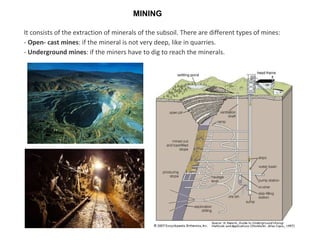
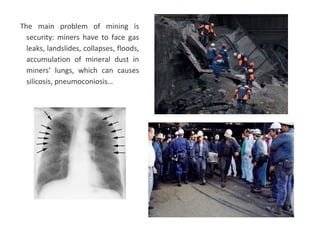
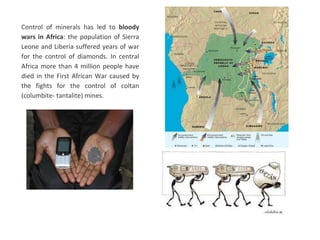
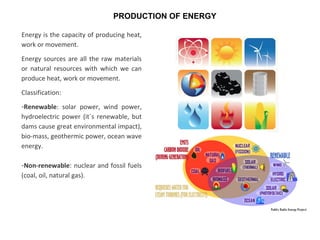
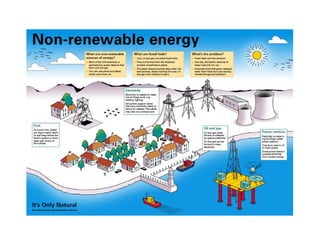
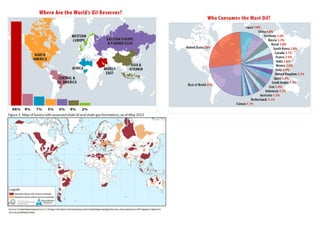
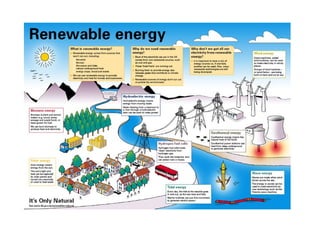
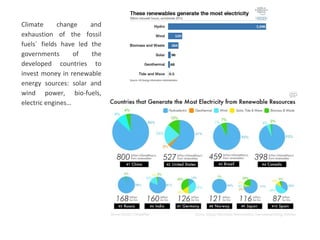
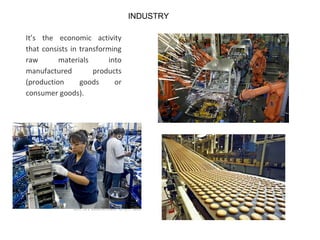
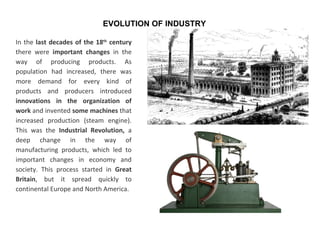
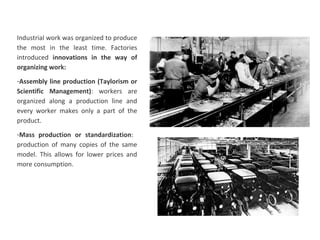
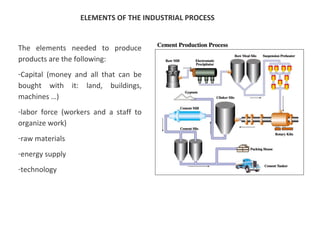
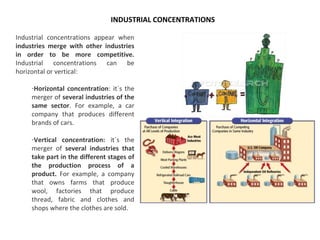
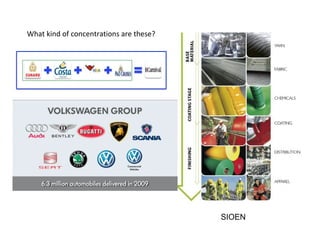
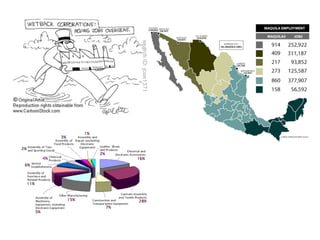
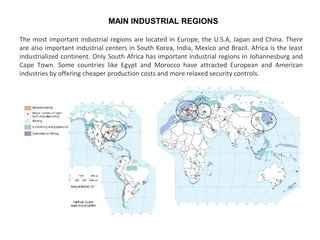
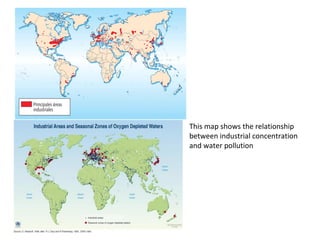
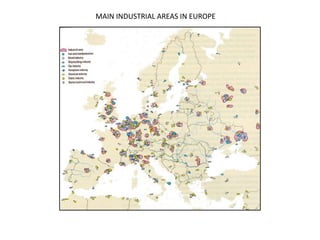
The secondary sector includes activities that transform raw materials into manufactured goods like construction, mining, energy production and industry. Mining extracts minerals from the earth through open-cast or underground mines. The main issues are safety hazards for miners. Minerals are important resources and their control has led to conflicts. Industry transforms raw materials and uses capital, labor, materials, energy and technology. It has evolved from small workshops to large factories using assembly lines and mass production. Industries can be heavy or light and locate based on access to markets, transportation and resources.