Embed presentation
Downloaded 111 times

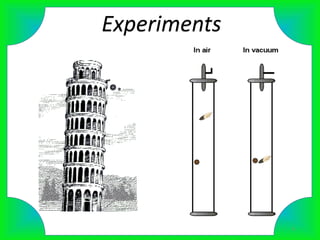

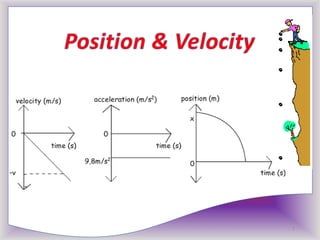
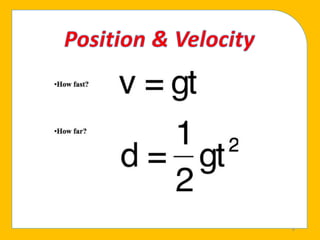



Free fall is the downward motion of objects under the influence of gravity alone. All objects in free fall accelerate at the same rate of 9.8 m/s2 regardless of mass. Experiments show that free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance and accelerate constantly at 9.8 m/s2. Applications of free fall include skydiving and parachuting.










