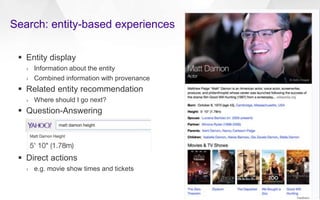
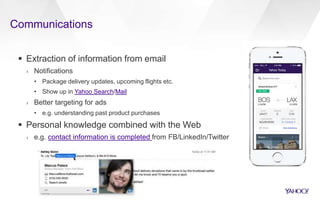
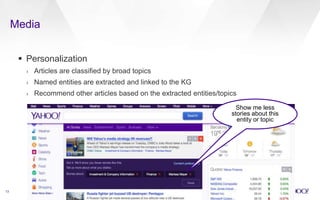
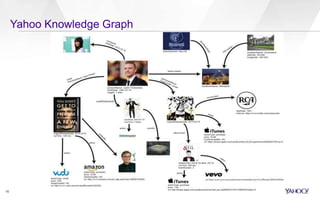
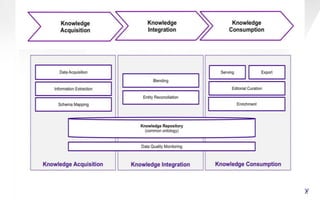
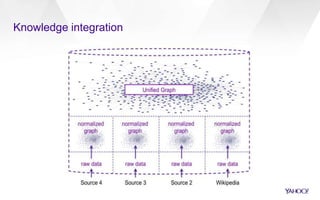
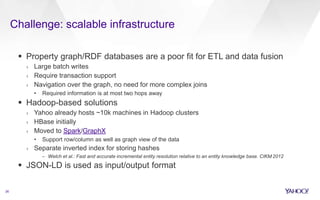
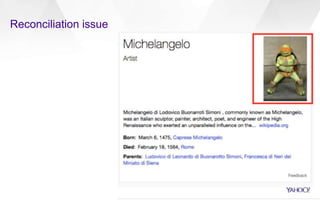
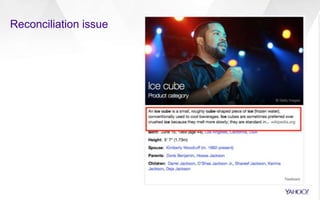
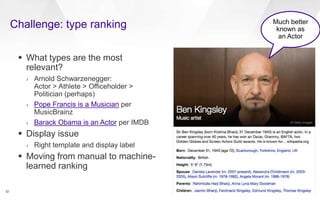
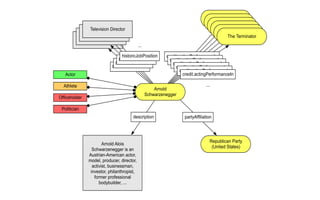
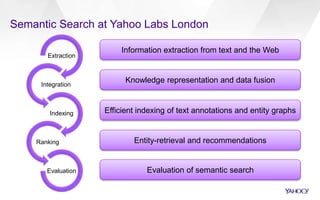
The document discusses Yahoo's knowledge graph, detailing the integration of various data sources to create a unified knowledge base encompassing approximately 100 million unique entities. It explains the processes involved in knowledge integration, including schema matching, entity reconciliation, and handling challenges like scalability and data quality. Future work aims to expand the knowledge graph's scope and improve extraction and integration capabilities.





![Search
10
Understand entity-based queries
› ~70% of queries contain a named entity* (entity mention queries)
• brad pitt height
› ~50% of queries have an entity focus* (entity seeking queries)
• brad pitt attacked by fans
› ~10% of queries are looking for a class of entities*
• brad pitt movies
Even more prominent on mobile
› Limited input/output
› Different types of queries
• Less research, more immediate needs
• Need answers or actions related to an entity, not pages to read
brad pitt height
how tall is
tall
…
* Statistics from [Pound et al. WWW2010]. Similar results in [Lin et al. WWW2012].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yahooknowledge-chile-160502083711/85/Knowledge-Integration-in-Practice-10-320.jpg)