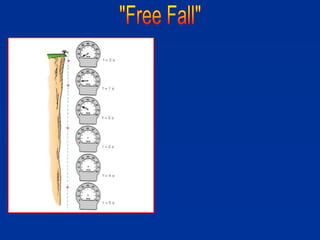
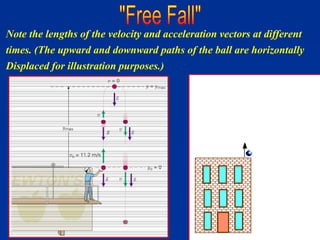
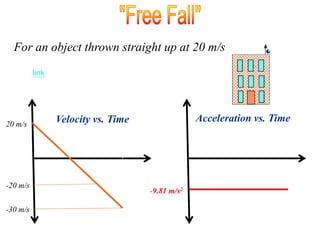
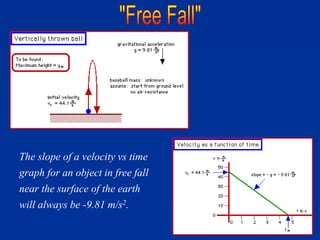
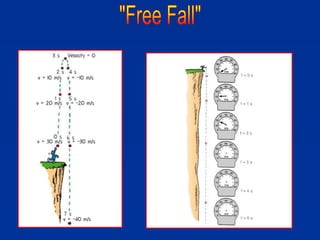
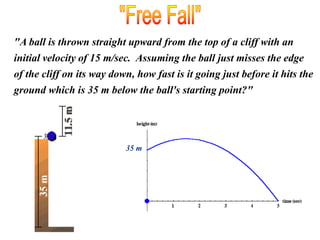
The document discusses free fall, which is when the only force acting on an object is gravity. It explains that in free fall, all objects accelerate at 9.81 m/s^2 toward the center of the Earth. Various examples are provided of objects in free fall, including apples falling from trees and balls being thrown upwards or dropped. Kinematic equations are also presented for calculating velocity, acceleration, distance, and time in free fall situations.