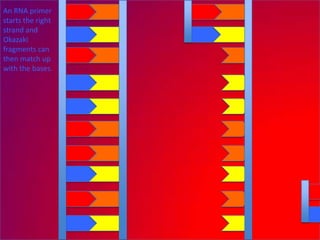
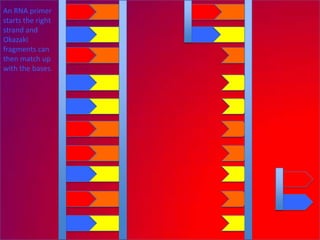
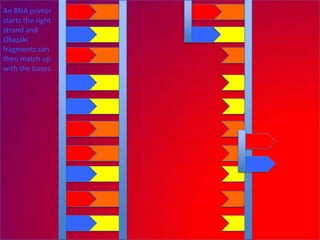
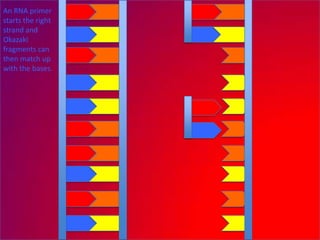
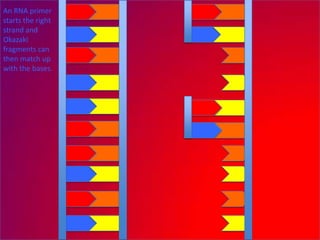
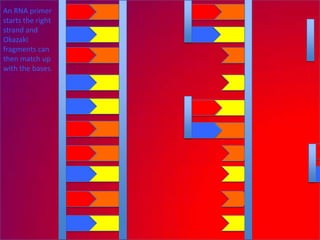
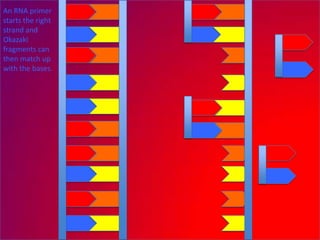
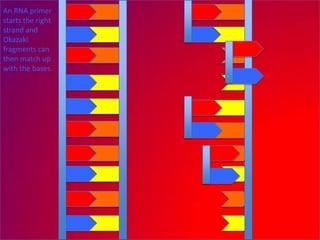
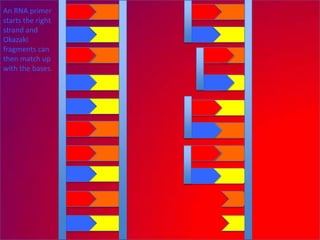
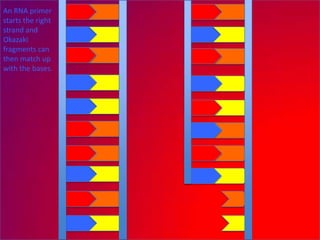
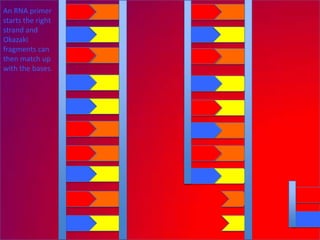
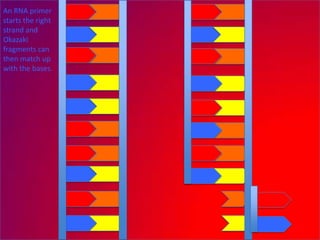
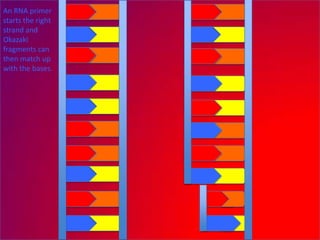
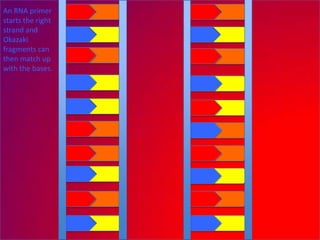
The document describes the process of DNA replication. It explains that the helicase enzyme first unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA. Then, DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to each strand to recreate the double helix structure. An RNA primer is used to initiate synthesis of the new lagging strand, which is synthesized as Okazaki fragments and later joined by DNA ligase.